Domperidon
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Domperidone is a dopamine receptor antagonist used primarily as an antiemetic and prokinetic agent. It is effective in treating nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal disorders such as gastroparesis. Domperidone works by blocking dopamine receptors in the gut and the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which helps to increase gastrointestinal motility and reduce symptoms of nausea .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Introduction to Domperidone
Domperidone is a dopamine-2 receptor antagonist primarily used as an antiemetic and prokinetic agent. It acts on the gastrointestinal tract to enhance gastric motility and alleviate nausea and vomiting. Unlike metoclopramide, domperidone does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier significantly, which minimizes neurological side effects and enhances its safety profile for long-term use . This article explores the diverse applications of domperidone in clinical settings, supported by comprehensive data tables and case studies.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastroparesis and Nonulcer Dyspepsia
Domperidone has been effectively utilized in managing gastroparesis, a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying. A study involving patients with idiopathic gastric stasis demonstrated that while motility was unchanged, symptom scores significantly improved in those treated with domperidone compared to placebo . This highlights its role in symptomatic relief rather than direct motility enhancement.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Recent research indicates that combining domperidone with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may provide superior outcomes in GERD management. A systematic review showed that this combination significantly reduced reflux episodes and improved symptom scores compared to PPIs alone . The efficacy of domperidone in this context is further illustrated in the following table:
| Study | Population | Treatment Duration | Treatment Regimen | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bediwy 2014 | Children | 12 weeks | Domperidone 0.5 mg/kg + Esomeprazole 2 mg/kg | Improved symptom scores |
| Huiying 2020 | Adults | 1 month | Domperidone 10 mg + Omeprazole 20 mg | Significant reduction in heartburn score |
| Jianzhong 2019 | Children | 2 months | Domperidone 10 mg + Omeprazole 20 mg | Enhanced symptom relief |
Lactation Support
Domperidone is frequently prescribed off-label to stimulate milk production in breastfeeding women. A case study documented a nursing mother who successfully increased her milk supply using domperidone, although she experienced withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation after prolonged use . This application underscores the compound's utility beyond gastrointestinal disorders.
Neurological Applications
While primarily indicated for gastrointestinal issues, domperidone has been investigated for its potential benefits in treating certain neurological conditions associated with nausea and vomiting, such as migraines. Its efficacy in these contexts remains an area of ongoing research.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Domperidone is generally well-tolerated, with a favorable safety profile due to its limited central nervous system penetration. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as abdominal cramps or diarrhea. However, serious adverse effects are rare when used at recommended doses .
Case Studies on Safety
A notable case involved a breastfeeding woman who experienced withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation of domperidone following eight months of use. Symptoms included tachycardia and anxiety, indicating that prolonged exposure may lead to tolerance and subsequent withdrawal challenges .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Domperidone is a dopamine receptor antagonist . It primarily targets dopamine receptors, specifically the D2 receptors . These receptors play a crucial role in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility and the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which is involved in the control of nausea and vomiting .
Mode of Action
Domperidone interacts with its targets by blocking dopamine receptors . This blockade results in two main actions: a central action on the chemoreceptor trigger zone and a peripheral action on gastrointestinal motility . By blocking dopamine receptors, domperidone enhances gastrointestinal peristalsis and lowers the incidence of nausea and vomiting .
Biochemical Pathways
Domperidone affects the dopaminergic pathways. Stimulation of dopaminergic receptors typically inhibits gastric motility. By antagonizing these receptors, domperidone enhances gastric motility and speeds up gastrointestinal peristalsis . This results in improved gastric emptying and reduced symptoms such as post-prandial bloating and pain, premature satiety, nausea, and vomiting .
Pharmacokinetics
Upon oral administration, domperidone is rapidly absorbed, with peak plasma levels achieved within 30 to 60 minutes . It demonstrates a high plasma protein binding rate of up to 93% . Domperidone is metabolized in the liver and gut wall during the first-pass effect . The systemic bioavailability after oral administration is 13 to 17% , while it is about 90% after intramuscular administration .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of domperidone’s action include enhanced gastrointestinal peristalsis and reduced incidence of nausea and vomiting . In addition, domperidone has been found to inhibit cell proliferation via targeting MEK and CDK4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Domperidone works by blocking the peripheral dopamine receptor, which results in its gastroprokinetic action . It increases gastric peristalsis and antroduodenal coordination to facilitate gastric emptying . The anti-emetic properties of Domperidone are due to its dopamine (D2) receptor-blocking activity at the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) .
Cellular Effects
Domperidone influences cell function by affecting the motor function of the stomach and small intestine, as well as the chemoreceptor trigger zone . It does not have any negative neurological effects like sedation and dystonia due to its very little penetration through the blood-brain barrier .
Molecular Mechanism
Domperidone exerts its effects at the molecular level by blocking dopamine receptors . This blockade speeds gastrointestinal peristalsis and causes prolactin release .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Domperidone has a very good safety profile for long-term oral administration in the prescribed doses . The drug induces cardiac arrest when given intravenously .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Domperidone vary with different dosages in animal models
Metabolic Pathways
Domperidone is involved in dopamine receptor pathways . It interacts with dopamine receptors and blocks them, which leads to its antiemetic and prokinetic effects .
Transport and Distribution
Domperidone is a lipophilic drug with a low oral bioavailability and a high rate of first-pass metabolism . To improve its bioavailability when administered orally, its water solubility must be increased and first-pass metabolism must be overcome .
Subcellular Localization
It is known that Domperidone has very little penetration through the blood-brain barrier, which prevents it from causing negative neurological effects .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Domperidon kann durch die Kupplungsreaktion zweier Benzimidazolonderivate synthetisiert werden. Die Synthesewege umfassen die Cyclisierung von o-Phenylendiamin mit Carbonylreagenzien, gefolgt von der Kupplung mit 1,3-Dihalogenpropan. Ein weiterer Weg umfasst die Kupplungsreaktion von o-Halogen- oder o-Aminonitrobenzol mit 1,3-disubstituiertem Propan, gefolgt von Reduktion und Cyclisierung. Der letztere Weg vermeidet die Bildung von disubstituierten Nebenprodukten und weist eine höhere Reaktionsselektivität auf .
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren für this compound-Tabletten umfassen die direkte Pulverkompression des Rohmaterials. Der Prozess umfasst das Vermahlen des Rohmaterials, das Mischen mit Hilfsstoffen wie Carboxymethylstärke-Natrium, vorgegelatinierter Stärke, mikrokristalliner Cellulose und Magnesiumstearat und anschliessend die Tablettierung des Gemisches .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
This compound unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden, was zur Bildung von oxidierten Derivaten führt.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können Nitrogruppen in Aminogruppen umwandeln, die für die Synthese von this compound-Zwischenprodukten essentiell sind.
Häufige Reagenzien, die in diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, sind Carbonylreagenzien, 1,3-Dihalogenpropan und Reduktionsmittel. Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind Benzimidazolonderivate und substituierte Nitrobbenzolderivate .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Domperidone undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Domperidone can be oxidized under specific conditions, leading to the formation of oxidized derivatives.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can convert nitro groups to amino groups, which are essential in the synthesis of domperidone intermediates.
Substitution: Substitution reactions, such as halogenation, can modify the chemical structure of domperidone, leading to different derivatives.
Common reagents used in these reactions include carbonyl reagents, 1,3-dihalopropane, and reducing agents. The major products formed from these reactions are benzimidazolone derivatives and substituted nitrobenzene derivatives .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Domperidon wird oft mit anderen Dopaminrezeptor-Antagonisten wie Metoclopramid verglichen. Im Gegensatz zu Metoclopramid hat this compound eine geringere Tendenz, die Blut-Hirn-Schranke zu überwinden, was zu weniger Nebenwirkungen auf das zentrale Nervensystem führt. Dies macht this compound zur bevorzugten Wahl für Patienten, die gegenüber neurologischen Nebenwirkungen empfindlich sind .
Ähnliche Verbindungen sind:
Metoclopramid: Ein weiterer Dopaminrezeptor-Antagonist, der für ähnliche Indikationen eingesetzt wird, aber ein höheres Risiko für Nebenwirkungen auf das zentrale Nervensystem aufweist.
Cisaprid: Ein Prokinetikum, das ebenfalls die Magen-Darm-Motilität verbessert, aber mit schweren kardialen Nebenwirkungen in Verbindung gebracht wurde.
Die einzigartige Fähigkeit von this compound, periphere Dopaminrezeptoren selektiv zu blockieren und gleichzeitig Nebenwirkungen auf das zentrale Nervensystem zu minimieren, unterscheidet es von anderen ähnlichen Verbindungen .
Biologische Aktivität
Domperidone is an antiemetic agent primarily used to treat nausea and vomiting. It acts as a peripheral dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, which influences gastrointestinal motility and has been explored for various therapeutic applications beyond its conventional uses. This article delves into the biological activity of domperidone, summarizing its mechanisms, pharmacological effects, and recent research findings.
Domperidone selectively blocks dopamine D2 and D3 receptors located in the gastrointestinal tract and the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) in the brain. By inhibiting these receptors, domperidone increases gastric motility and accelerates gastric emptying, which helps alleviate symptoms of nausea and vomiting. Additionally, it stimulates prolactin release from the pituitary gland, which may have immunomodulatory effects .
Pharmacological Effects
The pharmacological effects of domperidone can be summarized as follows:
- Antiemetic Activity : Reduces nausea and vomiting.
- Gastrointestinal Motility : Enhances gastric emptying and intestinal transit.
- Prolactin Stimulation : Increases prolactin levels, potentially influencing immune responses.
Recent Research Findings
-
Antiviral Activity Against SARS-CoV-2 :
A recent clinical trial investigated the efficacy of domperidone in reducing viral load in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The study found that while domperidone exhibited in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, it did not significantly reduce viral load compared to placebo in clinical settings. Adverse events were reported in both groups, with no hospitalizations occurring . -
Antitumor Activity in Breast Cancer :
Research has shown that domperidone exhibits cytotoxic effects on triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines (BT-549 and CAL-51). The study concluded that domperidone could be a potential therapeutic agent for TNBC due to its ability to induce apoptosis in cancer cells . -
Effects on Orthostatic Hypotension :
Domperidone has been evaluated for its effectiveness in managing orthostatic hypotension, particularly in Parkinson's disease patients. It was noted to help improve symptoms associated with this condition, although further studies are needed to establish its safety profile .
Case Study 1: Domperidone for COVID-19
A double-blind clinical trial conducted in Spain involved 173 outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who received either 30 mg/day of domperidone or a placebo for seven days. The primary endpoint was the reduction of viral load measured by RT-qPCR. While there was a statistically significant reduction in viral load at day 4 compared to baseline, the difference between treatment and placebo groups was not significant at later time points .
Case Study 2: Domperidone in Breast Cancer
In vitro studies on TNBC cells demonstrated that treatment with domperidone resulted in significant cytotoxicity. The mechanism was linked to the induction of apoptosis via modulation of signaling pathways associated with cell survival and death .
Summary of Biological Activities
| Activity Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Antiemetic | Reduces nausea and vomiting through D2 receptor antagonism |
| Gastrointestinal Motility | Enhances gastric emptying and intestinal transit |
| Prolactin Stimulation | Increases prolactin levels, potentially enhancing immune function |
| Antiviral | Exhibits in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2; unclear clinical efficacy |
| Antitumor | Induces apoptosis in TNBC cells |
| Orthostatic Hypotension Management | Improves symptoms related to orthostatic hypotension |
Eigenschaften
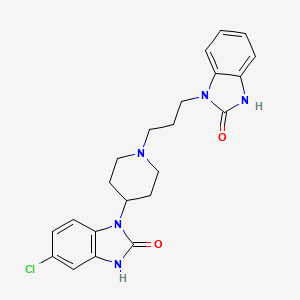
IUPAC Name |
6-chloro-3-[1-[3-(2-oxo-3H-benzimidazol-1-yl)propyl]piperidin-4-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H24ClN5O2/c23-15-6-7-20-18(14-15)25-22(30)28(20)16-8-12-26(13-9-16)10-3-11-27-19-5-2-1-4-17(19)24-21(27)29/h1-2,4-7,14,16H,3,8-13H2,(H,24,29)(H,25,30) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FGXWKSZFVQUSTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN(CCC1N2C3=C(C=C(C=C3)Cl)NC2=O)CCCN4C5=CC=CC=C5NC4=O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H24ClN5O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
83898-65-1 (maleate (1:1)), 99497-03-7 (maleate), 83898-65-1 (maleate salt/solvate) | |
| Record name | Domperidone [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0057808669 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID1045116 | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID1045116 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
425.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015315 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
50.4 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), 9.25e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855562 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01184 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015315 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Domperidone acts as a gastrointestinal emptying (delayed) adjunct and peristaltic stimulant. The gastroprokinetic properties of domperidone are related to its peripheral dopamine receptor blocking properties. Domperidone facilitates gastric emptying and decreases small bowel transit time by increasing esophageal and gastric peristalsis and by lowering esophageal sphincter pressure. Antiemetic: The antiemetic properties of domperidone are related to its dopamine receptor blocking activity at both the chemoreceptor trigger zone and at the gastric level. It has strong affinities for the D2 and D3 dopamine receptors, which are found in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, located just outside the blood brain barrier, which - among others - regulates nausea and vomiting | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01184 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
57808-66-9 | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=57808-66-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Domperidone [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0057808669 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01184 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | domperidone | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759575 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | domperidone | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=299589 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID1045116 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.055.408 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DOMPERIDONE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/5587267Z69 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015315 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
242.5 °C | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01184 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Domperidone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015315 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details








Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of Domperidone?
A1: Domperidone acts as a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, primarily in the periphery of the body. [] By blocking these receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone located outside the blood-brain barrier, Domperidone reduces the inhibitory effects of dopamine, thereby increasing gastrointestinal motility and decreasing nausea and vomiting. []
Q2: How does Domperidone affect prolactin levels?
A2: Domperidone's blockade of dopamine D2 receptors in the pituitary gland leads to increased prolactin secretion. [, ] This effect is exploited for its off-label use as a galactagogue to enhance breast milk production. [, , , ]
Q3: What is the molecular formula and weight of Domperidone?
A3: The molecular formula of Domperidone is C22H24ClN5O2, and its molecular weight is 425.91 g/mol. []
Q4: What formulation strategies are used to improve Domperidone's stability, solubility, or bioavailability?
A4: While the provided papers do not delve into specific formulation strategies, they highlight the development of various Domperidone formulations, including tablets [, ], injections [], gels [], and fast-dissolving tablets. [] These formulations likely employ excipients and techniques to optimize Domperidone's stability, solubility, and bioavailability.
Q5: How is Domperidone absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME)?
A5: Domperidone is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, reaching peak plasma concentrations within approximately one hour. [, ] It undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, primarily by CYP3A4 enzymes in the liver and gut. [, ] Domperidone and its metabolites are excreted in both urine and feces. []
Q6: What in vitro and in vivo models have been used to study the efficacy of Domperidone?
A8: In vitro studies have investigated Domperidone's inhibitory effects on C2 toxin and PT toxin using cell-based assays. [] Animal models, such as those employing mice, have been used to investigate the compound's antiemetic properties and potential for microwave-facilitated drug delivery. [, ] Clinical trials have primarily focused on evaluating its efficacy in treating gastroparesis, nausea, and vomiting, and as a galactagogue for increasing breast milk production. [, , , , , , , , , ]
Q7: What are the known safety concerns associated with Domperidone use?
A9: Domperidone has been associated with an increased risk of cardiac events, including QT interval prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death, particularly at higher doses and in specific patient populations. [, ] Careful consideration of individual patient risk factors and monitoring for potential cardiac adverse effects are crucial.
Q8: Has microwave irradiation been explored as a potential strategy for targeted Domperidone delivery?
A10: Yes, research has explored using microwave irradiation to facilitate Domperidone's penetration across the blood-brain barrier in mice models. [] This approach aims to enhance its central effects while minimizing peripheral side effects.
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.













