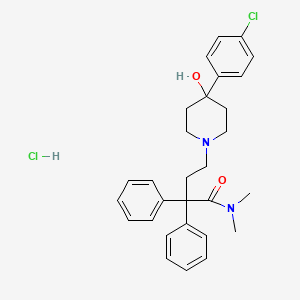
Loperamidhydrochlorid
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Loperamide hydrochloride is a synthetic opioid receptor agonist primarily used as an anti-diarrheal agent. It is effective in controlling acute nonspecific diarrhea, chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease, and diarrhea resulting from bowel resection . Loperamide hydrochloride works by slowing down intestinal motility and affecting water and electrolyte movement through the bowel .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Approved Medical Uses
Loperamide hydrochloride is FDA-approved for treating several forms of diarrhea, including:
- Acute nonspecific diarrhea
- Traveler's diarrhea
- Chronic diarrhea associated with irritable bowel syndrome
- Reduction of ileostomy output
Recent studies have also highlighted its effectiveness in managing chemotherapy-related diarrhea, particularly in patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, where it is recommended to rule out infections before administration .
Off-Label Uses and Misuse
Increasingly, loperamide has been used off-label for purposes that raise concerns about safety:
- Opioid Withdrawal Management : Some individuals with opioid dependence use loperamide to alleviate withdrawal symptoms due to its action on mu-opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. This has led to reports of misuse and dependence on loperamide itself .
- Euphoria Induction : There has been a rise in cases where loperamide is used recreationally to achieve euphoric effects, leading to high doses that pose significant health risks .
Health Risks and Cardiotoxicity
The misuse of loperamide can lead to severe cardiac events. The FDA has documented numerous cases of serious heart problems associated with high doses of loperamide, including:
- QT interval prolongation
- Torsades de Pointes
- Cardiac arrest
Between 1976 and 2015, 48 cases of serious cardiac events were reported, with some resulting in death. These events often occurred in the context of misuse or concurrent use with drugs that inhibit loperamide metabolism .
Case Studies and Clinical Insights
Several case studies illustrate the risks associated with loperamide misuse:
- A 28-year-old male with a history of heroin abuse took over 100 capsules daily for six months to manage withdrawal symptoms. He experienced severe cardiac arrhythmias as a result .
- Another study discussed a patient requiring methadone management due to protracted withdrawal symptoms from excessive loperamide use .
These cases underscore the importance of monitoring and educating patients about the potential dangers of self-medication with loperamide.
Research Findings on Efficacy and Safety
Recent research has focused on the pharmacokinetics and safety profile of loperamide:
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Loperamide hydrochloride primarily targets the mu-opioid receptors in the myenteric plexus of the large intestine . These receptors play a crucial role in regulating intestinal motility and fluid secretion .
Mode of Action
Loperamide hydrochloride acts as an agonist at the mu-opioid receptors . By binding to these receptors, it decreases the activity of the myenteric plexus, which in turn reduces the tone of the longitudinal and circular smooth muscles of the intestinal wall . This action slows down the contractions of the intestines .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary metabolic pathway of loperamide hydrochloride involves oxidative N-demethylation, mediated by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 enzymes . This process forms N-demethyl loperamide, which is pharmacologically inactive . CYP2B6 and CYP2D6 also play a minor role in loperamide N-demethylation .
Pharmacokinetics
Loperamide hydrochloride is a highly lipophilic synthetic phenylpiperidine opioid . It is extensively metabolized in the liver . The bioavailability of loperamide hydrochloride is low (0.3%) due to extensive first-pass metabolism . The elimination half-life of loperamide hydrochloride is approximately 9-14 hours , and it is excreted primarily in the feces (30-40%) and to a lesser extent in the urine (1%) .
Result of Action
The action of loperamide hydrochloride results in a decrease in intestinal motility and fluid secretion . This leads to an increase in the time for fluids and nutrients to be absorbed back into the body, which makes the stool less watery and decreases the frequency of bowel movements .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Loperamide hydrochloride plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by interacting with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It primarily binds to the mu-opioid receptors located on the circular and longitudinal intestinal muscles . This binding leads to the recruitment of G-protein receptor kinases and the activation of downstream molecular cascades that inhibit enteric nerve activity . Additionally, loperamide hydrochloride affects water and electrolyte movement through the bowel, thereby reducing propulsive peristalsis and increasing intestinal transit time .
Cellular Effects
Loperamide hydrochloride exerts several effects on different types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by inhibiting the excitability of enteric neurons, which suppresses gastrointestinal motility . This compound also affects cell signaling pathways by binding to the mu-opioid receptors and activating G-protein coupled receptor pathways . Furthermore, loperamide hydrochloride impacts gene expression and cellular metabolism by modulating the release of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine and prostaglandins .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of loperamide hydrochloride involves its action on the mu-opioid receptors in the gut. By binding to these receptors, loperamide hydrochloride inhibits the release of acetylcholine and prostaglandins, which reduces propulsive peristalsis and increases intestinal transit time . This compound also increases the tone of the anal sphincter, thereby reducing incontinence and urgency . The binding interactions with biomolecules and enzyme inhibition play a crucial role in its antidiarrheal effects .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of loperamide hydrochloride change over time. Studies have shown that loperamide hydrochloride is stable and maintains its efficacy in controlling diarrhea over extended periods . Higher than recommended dosages can lead to life-threatening cardiac, central nervous system, and respiratory adverse reactions . Long-term effects on cellular function include the potential for cardiac arrhythmias and other serious adverse effects .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of loperamide hydrochloride vary with different dosages in animal models. At therapeutic doses, it effectively controls diarrhea without significant adverse effects . At higher doses, loperamide hydrochloride can induce neurotoxic effects, including psychosis-like behaviors in mice . Additionally, high doses can lead to cardiac toxicity and other severe adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Loperamide hydrochloride is primarily metabolized in the liver through oxidative N-demethylation mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes, specifically CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 . The metabolites of loperamide hydrochloride are pharmacologically inactive and are excreted via the bile . This metabolic pathway ensures the efficient clearance of the compound from the body .
Transport and Distribution
Loperamide hydrochloride is transported and distributed within cells and tissues primarily through plasma protein binding. Approximately 95% of loperamide hydrochloride is bound to plasma proteins . It is also a substrate for P-glycoprotein, which limits its penetration across the blood-brain barrier . This transport mechanism ensures that loperamide hydrochloride remains localized in the gut, where it exerts its therapeutic effects .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of loperamide hydrochloride is primarily within the gut wall, where it binds to the mu-opioid receptors . This localization is facilitated by its high lipophilicity and affinity for the receptors in the intestinal muscles . The compound’s activity and function are directed towards reducing gastrointestinal motility and increasing intestinal transit time .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetische Routen und Reaktionsbedingungen: Loperamidhydrochlorid wird durch ein mehrstufiges Verfahren synthetisiert, bei dem 4-Chlorbenzhydrylchlorid mit 4-Hydroxypiperidin umgesetzt wird, um 4-(4-Chlorphenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin zu bilden. Dieser Zwischenstoff wird dann mit N,N-Dimethyl-2,2-diphenylbutanamid umgesetzt, um Loperamid zu erhalten .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: In industriellen Umgebungen wird this compound unter Verwendung der Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie (HPLC) zur Reinigung hergestellt. Der Prozess umfasst die potentiometrische Titration und die Verwendung mobiler Phasen, die Kaliumphosphatmonobasis und Acetonitril enthalten .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Loperamidhydrochlorid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Loperamid kann zu seinem N-Oxid-Derivat oxidiert werden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können Loperamid in sein entsprechendes Amin umwandeln.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können am Piperidinring oder an den Phenylgruppen auftreten.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Wasserstoffperoxid oder andere Oxidationsmittel.
Reduktion: Natriumborhydrid oder Lithiumaluminiumhydrid.
Substitution: Halogenierungsmittel oder Nukleophile.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden:
Oxidation: Loperamid-N-oxid.
Reduktion: Loperamidamin.
Substitution: Verschiedene substituierte Derivate, abhängig von den verwendeten Reagenzien.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Diphenoxylate: Another opioid receptor agonist used to treat diarrhea.
Atropine: Often combined with diphenoxylate to enhance its anti-diarrheal effects.
Imodium (another brand of loperamide): Similar in composition and function to loperamide hydrochloride
Uniqueness: Loperamide hydrochloride is unique due to its high affinity for peripheral opioid receptors and minimal central nervous system penetration, which reduces the risk of central opioid effects such as euphoria and dependence .
Biologische Aktivität
Loperamide hydrochloride, commonly known by its brand name Imodium, is an opioid receptor agonist primarily used to manage diarrhea. Its biological activity is multifaceted, involving interactions with various receptors and physiological pathways. This article explores the biological mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic effects, and case studies related to loperamide hydrochloride.
Loperamide acts primarily as a μ-opioid receptor agonist in the myenteric plexus of the large intestine. This action leads to:
- Decreased Intestinal Motility : By reducing the activity of the myenteric plexus, loperamide decreases the tone of both longitudinal and circular smooth muscles in the intestinal wall. This prolongs the time fecal material remains in the intestine, allowing for increased water absorption from stool .
- Inhibition of Gastrocolic Reflex : Loperamide suppresses colonic mass movements and the gastrocolic reflex, further contributing to its antidiarrheal effects .
Pharmacokinetics
Loperamide is characterized by low systemic bioavailability due to extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver. Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Bioavailability : Approximately 0.3% due to hepatic metabolism .
- Half-Life : The mean biological half-life is about 10.8 hours .
- Peak Plasma Concentration : Achieved within 2.5 hours for syrup formulations and 5 hours for capsule forms .
Biological Activities
In addition to its primary use as an antidiarrheal agent, loperamide exhibits several other biological activities:
- Calcium Channel Blocking : At low micromolar concentrations, loperamide blocks high-voltage activated (HVA) calcium channels, while at higher concentrations, it reduces calcium flux through NMDA receptor-operated channels .
- Immunomodulatory Effects : Loperamide has been shown to enhance antibacterial responses in macrophages against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, increasing the production of antimicrobial peptides and cytokines such as IL1β and IL10 .
- Antiviral Activity : In vitro studies indicate that loperamide inhibits replication of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV .
Cardiac Events Associated with Loperamide Use
Recent literature has documented cases of serious cardiac events linked to excessive loperamide use. For instance:
- A 28-year-old male with a history of heroin abuse took over 100 capsules daily for withdrawal symptoms, resulting in severe cardiac arrhythmias and cardiogenic shock. The patient required intensive treatment including intralipid emulsion therapy and showed significant recovery after management .
Formulation Studies
Research has focused on improving the bioavailability of loperamide through novel formulations:
- Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs) : A study developed ODTs using superdisintegrants to enhance dissolution rates. The best formulation released 95% of the drug within five minutes, significantly improving patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes .
Summary of Research Findings
| Study Focus | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | μ-opioid receptor agonist; decreases intestinal motility; calcium channel blocker |
| Pharmacokinetics | Bioavailability ~0.3%; half-life ~10.8 hours; peak plasma concentration at 2.5 hours (syrup) and 5 hours (capsule) |
| Immunomodulatory Effects | Enhances macrophage response against M. tuberculosis; increases cytokine production |
| Cardiac Events | Documented cases of arrhythmias linked to high doses; recovery observed with appropriate medical intervention |
| Novel Formulations | ODTs show rapid dissolution and improved bioavailability |
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
4-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-N,N-dimethyl-2,2-diphenylbutanamide;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H33ClN2O2.ClH/c1-31(2)27(33)29(24-9-5-3-6-10-24,25-11-7-4-8-12-25)19-22-32-20-17-28(34,18-21-32)23-13-15-26(30)16-14-23;/h3-16,34H,17-22H2,1-2H3;1H | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PGYPOBZJRVSMDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)C(=O)C(CCN1CCC(CC1)(C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)O)(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C29H34Cl2N2O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
53179-11-6 (Parent) | |
| Record name | Loperamide hydrochloride [USAN:USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0034552835 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID00880006 | |
| Record name | 4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-alpha,alpha-diphenylpiperidine-1-butyramide monohydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00880006 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
513.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
>77 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4) | |
| Record name | SID11533030 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
CAS No. |
34552-83-5 | |
| Record name | Loperamide hydrochloride | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=34552-83-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Loperamide hydrochloride [USAN:USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0034552835 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Loperamide hydrochloride | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759568 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-alpha,alpha-diphenylpiperidine-1-butyramide monohydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00880006 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-α,α-diphenylpiperidine-1-butyramide monohydrochloride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.047.333 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LOPERAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/77TI35393C | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
















