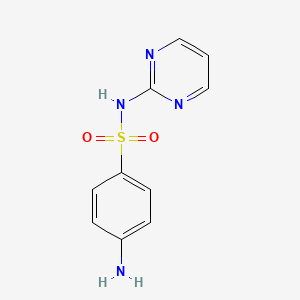
Sulfadiazin
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Sulfadiazin ist ein Sulfonamid-Antibiotikum, das häufig zur Behandlung verschiedener bakterieller Infektionen eingesetzt wird. Es ist besonders wirksam gegen Harnwegsinfektionen, Trachom und Chancroid . This compound wird auch in Kombination mit Pyrimethamin zur Behandlung von Toxoplasmose bei Patienten mit erworbenem Immundefizienzsyndrom und bei Neugeborenen mit kongenitalen Infektionen eingesetzt . Diese Verbindung ist bekannt für ihre Fähigkeit, die Synthese von Folsäure in Bakterien zu hemmen, wodurch deren Wachstum und Vermehrung verhindert werden .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with various applications in medicine, pharmacology, and other scientific fields . It functions by inhibiting bacteria's ability to produce folic acid, which is essential for DNA synthesis, thereby preventing the spread of infection .
Scientific Research Applications
Antibacterial Agent: Sulfadiazine is effective against various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections . It can also be used topically to treat burn and wound infections . The drug inhibits the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, which is crucial for folic acid synthesis .
Treatment of Infections: Sulfadiazine is used in the treatment of several infections, such as trachoma and chancroid . Laboratory studies on animals have indicated that sulfadiazine has less toxicity compared to other drugs like sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole and is highly effective against common pathogens .
Silver Sulfadiazine in Wound Care: Silver sulfadiazine (SSDZ) is a common choice for treating skin burns . It can be integrated into hydrogels for topical wound treatment because hydrogels have minimal toxicity and can sustain the release of pharmaceuticals .
Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), including those incorporating silver sulfadiazine, have demonstrated antimicrobial properties and have contributed to the development of nanotechnology . AgNPs can potentially replace traditional antibiotics due to increasing bacterial resistance .
Combination Therapies: Sulfadiazine can be combined with other substances like hyaluronic acid (HA) to treat conditions such as parastomal skin ulceration . The combination of HA and silver sulfadiazine has shown success in promoting healing and reducing pain in such cases .
Data Table: Properties and Applications of Sulfadiazine
Case Studies
Parastomal Ulcer Healing: A case study demonstrated the successful treatment of chronic parastomal skin ulceration using a combination cream of 0.2% Hyaluronic acid and 1% Silver sulfadiazine . Patients treated with this combination experienced complete healing, reduced pain, and decreased purulent fluid, leading to a reduced cost of treatment compared to standard protocols .
Silver Sulfadiazine Hydrogels for Wound Treatment: Silver sulfadiazine has been integrated into hydrogels for wound treatment due to the hydrogels' low toxicity and capacity for extended pharmaceutical release .
Research Findings and Insights
Efficacy of Silver Sulfadiazine: A systematic review comparing Silver Sulfadiazine with other dressings for burns showed a statistically significant difference in healing time for silver dressings . While some animal studies support the use of Silver Sulfadiazine for partial-thickness burns, others question its effectiveness .
Toxicity and Safety: Laboratory studies on animals suggest that sulfadiazine has lower toxicity compared to sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Sulfadiazine primarily targets the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase . This enzyme plays a crucial role in the synthesis of folic acid, which is essential for bacterial growth and reproduction .
Mode of Action
Sulfadiazine acts as a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthetase . It competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for binding to the enzyme, thereby inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid . This results in the inhibition of bacterial growth and reproduction .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by sulfadiazine is the folic acid synthesis pathway in bacteria . By inhibiting dihydropteroate synthetase, sulfadiazine prevents the proper processing of PABA, which is essential for folic acid synthesis . This leads to a decrease in the production of folic acid, which is necessary for bacterial growth and reproduction .
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfadiazine is rapidly and extensively absorbed from the gut and is 20 to 55% bound to plasma proteins . Its elimination half-life is 7-12 hours . Sulfadiazine can cross the placenta, achieving blood concentrations in the fetus of 50 to 90% of those in the mother . It also achieves high concentrations in breast milk (20% of plasma) .
Result of Action
The primary result of sulfadiazine’s action is the inhibition of bacterial growth and reproduction . By inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid, sulfadiazine prevents bacteria from growing and reproducing effectively . This makes it an effective treatment for a variety of bacterial infections .
Action Environment
The action of sulfadiazine can be influenced by various environmental factors. For example, the presence of pus can inhibit its antibacterial action . The degradation of sulfadiazine can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of certain ions .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von Sulfadiazin beginnt typischerweise mit der Acetylierung von Anilin-Derivaten unter Verwendung von Essigsäureanhydrid, um Acetanilid-Derivate zu bilden . Diese Derivate werden dann mit Chlorsulfonsäure umgesetzt, um 4-Acetylamino-benzolsulfonylchlorid zu erhalten . Parallel dazu wird 2-Aminopyrimidin hergestellt, indem Tetramethoxypropan mit einem Guanidinsalz umgesetzt wird . Der letzte Schritt beinhaltet die Umsetzung von 4-Acetylamino-benzolsulfonylchlorid mit 2-Aminopyrimidin, gefolgt von einer Hydrolyse mit Natriumhydroxid, um this compound zu ergeben .
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren
Die industrielle Produktion von this compound folgt ähnlichen Synthesewegen, jedoch in größerem Maßstab. Der Prozess beinhaltet eine strenge Kontrolle der Reaktionsbedingungen, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten. Die Verwendung von automatisierten Reaktoren und kontinuierlichen Fließsystemen trägt dazu bei, eine konstante Qualität und Effizienz in der Produktion zu gewährleisten .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Sulfadiazin unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, einschließlich Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution . Die Verbindung enthält zwei reaktive Gruppen: ein aromatisches Amin und eine Sulfonamidgruppe, die an diesen Reaktionen beteiligt sind .
Gängige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Reduktion: Die Reduktion von this compound kann mit Reduktionsmitteln wie Natriumborhydrid erreicht werden.
Substitution: Die aromatische Aminogruppe in this compound kann in Gegenwart von Katalysatoren Substitutionsreaktionen mit Elektrophilen eingehen.
Hauptprodukte
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, umfassen verschiedene Derivate von this compound, die in pharmazeutischen Anwendungen weiter verwendet werden können .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Sulfamethoxazol: Ein weiteres Sulfonamid-Antibiotikum, das in Kombination mit Trimethoprim zur Behandlung verschiedener bakterieller Infektionen eingesetzt wird.
Sulfisoxazol: Wird zur Behandlung von Harnwegsinfektionen und anderen bakteriellen Infektionen eingesetzt.
Silbersulfadiazin: Ein topisches Mittel, das zur Behandlung von Verbrennungen und Wundinfektionen eingesetzt wird.
Einzigartigkeit
This compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seiner breiten antibakteriellen Aktivität und seiner Fähigkeit, in Kombination mit anderen Medikamenten wie Pyrimethamin zur Behandlung bestimmter Infektionen wie Toxoplasmose eingesetzt zu werden . Seine Wirksamkeit sowohl in der Human- als auch in der Veterinärmedizin unterstreicht seine Vielseitigkeit .
Biologische Aktivität
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic that has been widely studied for its biological activity, particularly in the treatment of bacterial infections and its potential applications in various medical fields. This article discusses the compound's mechanisms of action, antimicrobial properties, clinical applications, and recent research findings.
Sulfadiazine functions primarily by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. It acts as a competitive antagonist of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate required for the synthesis of folate in bacteria. By blocking this pathway, sulfadiazine effectively prevents bacterial growth and reproduction, leading to cell death. This mechanism is common among sulfonamides, which have been utilized since their introduction in the 1930s.
Antimicrobial Properties
Sulfadiazine exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. It has been shown to be effective against:
- Gram-positive bacteria : Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative bacteria : Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Fungi : Candida albicans
- Protozoa : Toxoplasma gondii
Comparative Antimicrobial Efficacy
Recent studies have highlighted the enhanced efficacy of sulfadiazine when used in combination with metal complexes. For instance, metal complexes of sulfadiazine have demonstrated superior antibacterial activity compared to the free ligand itself, particularly against resistant strains of bacteria .
| Pathogen | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 32 µg/mL |
| Escherichia coli | 16 µg/mL |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 64 µg/mL |
| Candida albicans | 8 µg/mL |
Clinical Applications
Sulfadiazine is commonly used in clinical settings for treating various infections, including:
- Toxoplasmosis : Often administered in combination with pyrimethamine for effective treatment.
- Burn wounds : Silver sulfadiazine is a topical formulation used extensively for burn management due to its antimicrobial properties .
Case Studies
-
Silver Sulfadiazine in Burn Treatment :
A clinical trial involving children with severe burns demonstrated that silver sulfadiazine significantly reduced infection rates and facilitated wound healing compared to traditional treatments. The study reported no progression to critical infection stages among treated patients . -
Aerosol Formulation for Pressure Ulcers :
A novel aerosol formulation combining silver sulfadiazine with lidocaine and vitamin A showed promising results in treating scalp pressure ulcers in ICU patients. The treatment was associated with improved healing rates and reduced costs compared to conventional dressings .
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have explored the multifaceted biological activities of sulfadiazine beyond its antibacterial properties:
- Anticancer Activity : Research indicates that sulfadiazine exhibits antiproliferative effects on human liver cancer (HepG2) and breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines by inhibiting the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway. The IC50 values were determined to be approximately 245.69 µM for HepG2 cells and 215.68 µM for MCF7 cells .
- Cytotoxic Effects : Sulfadiazine derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines, revealing potential as therapeutic agents in oncology .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-pyrimidin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H10N4O2S/c11-8-2-4-9(5-3-8)17(15,16)14-10-12-6-1-7-13-10/h1-7H,11H2,(H,12,13,14) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SEEPANYCNGTZFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CN=C(N=C1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H10N4O2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7044130 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
250.28 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
6.01e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is needed for the proper processing of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) which is essential for folic acid synthesis. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
68-35-9 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=68-35-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000068359 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757324 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=35600 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.623 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFADIAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0N7609K889 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.















