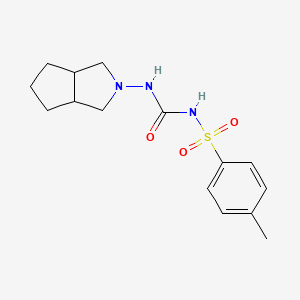
Gliclazide
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Gliclazid ist ein Sulfonylharnstoff-Antidiabetikum, das zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt wird . Es wird oral eingenommen und ist besonders nützlich, wenn Ernährungsumstellungen, Bewegung und Gewichtsabnahme nicht ausreichen, um den Blutzuckerspiegel zu kontrollieren . Gliclazid wirkt in erster Linie, indem es die Insulinsekretion aus der Bauchspeicheldrüse erhöht . Es wurde 1966 patentiert und 1972 für die medizinische Verwendung zugelassen .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Die Synthese von Gliclazid umfasst mehrere Schritte. Ein Verfahren beinhaltet die Reaktion von p-Toluolsulfonylharnstoff mit Hydrazinhydrat, um eine Zwischenverbindung zu erhalten, die dann mit 1,2-Cyclopentandicarbonsäureanhydrid umgesetzt wird, um eine weitere Zwischenverbindung zu bilden. Diese Zwischenverbindung wird schließlich reduziert, um Gliclazid zu erzeugen . Ein weiteres Verfahren beinhaltet die Herstellung von N-Amino-1,2-Cyclopentanphthalamid durch Reaktion von 1,2-Cyclopentanphthalanhydrid mit Hydrazinhydrat, gefolgt von Reduktion und anschließender Reaktion mit Methylphenylsulfonylharnstoff .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Gliclazid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Gliclazid kann oxidiert werden, um Sulfoxide und Sulfone zu bilden.
Reduktion: Die Reduktion von Gliclazid kann zur Bildung von Aminen führen.
Substitution: Gliclazid kann nucleophile Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, insbesondere an der Sulfonylgruppe.
Häufig verwendete Reagenzien in diesen Reaktionen sind Oxidationsmittel wie Wasserstoffperoxid und Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid . Die wichtigsten Produkte, die bei diesen Reaktionen entstehen, hängen von den spezifischen Bedingungen und Reagenzien ab, die verwendet werden.
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Gliclazid hat verschiedene wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen:
Chemie: Es wird als Modellverbindung in Studien zur Sulfonylharnstoffchemie und ihren Derivaten verwendet.
Biologie: Gliclazid wird hinsichtlich seiner Auswirkungen auf Pankreas-Betazellen und die Insulinsekretion untersucht.
Industrie: Gliclazid wird in der pharmazeutischen Industrie zur Herstellung von Antidiabetika eingesetzt.
Wirkmechanismus
Gliclazid entfaltet seine Wirkung, indem es an den Sulfonylharnstoffrezeptor auf Pankreas-Betazellen bindet. Diese Bindung blockiert ATP-sensitive Kaliumkanäle, was zu einer Zelldepolarisation und anschließendem Öffnen von spannungsabhängigen Kalziumkanälen führt. Der Einstrom von Kalziumionen löst die Freisetzung von Insulin aus . Zusätzlich erhöht Gliclazid die periphere Glukoseutilisation und verringert die hepatische Glukoneogenese .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Pharmacological Mechanism
Gliclazide works by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through binding to specific sulfonylurea receptors. This action enhances both the first and second phases of insulin release, leading to improved glycemic control. Additionally, this compound exhibits extrapancreatic effects, such as reducing hepatic glucose production and enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity, which contribute to its overall efficacy in managing blood glucose levels .
Type 2 Diabetes Management
This compound is primarily indicated for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical studies have demonstrated its efficacy in lowering glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels over extended periods. For instance, a two-year study indicated that this compound modified release (MR) significantly improved glycemic control with a low incidence of hypoglycemia, particularly in elderly patients and those with renal impairment .
Combination Therapy
This compound is often used in combination with other oral antidiabetic agents or insulin to achieve better glycemic control. A study comparing this compound MR with basal insulin showed that the combination therapy was effective in managing blood glucose levels more effectively than insulin monotherapy alone . The synergistic effects of this compound with other agents like metformin or DPP-4 inhibitors have also been documented, enhancing overall treatment outcomes .
Potential in Type 1 Diabetes
Recent research has explored the potential applications of this compound in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Its pleiotropic effects may offer benefits beyond glycemic control, such as anti-inflammatory properties and cellular protection. These effects could be particularly advantageous when combined with other therapies targeting T1DM .
Safety Profile
This compound is associated with a relatively low risk of hypoglycemia compared to other sulfonylureas, making it a preferred choice for many patients. Long-term studies indicate that it maintains cardiovascular safety while effectively controlling blood glucose levels . The safety profile is especially favorable among vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with renal dysfunction .
Case Study: Efficacy in Elderly Patients
A longitudinal study involving elderly patients demonstrated that this compound MR effectively managed diabetes without significant adverse effects. Over two years, participants showed a notable reduction in HbA1c levels, highlighting its suitability for older adults who may be more susceptible to hypoglycemia .
Research Findings: Cardiovascular Benefits
This compound has been shown to reduce platelet aggregation and improve fibrinolysis independently of its glucose-lowering effects. These properties may contribute to halting the progression of diabetic microangiopathy and reducing cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes .
Comparative Efficacy
To provide a clearer understanding of this compound's efficacy compared to other antidiabetic medications, the following table summarizes key findings from various studies:
| Medication | HbA1c Reduction | Hypoglycemia Incidence | Cardiovascular Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| This compound | -0.46% (2 years) | Low (4.8 episodes/100 patient-years) | Favorable |
| Metformin | -0.5% to -1.0% | Moderate | Favorable |
| Glimepiride | -0.5% to -0.9% | Higher than this compound | Moderate |
| DPP-4 Inhibitors | -0.5% | Low | Neutral |
Wirkmechanismus
Gliclazide exerts its effects by binding to the sulfonylurea receptor on pancreatic beta cells. This binding blocks ATP-sensitive potassium channels, leading to cell depolarization and subsequent opening of voltage-gated calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions triggers the release of insulin . Additionally, this compound increases peripheral glucose utilization and decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Gliclazid gehört zur Klasse der Sulfonylharnstoff-Medikamente, zu denen auch Glimepirid, Glyburid und Glipizid gehören . Im Vergleich zu diesen Verbindungen hat Gliclazid ein geringeres Risiko, Hypoglykämie zu verursachen, und ist mit weniger Nebenwirkungen verbunden . Es hat auch eine einzigartige chemische Struktur, die zu seinen spezifischen pharmakokinetischen und pharmakodynamischen Eigenschaften beiträgt .
Biologische Aktivität
Gliclazide is a second-generation sulfonylurea, primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its biological activity encompasses several mechanisms that contribute to its efficacy as a hypoglycemic agent. This article will explore the various aspects of this compound's biological activity, including its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, antioxidant properties, and clinical implications.
This compound functions primarily by stimulating insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells. The drug binds to the sulfonylurea receptor (SUR1) on these cells, leading to the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. This closure results in cell depolarization and the subsequent opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels, facilitating calcium influx and promoting insulin exocytosis .
Key Mechanisms:
- Insulin Secretion: Increases first and second-phase insulin release.
- Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity: Enhances sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- Hepatic Glucose Production: Reduces hepatic glucose output without altering insulin receptor sensitivity .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound has an intermediate half-life of approximately 11 hours and is extensively metabolized in the liver, with renal clearance accounting for only about 4% of total drug clearance . The pharmacokinetic profile supports its use as a once or twice-daily medication.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Half-life | ~11 hours |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Renal Clearance | ~4% |
Antioxidant Properties
Recent studies have highlighted this compound's antioxidant properties, which may provide additional benefits beyond glucose control. This compound has demonstrated free radical scavenging capabilities, thereby reducing oxidative stress—a significant contributor to diabetic complications .
Clinical Findings:
- This compound therapy led to a significant decrease in lipid oxidation markers (8-isoprostanes) and an increase in total plasma antioxidant capacity (TPAC) in type 2 diabetic patients .
- Comparatively, this compound outperformed other sulfonylureas like glibenclamide and glimepiride in inhibiting low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation .
Clinical Implications
This compound's unique properties make it a valuable option for managing type 2 diabetes. Its ability to enhance insulin secretion while reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain distinguishes it from other agents in its class. Additionally, its potential benefits in improving endothelial function and reducing platelet aggregation may help mitigate cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes .
Case Studies
-
Long-Term Efficacy Study:
A study involving 44 type 2 diabetic patients assessed the long-term effects of this compound on oxidative stress markers over ten months. Results indicated a significant improvement in antioxidant parameters alongside glycemic control. -
Comparison with Other Sulfonylureas:
In a clinical trial comparing this compound with glimepiride and glibenclamide, this compound was associated with fewer episodes of hypoglycemia and better weight management outcomes.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What analytical methods are validated for quantifying gliclazide and its impurities in pharmaceutical formulations?
A reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method is widely validated for specificity, accuracy, precision, linearity, robustness, and system suitability. The method employs a C18 column with a mobile phase of phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (70:30 v/v), detecting at 226 nm. Linearity ranges from 5–15 μg/mL (r² > 0.999), with LOD and LOQ at 0.5 μg/mL and 1.5 μg/mL, respectively. Robustness is confirmed by varying flow rates (±0.1 mL/min) and column temperatures (±2°C), showing <2% RSD in retention times .
Q. How can researchers mitigate this compound’s reproductive toxicity in laboratory settings?
Follow GHS08 safety protocols: use fume hoods for handling, wear nitrile gloves, and avoid inhalation/ingestion. Reproductive toxicity studies require strict dose controls (e.g., ≤240 mg/day in rodent models) and monitoring of teratogenicity via histopathology. Preclinical trials should align with OECD guidelines, including placental transfer assays and postnatal development tracking .
Q. What experimental designs are recommended for assessing this compound’s hypoglycemic efficacy in clinical trials?
Use randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a double-blind design, comparing this compound to other sulfonylureas or DPP-4 inhibitors. Stratify subgroups by HbA1c levels, disease duration, and comorbidities. Pre-specify endpoints: HbA1c reduction (Δ ≥0.5%), hypoglycemia incidence, and weight changes. Meta-analyses should address publication bias via funnel plots and sensitivity analysis .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can D-optimal mixture design optimize extended-release this compound formulations?
Apply D-optimal design to evaluate hydrophilic polymers (e.g., HPMC K15M and sodium alginate). Target zero-order release over 12 hours by optimizing polymer ratios. Response surface methodology (RSM) predicts release kinetics (e.g., 20–30% at 3h, 90–100% at 12h). Validate using dissolution testing in pH 6.8 buffer and confirm robustness via ANOVA (p < 0.05) .
Q. What mechanisms underlie this compound’s anti-inflammatory effects in colitis-associated cancer (CAC) models?
this compound activates AMPK, inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation. In murine CAC models (AOM/DSS-induced), administer 10 mg/kg/day orally. Assess colon tissue for p-AMPK upregulation via Western blot and NF-κB suppression via immunohistochemistry. Compare to controls using ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests (p < 0.01) .
Q. How do surfactant micelles enhance this compound’s solubility, and how does chain length influence partitioning?
Cationic surfactants (e.g., CTAB) solubilize this compound in micelle cores (Kp = 1.2 × 10³), while anionic surfactants (e.g., SDS) localize it in palisade layers (Kp = 4.5 × 10²). Solubility increases with cationic chain length (C16 > C12) but decreases with anionic chain length (C12 > C16). Validate via UV-Vis spectroscopy and phase solubility diagrams .
Q. How to address confounding factors in real-world studies comparing this compound to DPP-4 inhibitors?
Use propensity score matching (PSM) for variables like HbA1c, BMI, and eGFR. Adjust for metformin co-therapy and microangiopathy prevalence. In multivariable regression, test interactions between treatment type and insulin use. Sensitivity analyses should exclude outliers (e.g., HbA1c >10%) to reduce bias .
Q. What methodologies assess this compound’s stability under environmental stressors like mobile radiation?
Expose tablets to GSM 900 MHz radiation (SAR = 1.6 W/kg) for 24h. Analyze degradation via mass spectrometry (MS) and HPLC. Compare radiated vs. non-radiated samples for dissolution profiles (USP Apparatus II, 50 rpm). Statistical significance is determined by t-tests (p < 0.05) .
Q. Methodological Considerations
- Safety Protocols : Adhere to GHS07/08 guidelines for handling acute toxicity (LD50 = 3000 mg/kg in rats) .
- Data Contradictions : Resolve discrepancies in meta-analyses via Egger’s test and subgroup stratification (e.g., study duration ≥24 weeks) .
- Real-World Data : Collect fasting-specific outcomes (e.g., Ramadan studies) using structured questionnaires and HbA1c monitoring pre-/post-intervention .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
1-(3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H21N3O3S/c1-11-5-7-14(8-6-11)22(20,21)17-15(19)16-18-9-12-3-2-4-13(12)10-18/h5-8,12-13H,2-4,9-10H2,1H3,(H2,16,17,19) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BOVGTQGAOIONJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)NN2CC3CCCC3C2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C15H21N3O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9023095 | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9023095 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
323.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015252 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
42.6 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), 1.90e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID49646130 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015252 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Gliclazide binds to the β cell sulfonyl urea receptor (SUR1). This binding subsequently blocks the ATP sensitive potassium channels. The binding results in closure of the channels and leads to a resulting decrease in potassium efflux leads to depolarization of the β cells. This opens voltage-dependent calcium channels in the β cell resulting in calmodulin activation, which in turn leads to exocytosis of insulin containing secretorty granules. | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01120 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
21187-98-4 | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=21187-98-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01120 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | gliclazide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=758673 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9023095 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.040.221 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015252 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
180-182, 181 °C | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01120 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Gliclazide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015252 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
















