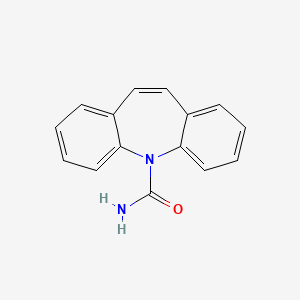
Carbamazepine
Descripción general
Descripción
La carbamazepina es un anticonvulsivo y analgésico conocido que se usa principalmente para tratar la epilepsia y el dolor neuropático. También se utiliza como tratamiento de segunda línea para el trastorno bipolar y como tratamiento adyuvante en la esquizofrenia. Descubierta en 1953 por el químico suizo Walter Schindler, la carbamazepina se comercializó por primera vez en 1962 y desde entonces se ha convertido en un elemento básico en el manejo de diversas afecciones neurológicas .
Mecanismo De Acción
La carbamazepina ejerce sus efectos principalmente inhibiendo la activación de los canales de sodio. Esta acción reduce la respuesta nerviosa polisináptica e inhibe la potenciación posttetánica, estabilizando así las membranas nerviosas hiperexcitadas. El compuesto también afecta la liberación de neurotransmisores y modula la transmisión sináptica .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Carbamazepine works by stabilizing the electrical activity in the brain and nerves . It stops electrical signals from building up in the nerve cells in the brain and also reduces the release of a chemical (neurotransmitter) called glutamate . It is structurally similar to tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a significant impact on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by stabilizing the electric signals in your nerves . This stops the pain signals being sent to your brain . It also has effects on serotonin systems but the relevance to its antiseizure effects is uncertain .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound is a sodium channel blocker . It binds preferentially to voltage-gated sodium channels in their inactive conformation, which prevents repetitive and sustained firing of an action potential . It also acts at adenosine receptors and as an anti-cholinergic .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
On chronic administration, this compound induces its own metabolism sometimes leading to requirement for increasing the dose after the first month of therapy to maintain effect . This compound metabolism is induced by phenobarbital and phenytoin but inhibited by valproate and lamotrigine .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, this compound at certain doses has shown to reduce immobility in the behavioral despair model . It neither modified the methamphetamine anorectic effect, nor induced anorexia when administered alone .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily by CYP3A4, to this compound-10,11-epoxide which is pharmacologically active . Additional isoenzymes that contribute to the metabolism of this compound include CYP2C8, CYP2B6, CYP2E1, CYP1A2, and CYP2A6 .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is rapidly absorbed with a bioavailability of 75–85% . Its volume of distribution is 0.8–2.0 L/kg, and plasma protein binding is 75% . The protein binding of the pharmacologically active metabolite, this compound-10,11-epoxide, is 50% .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción
La carbamazepina se sintetiza a partir de iminostilbeno mediante una reacción con urea en un medio protonante. Este proceso implica la formación de un intermedio, que posteriormente se convierte en carbamazepina. Las condiciones de reacción suelen incluir el uso de un solvente orgánico y un agente ácido para facilitar la conversión .
Métodos de producción industrial
En entornos industriales, la carbamazepina se produce mediante un proceso de síntesis continua. Este método emplea espectroscopia Raman en línea validada y modelado cinético para monitorear y optimizar las condiciones de reacción. El reactor de tanque agitado continuo (CSTR) se utiliza para mantener el equilibrio dinámico y garantizar la calidad constante del producto .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones
La carbamazepina experimenta diversas reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: La carbamazepina se puede oxidar para formar carbamazepina-10,11-epóxido, un metabolito activo.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción pueden convertir la carbamazepina-10,11-epóxido de nuevo a carbamazepina.
Sustitución: La carbamazepina puede sufrir reacciones de sustitución, particularmente en presencia de nucleófilos fuertes
Reactivos y condiciones comunes
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen el peroximonosulfato y otros peróxidos.
Reducción: Se pueden utilizar agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio.
Sustitución: A menudo se emplean nucleófilos fuertes como la amida de sodio.
Productos principales
Oxidación: Carbamazepina-10,11-epóxido
Reducción: Carbamazepina
Sustitución: Diversos derivados sustituidos según el nucleófilo utilizado
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
La carbamazepina tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Química: Se utiliza como compuesto modelo en estudios de metabolismo de fármacos y mecanismos de reacción.
Biología: Investigada por sus efectos sobre la actividad neuronal y la liberación de neurotransmisores.
Medicina: Extensamente estudiada por sus efectos terapéuticos en la epilepsia, el dolor neuropático y el trastorno bipolar.
Industria: Empleada en el desarrollo de nuevas formulaciones farmacéuticas y sistemas de administración de fármacos .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La carbamazepina se compara a menudo con otros fármacos anticonvulsivos como la oxcarbazepina y el acetato de eslicarbazepina. Si bien los tres compuestos comparten un mecanismo de acción similar, inhibiendo los canales de sodio dependientes de voltaje, difieren en sus perfiles farmacocinéticos y selectividad para el estado inactivo del canal de sodio. La oxcarbazepina y el acetato de eslicarbazepina son derivados más nuevos con perfiles de seguridad mejorados y menos efectos secundarios .
Compuestos similares
- Oxcarbazepina
- Acetato de eslicarbazepina
- Fenitoína
- Valproato
La carbamazepina sigue siendo un compuesto único y valioso en el tratamiento de los trastornos neurológicos debido a su eficacia bien establecida y su extensa historia de investigación.
Actividad Biológica
Carbamazepine (CBZ) is a widely used antiepileptic drug that has garnered significant attention for its biological activity and pharmacological effects. It is primarily indicated for the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and neuropathic pain. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, effects on various biological systems, and implications for antibiotic resistance.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits complex pharmacokinetics characterized by high plasma protein binding and extensive hepatic metabolism.
- Plasma Protein Binding : Approximately 75-80% of this compound is bound to plasma proteins, which affects its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy .
- Bioavailability : The bioavailability of this compound ranges from 75% to 85%, and food intake does not significantly alter absorption rates .
- Metabolism : The drug is predominantly metabolized in the liver via the cytochrome P450 system, primarily by CYP3A4, producing an active metabolite, this compound-10,11-epoxide (CBZ-E), which also exhibits anticonvulsant properties . this compound undergoes autoinduction, leading to increased clearance over time .
The mechanism of action of this compound is multifaceted but primarily involves:
- Sodium Channel Inhibition : this compound stabilizes inactive sodium channels, thereby inhibiting neuronal firing and preventing seizure activity .
- GABAergic Modulation : It enhances GABA transmission, which contributes to its mood-stabilizing effects in bipolar disorder .
- Reduction of Polysynaptic Nerve Responses : Studies indicate that this compound lowers polysynaptic nerve responses and inhibits post-tetanic potentiation in animal models .
Biological Effects
This compound's biological activity extends beyond its primary therapeutic uses, influencing various cellular processes:
- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation : Research has shown that this compound can increase ROS levels in cells, triggering oxidative stress responses that may have implications for antibiotic resistance mechanisms .
- Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT) : this compound has been demonstrated to enhance the conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes among bacterial populations. This effect is mediated through increased cell membrane permeability and pilus generation under oxidative stress conditions induced by the drug .
Study on HGT Enhancement
A study investigated the effects of this compound on horizontal gene transfer among bacteria. The results indicated that exposure to this compound significantly increased the frequency of conjugative transfer of plasmid-borne multiresistance genes across different bacterial genera. The study utilized various concentrations ranging from 0.05 mg/L to 50 mg/L to assess the impact on transfer rates:
| Concentration (mg/L) | Fold Change in Transfer Frequency |
|---|---|
| 0.05 | 4x |
| 10 | 4x |
| 12.5 | Significant increase |
| 50 | >9x |
These findings suggest potential environmental risks associated with this compound as a non-antibiotic pharmaceutical contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance .
Pharmacokinetic Study in Epileptic Patients
A pharmacokinetic study conducted on Iranian patients with epilepsy revealed critical insights into the drug's metabolism and clearance dynamics. Key findings included:
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
benzo[b][1]benzazepine-11-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H12N2O/c16-15(18)17-13-7-3-1-5-11(13)9-10-12-6-2-4-8-14(12)17/h1-10H,(H2,16,18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FFGPTBGBLSHEPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC3=CC=CC=C3N2C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C15H12N2O | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | Wikipedia | |
| URL | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbamazepine | |
| Description | Chemical information link to Wikipedia. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
85756-57-6 (di-hydrate) | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000298464 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4022731 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4022731 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
236.27 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
399.6±45.0 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Solubility |
>35.4 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), Sol in alcohol, acetone, propylene glycol; practically insol in water, Soluble in chloroform, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, or methanol; only slightly soluble in ethanol or glacial acetic acid, 1.52e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855967 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Carbamazepine's mechanism of action is not fully elucidated and is widely debated. One major hypothesis is that carbamazepine inhibits sodium channel firing, treating seizure activity. Animal research studies have demonstrated that carbamazepine exerts its effects by lowering polysynaptic nerve response and inhibiting post-tetanic potentiation. In both cats and rats, carbamazepine was shown to decrease pain caused by infraorbital nerve stimulation. A decrease in the action potential in the nucleus ventralis of the thalamus in the brain and inhibition of the lingual mandibular reflex were observed in other studies after carbamazepine use. Carbamazepine causes the above effects by binding to voltage-dependent sodium channels and preventing action potentials, which normally lead to stimulatory effects on nerves. In bipolar disorder, carbamazepine is thought to increase dopamine turnover and increase GABA transmission, treating manic and depressive symptoms. A common issue that has arisen is resistance to this drug in up to 30% of epileptic patients, which may occur to altered metabolism in patients with variant genotypes. A potential therapeutic target to combat carbamazepine resistance has recently been identified as the EPHX1 gene promoter, potentially conferring resistance to carbamazepine through methylation., Anticonvulsant: Exact mechanism unknown; may act postsynaptically by limiting the ability of neurons to sustain high frequency repetitive firing of action potentials through enhancement of sodium channel inactivation; in addition to altering neuronal excitability, may act presynaptically to block the release of neurotransmitter by blocking presynaptic sodium channels and the firing of action potentials, which in turn decreases synaptic transmission., Antineuralgic: Exact mechanism unknown; may involve gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAB) receptors, which may be linked to calcium channels., Antimanic; antipsychotic: Exact mechanism is unknown; may be related to either the anticonvulsant or the antineuralgic effects of carbamazepine, or to tis effects on neurotransmitter modulator systems., Antidiuretic: Exact mechanism unknown; may exert a hypothalamic effect on the osmoreceptors mediated via secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), or may have a direct effect on the renal tubule., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CARBAMAZEPINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from absolute ethanol and benzene, White to off-white powder | |
CAS No. |
298-46-4 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=298-46-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000298464 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=755920 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=169864 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4022731 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.005.512 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/33CM23913M | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
189-192, 190.2 °C | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













