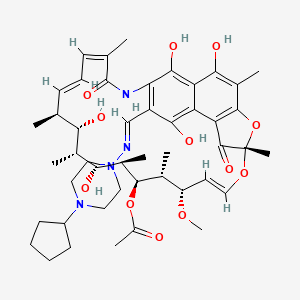
Rifapentin
- Klicken Sie auf QUICK INQUIRY, um ein Angebot von unserem Expertenteam zu erhalten.
- Mit qualitativ hochwertigen Produkten zu einem WETTBEWERBSFÄHIGEN Preis können Sie sich mehr auf Ihre Forschung konzentrieren.
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Rifapentine, sold under the brand name Priftin, is an antibiotic used primarily in the treatment of tuberculosis. It belongs to the rifamycin class of antibiotics and is known for its ability to inhibit bacterial RNA synthesis by targeting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase . This compound is particularly effective against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Treatment of Tuberculosis
Active Tuberculosis
Rifapentine is effective in treating drug-susceptible TB. It is often used in combination with other antitubercular agents such as isoniazid. The efficacy of rifapentine in short-course regimens has been demonstrated in clinical trials, showing comparable results to standard treatments while reducing treatment duration from six months to four months .
Latent Tuberculosis Infection
Rifapentine has gained prominence in treating latent TB infection, particularly among high-risk populations. A regimen combining rifapentine and isoniazid (3HP) has been shown to be highly effective, allowing for a more manageable treatment course that enhances patient adherence . This combination therapy is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes, who are at increased risk for progression to active TB .
Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Strategies
Recent studies have focused on the pharmacokinetics of rifapentine to optimize dosing strategies. Research indicates that weight-based dosing may not be appropriate for all patients, particularly those with lower body weights or those co-infected with HIV. Higher doses may be necessary to achieve therapeutic levels .
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Rifapentine
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | Decreases by 27% with HIV infection |
| Clearance Increase | Up to 72% after 21 days |
| Impact of Diet | Increased by 49% with high-fat meals |
| Recommended Dosing | Flat dosing suggested over weight-based |
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have explored the safety and efficacy of rifapentine in various populations:
- Study on Age Impact : A study examined how age affects treatment outcomes with rifapentine-based weekly therapy. Older patients exhibited different systemic drug reactions compared to younger cohorts, highlighting the need for age-specific treatment protocols .
- Combination Therapy : In trials assessing the combination of rifapentine with newer anti-TB drugs like SQ109, results indicated that while rifapentine was safe, its interaction with SQ109 did not enhance bacteriological outcomes significantly .
- Adverse Effects : A rare case of disseminated intravascular coagulation induced by rifampicin therapy was documented, underscoring the importance of monitoring patients for severe adverse effects during treatment .
Immunomodulatory Effects
Emerging research suggests that rifapentine may have immunomodulatory properties. It has been shown to influence immune pathways, potentially benefiting patients with inflammatory conditions . This aspect opens new avenues for research into its use beyond infectious diseases.
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Rifapentine, an antibiotic agent used in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis, primarily targets the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in susceptible cells . This enzyme plays a crucial role in the transcription process, where it catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from DNA.
Mode of Action
It acts via the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, leading to a suppression of RNA synthesis and cell death . This interaction disrupts the transcription process, preventing the bacteria from synthesizing essential proteins, thereby inhibiting their growth and proliferation .
Biochemical Pathways
Rifapentine affects the transcription pathway in bacteria. By inhibiting the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, it disrupts the conversion of DNA into RNA, a critical step in protein synthesis . This disruption affects downstream processes, including protein synthesis and subsequent cellular functions, ultimately leading to bacterial cell death .
Pharmacokinetics
Rifapentine exhibits certain ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion) properties that impact its bioavailability. It is well absorbed when taken orally and is distributed widely in body tissues and fluids, including the cerebrospinal fluid . It undergoes hepatic metabolism, where it is hydrolyzed by an esterase enzyme to form the active metabolite 25-desacetyl rifapentine . The drug is primarily excreted in the feces (70%), with a smaller portion excreted in the urine (17%, primarily as metabolites) . The time to peak serum concentration is between 3 to 10 hours, and the elimination half-life of rifapentine is approximately 17 hours .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of rifapentine’s action result in the suppression of RNA synthesis, leading to cell death . It has shown higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities, especially against intracellular bacteria growing in human monocyte-derived macrophages . It is bactericidal and has a very broad spectrum of activity against most gram-positive and gram-negative organisms, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis .
Action Environment
Environmental factors can influence the action, efficacy, and stability of rifapentine. For instance, the presence of food can increase the absorption of rifapentine, enhancing its bioavailability . Additionally, rifapentine’s efficacy can be influenced by the patient’s age, with clearance decreasing with increasing age . Furthermore, rifapentine’s action can be affected by the presence of other drugs, as it is known to induce the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, potentially leading to reduced bioavailability and enhanced clearance of some coadministered medications .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Rifapentine inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in susceptible cells . Specifically, it interacts with bacterial RNA polymerase but does not inhibit the mammalian enzyme . This interaction is crucial for its role in biochemical reactions.
Cellular Effects
Rifapentine has shown higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities especially against intracellular bacteria growing in human monocyte-derived macrophages . It influences cell function by suppressing RNA synthesis, leading to cell death .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Rifapentine involves the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, leading to a suppression of RNA synthesis and cell death . It exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, specifically bacterial RNA polymerase .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Stability concerns have been raised for Rifapentine stored under certain conditions .
Metabolic Pathways
Rifapentine is metabolized in the liver and eliminated in bile and, to a much lesser extent, in urine
Transport and Distribution
Rifapentine is well absorbed when taken orally and is distributed widely in body tissues and fluids, including the cerebrospinal fluid
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Rifapentine is synthesized starting from rifamycin S. The process involves several key steps:
Conversion to Intermediate: Rifamycin S reacts with dihydroxy methyl tert-butyl amine in an organic solvent to form an intermediate called rifaoxazine.
Hydrolysis and Ring Opening: The intermediate undergoes hydrolysis and ring opening in the presence of a catalyst and a reductant in a second organic solvent.
Condensation: The hydrolysis product is then condensed with 1-amino-4-cyclopentyl piperazine to form rifapentine.
Industrial Production Methods: The industrial production of rifapentine involves scaling up the laboratory synthesis process. Key challenges include maintaining the purity and uniformity of the product, optimizing reaction conditions, and ensuring efficient crystallization and drying processes .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions: Rifapentine undergoes several types of chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Rifapentine can be oxidized under certain conditions, leading to the formation of various oxidation products.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can modify the functional groups on the rifapentine molecule.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur, particularly at the piperazine ring, leading to the formation of different derivatives.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate.
Reduction: Reducing agents such as sodium borohydride and lithium aluminum hydride are often used.
Substitution: Substitution reactions typically involve nucleophiles like amines and alcohols.
Major Products: The major products formed from these reactions include various oxidized, reduced, and substituted derivatives of rifapentine .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Rifampin: Commonly used in combination therapy for tuberculosis.
Rifabutin: Used primarily in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Rifapentine’s unique pharmacokinetic properties and its efficacy in shorter treatment regimens make it a valuable addition to the arsenal against tuberculosis .
Eigenschaften
Key on ui mechanism of action |
Rifapentine has shown higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities especially against intracellular bacteria growing in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Rifapentine inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in susceptible strains of M. tuberculosis. Rifapentine acts via the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, leading to a suppression of RNA synthesis and cell death. |
|---|---|
CAS-Nummer |
61379-65-5 |
Molekularformel |
C47H64N4O12 |
Molekulargewicht |
877.0 g/mol |
IUPAC-Name |
[(7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-26-[(4-cyclopentylpiperazin-1-yl)iminomethyl]-2,15,17,27,29-pentahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23-dioxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.14,7.05,28]triaconta-1(29),2,4,9,19,21,25,27-octaen-13-yl] acetate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C47H64N4O12/c1-24-13-12-14-25(2)46(59)49-37-32(23-48-51-20-18-50(19-21-51)31-15-10-11-16-31)41(56)34-35(42(37)57)40(55)29(6)44-36(34)45(58)47(8,63-44)61-22-17-33(60-9)26(3)43(62-30(7)52)28(5)39(54)27(4)38(24)53/h12-14,17,22-24,26-28,31,33,38-39,43,53-57H,10-11,15-16,18-21H2,1-9H3,(H,49,59)/b13-12+,22-17+,25-14-,48-23?/t24-,26+,27+,28+,33-,38-,39+,43+,47-/m0/s1 |
InChI-Schlüssel |
WDZCUPBHRAEYDL-LYDPARFQSA-N |
SMILES |
CC1C=CC=C(C(=O)NC2=C(C(=C3C(=C2O)C(=C(C4=C3C(=O)C(O4)(OC=CC(C(C(C(C(C(C1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)C)O)O)C=NN5CCN(CC5)C6CCCC6)C |
Isomerische SMILES |
C[C@H]1/C=C/C=C(\C(=O)NC2=C(C(=C3C(=C2O)C(=C(C4=C3C(=O)[C@](O4)(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)C)O)O)C=NN5CCN(CC5)C6CCCC6)/C |
Kanonische SMILES |
CC1C=CC=C(C(=O)NC2=C(C(=C3C(=C2O)C(=C(C4=C3C(=O)C(O4)(OC=CC(C(C(C(C(C(C1O)C)O)C)OC(=O)C)C)OC)C)C)O)O)C=NN5CCN(CC5)C6CCCC6)C |
Aussehen |
Solid powder |
Reinheit |
>98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
Haltbarkeit |
>3 years if stored properly |
Löslichkeit |
Soluble in DMSO |
Lagerung |
Dry, dark and at 0 - 4 C for short term (days to weeks) or -20 C for long term (months to years). |
Synonyme |
Rifapentine; DL 473; DL-473; DL473; R 773; R-773; R773; |
Herkunft des Produkts |
United States |
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.















