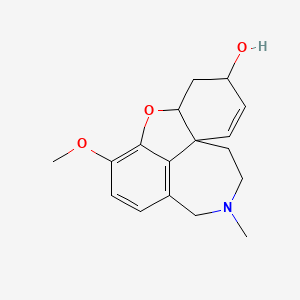
galanthamine
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Galantamin: ist ein natürliches Alkaloid, das aus den Zwiebeln und Blüten verschiedener Pflanzen der Familie der Amaryllidaceae gewonnen wird, wie z. B. Galanthus nivalis (gemeiner Schneeglöckchen), Galanthus caucasicus (kaukasischer Schneeglöckchen) und andere . Es ist vor allem für sein Potenzial zur Verlangsamung des kognitiven Abbaus bekannt und wird klinisch zur Behandlung von Alzheimer-Krankheit im Frühstadium und Gedächtnisstörungen eingesetzt .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetische Routen und Reaktionsbedingungen: Galantamin kann durch verschiedene Methoden synthetisiert werden, darunter biomimetische oxidative Kupplungsreaktionen, Übergangsmetall-katalysierte Reaktionen und Umlagerungsreaktionen . Einige wichtige synthetische Strategien beinhalten:
Oxidative Phenolkupplung: Diese Methode beinhaltet die oxidative Kupplung von Phenolen, die für die Totalsynthese von Galantamin umfassend untersucht wurde.
Übergangsmetall-katalysierte Reaktionen: Dazu gehören die Heck-Reaktion, die Enyn-Ringschlussmetathese (RCM) und die dynamische kinetische Auflösung.
Umlagerungsreaktionen: Beispiele sind die Semipinacol-Umlagerung und die Johnson-Claisen-Umlagerung.
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: Die industrielle Produktion von Galantamin beinhaltet die Extraktion aus natürlichen Quellen oder die synthetische Produktion. Das erste industrielle Verfahren wurde 1959 entwickelt . Neuere Fortschritte konzentrierten sich auf die Optimierung synthetischer Routen, um die Ausbeute zu verbessern und die Kosten zu senken .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Galantamin unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Galantamin kann oxidiert werden, um verschiedene Derivate zu bilden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können die funktionellen Gruppen in Galantamin modifizieren.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können verschiedene funktionelle Gruppen in das Galantaminmolekül einführen.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Es werden Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid und Lithiumaluminiumhydrid verwendet.
Substitution: Verschiedene Reagenzien, darunter Halogene und Alkylierungsmittel, werden für Substitutionsreaktionen verwendet.
Hauptprodukte: Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind verschiedene Galantamin-Derivate mit modifizierten funktionellen Gruppen, die unterschiedliche pharmakologische Eigenschaften haben können .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Galanthamine is a naturally occurring compound that has garnered attention for its clinical applications, particularly in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) . It is derived from plants such as Galanthus nivalis and Narcissus pseudonarcissus .
Scientific Research Applications
Alzheimer's Disease Treatment
- This compound is clinically approved for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease due to its ability to inhibit acetylcholine esterase (AChE) . By blocking the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, galantamine increases acetylcholine neurotransmission . It also acts as an allosteric modulator of the nicotinic receptor, giving its dual mechanism of action clinical significance .
- Clinical trials have demonstrated that galantamine can significantly improve cognitive function and global function in patients with mild to moderate AD . Studies have shown that galantamine, at recommended doses of 16 mg to 24 mg daily, slows the decline in memory and the ability to perform self-care activities at 6 months and 2 years .
- Long-term treatment with galantamine has been shown to reduce mortality and the decline in cognition and daily living activities in patients with mild to moderate AD .
Cognitive and Neuropathic Conditions
- Early research explored galantamine's use in paralytic and neuropathic conditions, as well as for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade . It has also been studied for its cognitive effects in various psychiatric disorders, including mild cognitive impairment, cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, and autism .
- In one study, galantamine reversed scopolamine-induced acute anticholinergic syndrome, which was characterized by drowsiness, disorientation, and delirium .
Dual Cropping for this compound Production
- Innovative approaches have explored the dual cropping of Narcissus pseudonarcissus with grassland-based ruminant production to produce plant-derived this compound . This method involves planting N. pseudonarcissus into existing grassland, which could offer a triple win scenario: (1) maintaining traditional upland farming systems and increasing their economic viability, (2) improving access to AD treatment, and (3) reducing the environmental impacts of this compound production .
- A three-year systems study verified the feasibility of this dual cropping approach, demonstrating that incorporating N. pseudonarcissus into grazed permanent pasture had no detrimental effects on the health or performance of sheep that grazed the pasture .
Data Tables and Case Studies
Efficacy of Galantamine in Alzheimer's Disease
| Metric | Galantamine Group | Placebo Group | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Change in MMSE scores from baseline | -1.41 | -2.14 | <0.021 |
| Mortality Rate (Hazard Ratio) | 0.58 | N/A | 0.011 |
| Deaths | 33 (3.2%) | 56 (5.5%) | 0.011 |
MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination
Case Study: Galantamine for Cognition and Global Function
A 6-month, multicenter, double-blind trial was conducted with 636 patients with mild to moderate AD. Patients were randomly assigned to placebo or galantamine and escalated to maintenance doses of 24 or 32 mg/d. The results showed that galantamine significantly improved cognitive function relative to placebo, with treatment effects of 3.9 points (lower dose) and 3.8 points (higher dose) on the ADAS-cog/11 scale at month 6 (p < 0.001 in both cases) . Both doses of galantamine produced a better outcome on CIBIC-plus than placebo (p < 0.05) . At 12 months, mean ADAS-cog/11 and DAD scores had not significantly changed from baseline for patients who received galantamine 24 mg/d throughout the 12 months .
Safety and Tolerability
Wirkmechanismus
Galantamine works by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine . By inhibiting this enzyme, galantamine increases the levels of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, enhancing cholinergic neurotransmission . Additionally, galantamine acts as an allosteric modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, further enhancing its therapeutic effects .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Rivastigmin: Ein weiterer Acetylcholinesterase-Hemmer zur Behandlung der Alzheimer-Krankheit.
Donepezil: Ein weit verbreiteter Acetylcholinesterase-Hemmer mit einem ähnlichen Wirkmechanismus.
Lycorin: Ein Alkaloid mit Acetylcholinesterase-hemmender Aktivität, jedoch weniger potent als Galantamin.
Einzigartigkeit: Galantamin ist einzigartig aufgrund seines dualen Wirkmechanismus, der sowohl die Acetylcholinesterase hemmt als auch die nikotinergen Acetylcholinrezeptoren moduliert . Diese duale Wirkung verstärkt seine therapeutische Wirksamkeit im Vergleich zu anderen Acetylcholinesterase-Hemmern .
Biologische Aktivität
Galanthamine is a natural alkaloid derived primarily from the bulbs of plants in the Amaryllidaceae family, particularly from the snowdrop (Galanthus spp.). It has garnered significant attention due to its biological activities, especially its role as an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor, making it a crucial compound in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). This article explores the diverse biological activities of this compound, supported by case studies and research findings.
This compound functions primarily as a reversible inhibitor of AChE, an enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of acetylcholine (ACh) in the synaptic cleft. By inhibiting AChE, this compound increases the availability of ACh, enhancing cholinergic neurotransmission. This mechanism is particularly beneficial in conditions characterized by cholinergic deficits, such as AD. Additionally, this compound interacts with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), which may provide neuroprotective effects against β-amyloid toxicity in neurons .
Biological Activities
1. Neuroprotective Effects:
Research indicates that this compound exhibits neuroprotective properties by modulating various neurotransmitter systems. It has been shown to:
- Enhance synaptic plasticity.
- Protect neurons from apoptosis induced by β-amyloid peptides.
- Improve cognitive function in animal models of AD .
2. Antioxidant Properties:
this compound has demonstrated antioxidant activity, which helps mitigate oxidative stress—an important factor in neurodegeneration. Studies have reported that it can reduce lipid peroxidation and increase levels of glutathione, a critical antioxidant in the brain .
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
The compound also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which may contribute to its therapeutic effects in neurodegenerative diseases. Inflammation is a key component of AD pathology, and this compound's ability to modulate inflammatory responses is beneficial .
Case Study 1: Efficacy in Alzheimer's Disease
A clinical trial assessed the effectiveness of this compound in patients with mild to moderate AD. Results indicated that patients receiving this compound showed significant improvements in cognitive function compared to placebo groups. The study highlighted improvements in both memory and overall cognitive performance, reinforcing its role as a valuable therapeutic agent .
Case Study 2: Synthesis of this compound Derivatives
Recent research focused on synthesizing new derivatives of this compound that incorporate peptide moieties to enhance its pharmacological profile. These derivatives were tested for their AChE inhibitory activity and showed promising results with improved potency and reduced toxicity compared to this compound itself. The study utilized various biochemical assays to evaluate their efficacy .
Data Summary
| Biological Activity | Mechanism | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| AChE Inhibition | Competitive inhibition at the active site | Increased ACh levels; improved cognition |
| Neuroprotection | Modulation of nAChRs; reduction of β-amyloid toxicity | Enhanced neuronal survival; improved memory |
| Antioxidant Activity | Reduction of oxidative stress markers | Decreased lipid peroxidation; increased GSH levels |
| Anti-inflammatory | Modulation of inflammatory pathways | Reduced neuroinflammation; potential cognitive benefits |
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
(1S,12S,14R)-9-methoxy-4-methyl-11-oxa-4-azatetracyclo[8.6.1.01,12.06,17]heptadeca-6(17),7,9,15-tetraen-14-ol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H21NO3/c1-18-8-7-17-6-5-12(19)9-14(17)21-16-13(20-2)4-3-11(10-18)15(16)17/h3-6,12,14,19H,7-10H2,1-2H3/t12-,14-,17-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ASUTZQLVASHGKV-JDFRZJQESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1CCC23C=CC(CC2OC4=C(C=CC(=C34)C1)OC)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CN1CC[C@@]23C=C[C@@H](C[C@@H]2OC4=C(C=CC(=C34)C1)OC)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C17H21NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2045606 | |
| Record name | Galanthamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2045606 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
287.35 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Crystals from water; decomposition 256-257 °C. Sparingly sol in cold; more sol in hot water. Very sparingly sol in alcohol, acetone. /Hydrochloride/, Fairly soluble in hot water; freely soluble in alcohol, acetone, chloroform. Less sol in benzene, ether., 1.70e+00 g/L | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by progressive, irreversible degeneration of acetylcholine-producing neurons, cognitive impairment, and the accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques. The cholinergic system plays a critical role in memory, alongside other important neural functions such as attention, learning, stress response, wakefulness and sleep, and sensory information. Studies show that acetylcholine (ACh) is involved in the modulation of acquisition, encoding, consolidation, reconsolidation, extinction, and retrieval of memory. The gradual loss of cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may, therefore, contribute to the memory loss exhibited by AD patients. Acetylcholinesterase is secreted by cholinergic neurons to rapidly hydrolyze ACh at the synaptic cleft to release acetate and choline. Choline is later recycled back into the presynaptic cholinergic neuron via reuptake by the high-affinity choline transporter. There is some evidence demonstrating the potential involvement of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme in the formation of amyloid fibrils. Galantamine competitively and reversibly inhibits the anticholinesterase enzyme in the CNS (namely in the frontal cortex and hippocampal regions) by binding to the choline-binding site and acyl-binding pocket of the enzyme active site. By blocking the breakdown of ACh, galantamine enhances ACh levels in the synaptic cleft. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) in the CNS are mostly expressed at the presynaptic neuronal membrane to control the release of multiple neurotransmitters, such as ACh, glutamate, GABA, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine. Agonists of nAChRs improve performance in cognitive tasks, while antagonists of nAChR impair cognitive processes. Some studies show a decrease in the expression and activity of nAChRs in patients with AD, which may explain the reduction in central cholinergic neurotransmission in these patients. Galantamine binds to nAChRs at the allosteric site, leading to a conformational change of the receptor, increased ACh release, and increased activity of neighbouring glutaminergic and serotoninergic neurons. The modulation of nAChRs facilitates both excitatory and inhibitory cholinergic transmissions in brain tissues and increases receptor sensitivity. The modulated release of other neurotransmitters by galantamine may also contribute to the upregulation of nAChRs and amelioration of behavioural symptoms in AD., Galantamine, a tertiary alkaloid, is a competitive and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. While the precise mechanism of galantamine's action is unknown, it is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this mechanism is correct, galantamine's effect may lessen as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact. There is no evidence that galantamine alters the course of the underlying dementing process., The cause of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's Disease is not fully understood, it has been shown that acetylcholine producing neurons degenerate. The cholinergic loss has been correlated with cognitive impairment and a density of amyloid plaques. Galantamine is a tertiary alkaloid and it competes with and is a reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. The exact mechanism of galantamine is not known, but it is believed to enhance cholinergic function. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00674 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from benzene | |
CAS No. |
357-70-0, 23173-12-8 | |
| Record name | (-)-Galantamine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=357-70-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Galantamine [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000357700 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | (+/-)-Galantamine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0023173128 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00674 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759861 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Galanthamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2045606 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0D3Q044KCA | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE, (±)- | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1T835Z585R | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
126-127 °C, 269 - 270 °C (hydrogen bromide salt) | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details












Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details











Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.













