Closantel
Descripción general
Descripción
Closantel es un agente antiparasitario sintético que pertenece a la clase química de las salicianilidas. Se utiliza principalmente en medicina veterinaria para controlar parásitos internos como nematodos y duelas hepáticas, así como algunos parásitos externos como la mosca nasal de las ovejas y los gusanos de la carne de los bovinos . This compound no se utiliza contra plagas agrícolas o domésticas y no está destinado al uso humano .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Antiparasitic Applications
Closantel is widely recognized for its effectiveness against various parasitic infections in ruminants, particularly against blood-feeding helminths such as Fasciola hepatica and Haemonchus contortus. It operates by inhibiting the metabolism of these parasites, leading to their death.
Efficacy Against Specific Parasites
- Fasciola spp. : this compound has shown a 100% efficacy rate against Fasciola spp. in clinical settings, significantly reducing fecal egg counts within a week post-treatment .
- Haemonchus spp. : In studies comparing various anthelmintics, this compound demonstrated superior effectiveness against Haemonchus spp., outperforming other treatments like levamisole and fenbendazole .
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
The pharmacokinetic profile of this compound has been extensively studied to optimize its use in livestock. Key findings include:
- High Plasma Protein Binding : this compound exhibits a high degree of plasma protein binding (approximately 99%), contributing to its prolonged action in the body .
- Bioequivalence Studies : Research has confirmed that different formulations of this compound show similar pharmacokinetic parameters, ensuring consistent therapeutic outcomes across formulations .
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of this compound
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Cmax | Varies by formulation |
| Tmax | 24-48 hours |
| Half-life | 5-7 days |
| Plasma Protein Binding | ~99% |
Clinical Studies and Milk Production
A randomized controlled trial evaluated the impact of this compound on milk production in dairy cattle. The study found that administering this compound improved milk yield and reduced antibody levels against Fasciola hepatica in milk samples .
Study Design Overview
- Population : First-calf heifers.
- Dosage : 0.2 ml/kg body weight.
- Duration : Administered at dry-off, between 80 and 42 days before calving.
Novel Applications in Oncology
Recent research indicates potential applications of this compound beyond veterinary medicine. It has been identified as a BRAFV600E enzyme inhibitor, suggesting its potential use in preparing drugs for treating certain tumors, including melanoma and colorectal cancer .
Conclusion and Future Directions
This compound remains a vital compound in veterinary medicine with proven efficacy against various parasitic infections in livestock. Its pharmacokinetic properties support its long-term use, while emerging research suggests novel applications in oncology. Future studies should focus on expanding its therapeutic uses and understanding its mechanisms further.
Mecanismo De Acción
Closantel ejerce sus efectos antiparasitarios al desacoplar la fosforilación oxidativa en las mitocondrias de los parásitos, lo que interrumpe la producción de trifosfato de adenosina (ATP), el "combustible" celular . Este mecanismo conduce a la acumulación de fumarato y, en última instancia, a la muerte del parásito . This compound también inhibe la reductasa de fumarato, una enzima esencial involucrada en la síntesis de fumarato .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Closantel acts mainly via the energy metabolism pathway by uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation in liver flukes . This interaction disrupts the energy balance within the parasite, leading to its death .
Cellular Effects
This compound has been found to reverse antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacteria . It increases the activity of antibiotics against these bacteria, both in vitro and in vivo . In humans, accidental ingestion of this compound can lead to severe visual loss due to the destruction of neurosensory retina and visual pathways .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound’s mechanism of action involves the disruption of energy metabolism within parasites . It uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, a process crucial for the production of ATP, the energy currency of the cell . This disruption leads to energy depletion within the parasite, ultimately causing its death .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that this compound has a long half-life in plasma, around 15 days , indicating its stability and potential for long-term effects on cellular function.
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animals, the usual dose of this compound is 7.5-10 mg/kg . Overdosing can lead to hypersensitivity reactions, including skin rash, fever, facial swelling, or difficulty breathing . Severe side effects have been reported in humans following accidental ingestion of this compound .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in the energy metabolism pathway within parasites, specifically in the process of oxidative phosphorylation . It acts as an uncoupler, disrupting the flow of protons across the mitochondrial membrane, which is essential for ATP production .
Transport and Distribution
Information on the transport and distribution of this compound within cells and tissues is limited. It is known that this compound reaches maximum plasma levels 8 to 24 hours after dosing, and up to 60% of an intramuscular dose is present in the plasma up to about 4 days after injection .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely that this compound localizes to the mitochondria, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs .
Métodos De Preparación
Closantel se puede sintetizar mediante varios métodos. Un método implica la preparación del intermedio de this compound sódico mediante hidrogenación catalítica . Otro método incluye la preparación de la inyección de this compound sódico, que implica mezclar etanol y propilenglicol, calentar la mezcla, agregar this compound sódico y ajustar el pH con una solución de hidróxido de sodio . Estos métodos son eficientes y adecuados para la producción industrial.
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Closantel experimenta varios tipos de reacciones químicas, incluyendo oxidación, reducción y sustitución. Por ejemplo, la separación enantiomérica del this compound se puede lograr mediante cromatografía líquida de alta resolución (HPLC) con diferentes fases estacionarias quirales y composiciones de fase móvil . Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones son los enantiómeros del this compound, que se pueden separar y analizar para futuras investigaciones .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Closantel es único entre los agentes antiparasitarios debido a su mecanismo de acción específico y su actividad de amplio espectro contra varios parásitos. Compuestos similares incluyen otros derivados de salicianilida como oxiclozanida y rafoxanida . Estos compuestos comparten estructuras químicas y mecanismos de acción similares, pero pueden diferir en su espectro de actividad y eficacia contra parásitos específicos .
Actividad Biológica
Closantel is an anthelmintic compound primarily used in veterinary medicine for the treatment of parasitic infections, particularly those caused by trematodes and nematodes. Recent studies have expanded its application to include antibacterial properties, showcasing its potential in combating multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its antimicrobial effects, toxicity, and pharmacokinetics.
Antimicrobial Activity
This compound has demonstrated significant antibacterial activity, particularly against gram-negative bacteria. A study highlighted the synergistic effects of this compound when combined with polymyxin B against Acinetobacter baumannii, a notorious multidrug-resistant pathogen. The combination therapy was effective in inhibiting the development of resistance to polymyxin B, suggesting that this compound can serve as a valuable adjuvant in treating severe bacterial infections.
Key Findings:
- Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) : this compound alone showed MIC values greater than 128 mg/L against most A. baumannii isolates but achieved lower MICs (0.5 mg/L) against certain polymyxin-resistant strains when used in combination with polymyxin B .
- Synergistic Effects : The combination of polymyxin B (2 mg/L) with this compound (4-16 mg/L) effectively inhibited bacterial growth and prevented the emergence of resistance .
Case Studies on Toxicity
Despite its therapeutic benefits, this compound has been associated with adverse effects, particularly ocular toxicity. A notable case involved a 20-year-old female patient who experienced reversible blindness after receiving an incorrect prescription of this compound instead of triclabendazole for Fasciola hepatica infection. The patient's vision impairment was linked to retinal damage caused by the drug.
Case Highlights:
- Symptoms : The patient reported bilateral blurred vision and color blindness after taking this compound for three days.
- Treatment : Plasma exchange and high-dose corticosteroids were administered, resulting in partial recovery of vision over a follow-up period .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits a long half-life and high plasma protein binding capacity, which influences its distribution and elimination from the body. Studies indicate that after oral administration, this compound's half-life ranges from 22.7 to 26.7 days, with approximately 80% of the administered dose excreted in feces within eight weeks .
Pharmacokinetic Data:
| Administration Route | Half-Life (Days) | Excretion (Feces) | Excretion (Urine) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | 26.7 | ~80% | ~0.5% |
| Intramuscular | 22.7 | ~80% | ~0.5% |
Propiedades
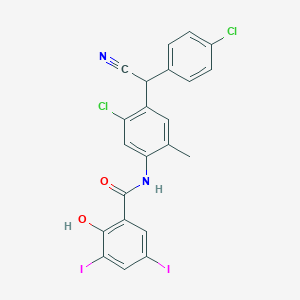
IUPAC Name |
N-[5-chloro-4-[(4-chlorophenyl)-cyanomethyl]-2-methylphenyl]-2-hydroxy-3,5-diiodobenzamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H14Cl2I2N2O2/c1-11-6-15(17(10-27)12-2-4-13(23)5-3-12)18(24)9-20(11)28-22(30)16-7-14(25)8-19(26)21(16)29/h2-9,17,29H,1H3,(H,28,30) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
JMPFSEBWVLAJKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CC(=C(C=C1NC(=O)C2=C(C(=CC(=C2)I)I)O)Cl)C(C#N)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H14Cl2I2N2O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6040662 | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6040662 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
663.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
57808-65-8 | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=57808-65-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Closantel [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0057808658 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759819 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=335306 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6040662 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Closantel | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.055.407 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CLOSANTEL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/EUL532EI54 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















