Prometazina
Descripción general
Descripción
La prometazina es un antihistamínico de primera generación que pertenece a la clase de compuestos de fenotiazina. Se utiliza ampliamente por sus propiedades sedantes, antieméticas y antialérgicas. La this compound se prescribe comúnmente para tratar alergias, mareos por movimiento, náuseas y vómitos. Fue sintetizada por primera vez en la década de 1940 por científicos de los laboratorios Rhône-Poulenc y fue aprobada para uso médico en los Estados Unidos en 1951 .
Mecanismo De Acción
La prometazina ejerce sus efectos al antagonizar múltiples receptores, incluyendo los receptores de histamina H1, dopamina mesolímbica postsináptica, alfa-adrenérgicos, muscarínicos y NMDA . Su acción antihistamínica es la principal responsable del tratamiento de reacciones alérgicas, mientras que el antagonismo de los receptores muscarínicos y NMDA contribuye a sus efectos sedantes y antieméticos .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Pharmacological Profile
Promethazine acts primarily as an antagonist at the H1 receptor, providing antihistaminic effects. It also exhibits moderate anticholinergic properties and has been shown to block sodium channels, contributing to its local anesthetic effects. The compound's mechanism of action includes inhibition of various neurotransmitter receptors, which underlies its diverse therapeutic applications.
Clinical Applications
-
Allergic Conditions
- Indications : Seasonal allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, urticaria, and angioedema.
- Mechanism : By blocking H1 receptors, promethazine alleviates symptoms such as itching and inflammation.
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Motion Sickness
- Sedation
- Cough Relief
Table 1: Summary of Clinical Applications of Promethazine
| Application | Indication | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic Conditions | Rhinitis, conjunctivitis | H1 receptor antagonism |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Chemotherapy-induced nausea | Antiemetic activity |
| Motion Sickness | Prophylaxis for travel | CNS depressant effects |
| Sedation | Preoperative sedation | Antihistaminic and anticholinergic actions |
| Cough Relief | Cough associated with colds | Combination with codeine |
Case Study 1: Efficacy in Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea
A clinical trial involving 200 patients undergoing chemotherapy demonstrated that those receiving promethazine reported a 40% reduction in nausea compared to a placebo group. The study highlighted the drug's effectiveness as an antiemetic when administered before chemotherapy sessions .
Case Study 2: Pediatric Use and Safety Concerns
A retrospective analysis of pediatric emergency visits revealed that promethazine was implicated in several adverse events, including respiratory depression in children under two years old. This prompted further investigation into its safety profile in younger populations .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Promethazine acts mainly as a strong H1 receptor antagonist (antihistamine) . Additionally, it has high anticholinergic properties, since it blocks acetylcholine responses through the mediation of muscarinic receptors . The binding affinity to human serum albumin (HSA) of Promethazine and its primary metabolites [N-desmethyl promethazine (DMPMZ) and promethazine sulphoxide (PMZSO)] was investigated by high-performance affinity chromatography (HPAC) though zonal approach .
Cellular Effects
Promethazine easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier and is associated with adverse effects such as moderate/intense sedation . An overdose of Promethazine can lead to anticholinergic toxidrome, where signs and symptoms such as dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, mydriasis with blurred vision, and photophobia can be seen .
Molecular Mechanism
Promethazine and its metabolites exhibited a notable binding affinity for HSA (% b values higher than 80%) . Molecular docking studies corroborated the experimental results, reinforcing the insights gained from the empirical data .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Promethazine alone in either formulation is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with peak concentrations after 2–3 h . Clinical effects are seen within 20 min and its effects last 4–6 h .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The main feature of Promethazine toxicity is delirium, the probability of which can be predicted from the dose ingested . The administration of charcoal and the presence of co-ingestants appears to reduce the probability of delirium in a predictable manner .
Metabolic Pathways
Promethazine is rapidly metabolized into its main metabolites: promethazine sulphoxide (PMZSO) and N-desmonomethyl promethazine (DMPMZ) .
Transport and Distribution
Promethazine and its metabolites bind to both sites of HSA, but mainly in site II . The in silico data also suggested that competition between Promethazine and its metabolites can occur in both sites of HSA .
Subcellular Localization
Given its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier , it can be inferred that Promethazine may localize in various compartments within the cell.
Métodos De Preparación
La prometazina se puede sintetizar a través de varios métodos. Una ruta sintética común implica la reacción de dietilamina con epóxido de propano para obtener 1-dietilamino-2-propanol. Este intermedio luego se hace reaccionar con cloruro de tionilo y tolueno para producir 1-dietilamino-2-cloropropano. Finalmente, 1-dietilamino-2-cloropropano se hace reaccionar con fenotiazina para producir this compound cruda, que se purifica y se salifica con ácido clorhídrico para obtener clorhidrato de this compound .
Los métodos de producción industrial a menudo implican procesos de cristalización y salificación para lograr alta pureza y rendimiento. Por ejemplo, la base de this compound se puede preparar y luego convertir a clorhidrato de this compound por cristalización utilizando gas de cloruro de hidrógeno seco .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
La prometazina se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, incluyendo oxidación, reducción y sustitución. Una reacción notable es su oxidación por cerio (IV) en medio ácido, que conduce a la formación de un producto coloreado detectable por espectrometría . Otra reacción implica el acoplamiento oxidativo de this compound con anilina, que sigue un modelo cinético de primer orden y produce un producto estable .
Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen iones de cerio (IV), anilina e iones de hidrógeno. Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones dependen de las condiciones y reactivos específicos utilizados.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La prometazina a menudo se compara con otros antihistamínicos y antieméticos. Los compuestos similares incluyen clorpromazina, levomepromazina y metoclopramida. Si bien la clorpromazina y la levomepromazina también son derivados de fenotiazina, se utilizan principalmente como antipsicóticos . La metoclopramida, por otro lado, se utiliza para trastornos gastrointestinales y tiene un mecanismo de acción diferente .
La singularidad de la this compound radica en su amplia gama de aplicaciones, desde el tratamiento de alergias y mareos por movimiento hasta su posible uso en estudios de neuroprotección e imagen. Su capacidad para interactuar con múltiples tipos de receptores también la diferencia de otros compuestos similares.
Actividad Biológica
Promethazine is a phenothiazine derivative primarily recognized for its antihistaminic properties, but it also exhibits a range of biological activities that make it a subject of extensive research. This article explores the diverse biological activities of promethazine, including its mechanisms of action, therapeutic applications, and potential for repurposing in various medical conditions.
Promethazine functions as an antagonist at several receptor sites, including:
- Histamine H1 Receptors : Its primary action as an antihistamine helps alleviate allergic reactions and symptoms of motion sickness.
- Dopamine Receptors : It acts on mesolimbic dopamine receptors, contributing to its antiemetic effects.
- Muscarinic and NMDA Receptors : These actions enhance its sedative properties and may play a role in reducing anxiety and tension.
Promethazine's complex pharmacological profile allows it to be effective in treating various conditions, including nausea, vomiting, and sedation .
Antimicrobial and Antiparasitic Properties
Recent studies have highlighted promethazine's potential beyond traditional antihistaminic use:
- Antifungal Activity : Promethazine has shown effectiveness against Candida tropicalis, inhibiting biofilm formation and reducing the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for azole antifungals. It was found to decrease cell size and membrane integrity in fungal cells, indicating cytotoxic effects .
- Antiparasitic Effects : In vitro studies demonstrated that promethazine affects the motility and viability of schistosomes, causing significant tegumental damage. The compound exhibited a 50% lethal concentration (LC50) indicating its potential use in treating parasitic infections .
Biofilm Inhibition
Promethazine has been investigated for its ability to inhibit biofilm formation in various pathogens:
- A study on Burkholderia thailandensis revealed that promethazine significantly reduced biofilm biomass and lipase activity in a concentration-dependent manner. This suggests a potential role in combating infections associated with biofilms .
Clinical Applications
Promethazine is widely used in clinical settings for several indications:
- Nausea and Vomiting : Its efficacy in managing nausea related to surgery or chemotherapy is well-documented. A study indicated that the combination of promethazine with opioids resulted in a significant reduction in opioid usage post-surgery .
- Sedation : Due to its sedative properties, promethazine is often used preoperatively to calm patients.
- Chronic Pain Management : Research has shown that promethazine is frequently detected in urine samples of chronic pain patients, indicating its use as an adjunctive therapy in pain management .
Case Studies and Research Findings
- Case Study on Overdose Effects : A study examined the clinical effects of promethazine overdose, highlighting symptoms such as CNS depression and delirium. This underscores the importance of monitoring dosages carefully due to potential severe side effects .
- Repurposing for Melioidosis : Research into melioidosis treatment indicated that promethazine could be repurposed to inhibit biofilm formation in Burkholderia pseudomallei, demonstrating its versatility as an antimicrobial agent .
Summary Table of Biological Activities
Propiedades
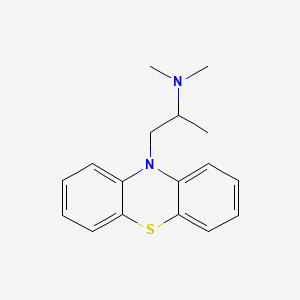
IUPAC Name |
N,N-dimethyl-1-phenothiazin-10-ylpropan-2-amine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H20N2S/c1-13(18(2)3)12-19-14-8-4-6-10-16(14)20-17-11-7-5-9-15(17)19/h4-11,13H,12H2,1-3H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PWWVAXIEGOYWEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(CN1C2=CC=CC=C2SC3=CC=CC=C31)N(C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C17H20N2S | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20956 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7023518 | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7023518 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
284.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Crystals. Melting point 60 °C. Used as an antihistamine., Solid | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20956 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015202 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
374 to 379 °F at 3 mmHg (NTP, 1992), 190-192 °C at 3.00E+00 mm Hg, BP: 190-192 °C at 3 mm Hg, BP: 191 °C at 0.5 mm Hg | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20956 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01069 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3173 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Solubility |
Very soluble in dilute hydrogen chloride, In water, 1.56X10-2 g/L (15.6 mg/L) at 24 °C, 2.45e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01069 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3173 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015202 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Promethazine is a an antagonist of histamine H1, post-synaptic mesolimbic dopamine, alpha adrenergic, muscarinic, and NMDA receptors. The antihistamine action is used to treat allergic reactions. Antagonism of muscarinic and NMDA receptors contribute to its use as a sleep aid, as well as for anxiety and tension. Antagonism of histamine H1, muscarinic, and dopamine receptors in the medullary vomiting center make promethazine useful in the treatment of nausea and vomiting., Promethazine is a phenothiazine derivative with potent sedative properties. Although the drug can produce either CNS stimulation or CNS depression, CNS depression manifested by sedation is more common with therapeutic doses of promethazine. The precise mechanism of the CNS effects of the drug is not known., Although it has been reported that the drug has slight antitussive activity, this may result from its anticholinergic and CNS depressant effects. In therapeutic doses, promethazine appears to have no substantial effect on the cardiovascular system. Although rapid IV administration of promethazine may produce a transient fall in blood pressure, blood pressure usually is maintained or slightly elevated when the drug is given slowly., Promethazine hydrochloride is a phenothiazine derivative which possesses antihistaminic, sedative, antimotion-sickness, antiemetic, and anticholinergic effects. Promethazine is a competitive H1 receptor antagonist, but does not block the release of histamine. Structural differences from the neuroleptic phenothiazines result in its relative lack (1/10 that of chlorpromazine) of dopamine antagonist properties., The development of phenothiazine derivatives as psychopharmacologic agents resulted from the observation that certain phenothiazine antihistaminic compounds produced sedation. In an attempt to enhance the sedative effects of these drugs, promethazine and chlorpromazine were synthesized. Chlorpromazine is the pharmacologic prototype of the phenothiazines. The pharmacology of phenothiazines is complex, and because of their actions on the central and autonomic nervous systems, the drugs affect many different sites in the body. Although the actions of the various phenothiazines are generally similar, these drugs differ both quantitatively and qualitatively in the extent to which they produce specific pharmacologic effects. /Phenothiazine General Statement/, For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Promethazine (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01069 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3173 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals, White to faint yellow crystalline powder | |
CAS No. |
60-87-7, 38878-40-9 | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20956 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | (±)-Promethazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=60-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | 10H-Phenothiazine-10-ethanamine, N,N,α-trimethyl-, radical ion(1+) | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=38878-40-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Promethazine [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000060877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | 10H-Phenothiazine-10-ethanamine, N,N,alpha-trimethyl-, radical ion(1+) | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0038878409 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01069 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | promethazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=30321 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7023518 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.445 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/FF28EJQ494 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3173 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015202 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
140 °F (NTP, 1992), 60 °C, Crystals from ethylene dichloride. Freely soluble in water. Soluble in alcohol, chlorform, practically insoluble in acetone, ether, ethyl acetate; MP: 230-232 °C with some decomp. Max absorption (water): 249, 297 nm (epsilon 28770, 3400). pH of 10% aqueous solution 5.3 /Promethazine hydrochloride/ | |
| Record name | PROMETHAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20956 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01069 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3173 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Promethazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015202 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details








Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.














