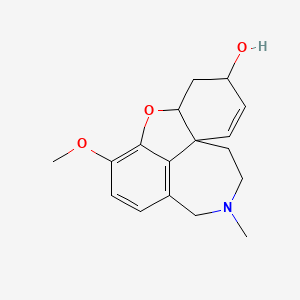
galantamina
Descripción general
Descripción
Galantamina: es un alcaloide natural extraído de los bulbos y flores de varias plantas de la familia Amaryllidaceae, como Galanthus nivalis (campanilla de invierno común), Galanthus caucasicus (campanilla de invierno del Cáucaso) y otras . Es principalmente conocida por su potencial para retrasar el deterioro cognitivo y se utiliza clínicamente para tratar la enfermedad de Alzheimer en etapa temprana y los deterioros de la memoria .
Mecanismo De Acción
La galantamina funciona inhibiendo la enzima acetilcolinesterasa, que descompone el neurotransmisor acetilcolina . Al inhibir esta enzima, la this compound aumenta los niveles de acetilcolina en la hendidura sináptica, mejorando la neurotransmisión colinérgica . Además, la this compound actúa como un modulador alostérico de los receptores nicotínicos de acetilcolina, lo que mejora aún más sus efectos terapéuticos .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Química: La galantamina se utiliza como compuesto modelo en química orgánica sintética para estudiar la síntesis de productos naturales complejos .
Biología: En la investigación biológica, la this compound se utiliza para estudiar los mecanismos de inhibición de la acetilcolinesterasa y sus efectos sobre la neurotransmisión .
Medicina: La this compound se utiliza clínicamente para controlar la demencia leve a moderada asociada con la enfermedad de Alzheimer . También se está investigando su posible uso en otros trastornos neurodegenerativos .
Industria: En la industria farmacéutica, la this compound se utiliza como ingrediente activo en medicamentos para tratar el deterioro cognitivo .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Galanthamine inhibits the degradation of neurotransmitters acetylcholine (ACh) by binding to the enzyme, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) which is responsible for degrading ACh . The resulting accumulation of ACh caused by galanthamine leads to increased neurotransmission causing continuous stimulation of the muscles, glands .
Cellular Effects
The increased neurotransmission caused by galanthamine can have various effects on cells. It can influence cell function by impacting cell signaling pathways and gene expression. It can also affect cellular metabolism by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the cell .
Molecular Mechanism
Galanthamine exerts its effects at the molecular level through its binding interactions with acetylcholinesterase. By inhibiting this enzyme, galanthamine prevents the degradation of acetylcholine, leading to an increase in the levels of this neurotransmitter. This can result in changes in gene expression and cellular function .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of galanthamine can change over time in laboratory settings. Information on the product’s stability, degradation, and any long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies is currently being researched .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of galanthamine can vary with different dosages in animal models. Studies are being conducted to determine any threshold effects observed in these studies, as well as any toxic or adverse effects at high doses .
Metabolic Pathways
Galanthamine is involved in various metabolic pathways. It interacts with enzymes such as acetylcholinesterase and can affect metabolic flux or metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
Research is ongoing to determine how galanthamine is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. This includes studying any transporters or binding proteins that it interacts with, as well as any effects on its localization or accumulation .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of galanthamine and any effects on its activity or function are currently being researched. This includes studying any targeting signals or post-translational modifications that direct it to specific compartments or organelles .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas Sintéticas y Condiciones de Reacción: La galantamina se puede sintetizar a través de varios métodos, incluyendo reacciones de acoplamiento oxidativo biomimético, reacciones catalizadas por metales de transición y reacciones de reordenamiento . Algunas estrategias sintéticas clave incluyen:
Acoplamiento Oxidativo de Fenoles: Este método implica el acoplamiento oxidativo de fenoles, que ha sido ampliamente estudiado para la síntesis total de this compound.
Reacciones Catalizadas por Metales de Transición: Estas incluyen la reacción de Heck, la metátesis de cierre de anillo enino (RCM) y la resolución cinética dinámica.
Reacciones de Reordenamiento: Los ejemplos incluyen el reordenamiento semipinacol y el reordenamiento de Johnson-Claisen.
Métodos de Producción Industrial: La producción industrial de this compound implica la extracción de fuentes naturales o la producción sintética. El primer proceso industrial se desarrolló en 1959 . Los avances recientes se han centrado en optimizar las rutas sintéticas para mejorar el rendimiento y reducir los costes .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de Reacciones: La galantamina experimenta varias reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: La this compound se puede oxidar para formar varios derivados.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción pueden modificar los grupos funcionales en la this compound.
Sustitución: Las reacciones de sustitución pueden introducir diferentes grupos funcionales en la molécula de this compound.
Reactivos y Condiciones Comunes:
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen el peróxido de hidrógeno y el permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Se utilizan agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio y el hidruro de aluminio y litio.
Sustitución: Se utilizan varios reactivos, incluyendo halógenos y agentes alquilantes, para las reacciones de sustitución.
Productos Principales: Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen varios derivados de this compound con grupos funcionales modificados, que pueden tener diferentes propiedades farmacológicas .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Compuestos Similares:
Rivastigmina: Otro inhibidor de la acetilcolinesterasa utilizado para tratar la enfermedad de Alzheimer.
Donepezilo: Un inhibidor de la acetilcolinesterasa ampliamente utilizado con un mecanismo de acción similar.
Singularidad: La this compound es única debido a su doble mecanismo de acción, tanto inhibiendo la acetilcolinesterasa como modulando los receptores nicotínicos de acetilcolina . Esta doble acción mejora su eficacia terapéutica en comparación con otros inhibidores de la acetilcolinesterasa .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(1S,12S,14R)-9-methoxy-4-methyl-11-oxa-4-azatetracyclo[8.6.1.01,12.06,17]heptadeca-6(17),7,9,15-tetraen-14-ol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H21NO3/c1-18-8-7-17-6-5-12(19)9-14(17)21-16-13(20-2)4-3-11(10-18)15(16)17/h3-6,12,14,19H,7-10H2,1-2H3/t12-,14-,17-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ASUTZQLVASHGKV-JDFRZJQESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1CCC23C=CC(CC2OC4=C(C=CC(=C34)C1)OC)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CN1CC[C@@]23C=C[C@@H](C[C@@H]2OC4=C(C=CC(=C34)C1)OC)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C17H21NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2045606 | |
| Record name | Galanthamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2045606 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
287.35 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Crystals from water; decomposition 256-257 °C. Sparingly sol in cold; more sol in hot water. Very sparingly sol in alcohol, acetone. /Hydrochloride/, Fairly soluble in hot water; freely soluble in alcohol, acetone, chloroform. Less sol in benzene, ether., 1.70e+00 g/L | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by progressive, irreversible degeneration of acetylcholine-producing neurons, cognitive impairment, and the accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques. The cholinergic system plays a critical role in memory, alongside other important neural functions such as attention, learning, stress response, wakefulness and sleep, and sensory information. Studies show that acetylcholine (ACh) is involved in the modulation of acquisition, encoding, consolidation, reconsolidation, extinction, and retrieval of memory. The gradual loss of cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may, therefore, contribute to the memory loss exhibited by AD patients. Acetylcholinesterase is secreted by cholinergic neurons to rapidly hydrolyze ACh at the synaptic cleft to release acetate and choline. Choline is later recycled back into the presynaptic cholinergic neuron via reuptake by the high-affinity choline transporter. There is some evidence demonstrating the potential involvement of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme in the formation of amyloid fibrils. Galantamine competitively and reversibly inhibits the anticholinesterase enzyme in the CNS (namely in the frontal cortex and hippocampal regions) by binding to the choline-binding site and acyl-binding pocket of the enzyme active site. By blocking the breakdown of ACh, galantamine enhances ACh levels in the synaptic cleft. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) in the CNS are mostly expressed at the presynaptic neuronal membrane to control the release of multiple neurotransmitters, such as ACh, glutamate, GABA, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine. Agonists of nAChRs improve performance in cognitive tasks, while antagonists of nAChR impair cognitive processes. Some studies show a decrease in the expression and activity of nAChRs in patients with AD, which may explain the reduction in central cholinergic neurotransmission in these patients. Galantamine binds to nAChRs at the allosteric site, leading to a conformational change of the receptor, increased ACh release, and increased activity of neighbouring glutaminergic and serotoninergic neurons. The modulation of nAChRs facilitates both excitatory and inhibitory cholinergic transmissions in brain tissues and increases receptor sensitivity. The modulated release of other neurotransmitters by galantamine may also contribute to the upregulation of nAChRs and amelioration of behavioural symptoms in AD., Galantamine, a tertiary alkaloid, is a competitive and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. While the precise mechanism of galantamine's action is unknown, it is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this mechanism is correct, galantamine's effect may lessen as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact. There is no evidence that galantamine alters the course of the underlying dementing process., The cause of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's Disease is not fully understood, it has been shown that acetylcholine producing neurons degenerate. The cholinergic loss has been correlated with cognitive impairment and a density of amyloid plaques. Galantamine is a tertiary alkaloid and it competes with and is a reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. The exact mechanism of galantamine is not known, but it is believed to enhance cholinergic function. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00674 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from benzene | |
CAS No. |
357-70-0, 23173-12-8 | |
| Record name | (-)-Galantamine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=357-70-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Galantamine [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000357700 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | (+/-)-Galantamine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0023173128 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00674 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759861 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Galanthamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2045606 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0D3Q044KCA | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE, (±)- | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1T835Z585R | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
126-127 °C, 269 - 270 °C (hydrogen bromide salt) | |
| Record name | GALANTAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7361 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Galantamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014812 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details












Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details











Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
![[(1s)-1-Isothiocyanatoethyl]benzene](/img/structure/B1674335.png)
