Sulfadiazina
Descripción general
Descripción
La sulfadiazina es un antibiótico sulfonamida ampliamente utilizado en el tratamiento de diversas infecciones bacterianas. Es particularmente eficaz contra las infecciones del tracto urinario, el tracoma y el chancroide . La this compound también se utiliza en combinación con pirimetamina para tratar la toxoplasmosis en pacientes con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida y en recién nacidos con infecciones congénitas . Este compuesto es conocido por su capacidad para inhibir la síntesis de ácido fólico en las bacterias, evitando así su crecimiento y proliferación .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with various applications in medicine, pharmacology, and other scientific fields . It functions by inhibiting bacteria's ability to produce folic acid, which is essential for DNA synthesis, thereby preventing the spread of infection .
Scientific Research Applications
Antibacterial Agent: Sulfadiazine is effective against various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections . It can also be used topically to treat burn and wound infections . The drug inhibits the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, which is crucial for folic acid synthesis .
Treatment of Infections: Sulfadiazine is used in the treatment of several infections, such as trachoma and chancroid . Laboratory studies on animals have indicated that sulfadiazine has less toxicity compared to other drugs like sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole and is highly effective against common pathogens .
Silver Sulfadiazine in Wound Care: Silver sulfadiazine (SSDZ) is a common choice for treating skin burns . It can be integrated into hydrogels for topical wound treatment because hydrogels have minimal toxicity and can sustain the release of pharmaceuticals .
Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), including those incorporating silver sulfadiazine, have demonstrated antimicrobial properties and have contributed to the development of nanotechnology . AgNPs can potentially replace traditional antibiotics due to increasing bacterial resistance .
Combination Therapies: Sulfadiazine can be combined with other substances like hyaluronic acid (HA) to treat conditions such as parastomal skin ulceration . The combination of HA and silver sulfadiazine has shown success in promoting healing and reducing pain in such cases .
Data Table: Properties and Applications of Sulfadiazine
Case Studies
Parastomal Ulcer Healing: A case study demonstrated the successful treatment of chronic parastomal skin ulceration using a combination cream of 0.2% Hyaluronic acid and 1% Silver sulfadiazine . Patients treated with this combination experienced complete healing, reduced pain, and decreased purulent fluid, leading to a reduced cost of treatment compared to standard protocols .
Silver Sulfadiazine Hydrogels for Wound Treatment: Silver sulfadiazine has been integrated into hydrogels for wound treatment due to the hydrogels' low toxicity and capacity for extended pharmaceutical release .
Research Findings and Insights
Efficacy of Silver Sulfadiazine: A systematic review comparing Silver Sulfadiazine with other dressings for burns showed a statistically significant difference in healing time for silver dressings . While some animal studies support the use of Silver Sulfadiazine for partial-thickness burns, others question its effectiveness .
Toxicity and Safety: Laboratory studies on animals suggest that sulfadiazine has lower toxicity compared to sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole .
Mecanismo De Acción
La sulfadiazina actúa inhibiendo la enzima bacteriana dihidrofolato reductasa . Esta enzima es crucial para la síntesis de ácido fólico, que es esencial para el crecimiento y la replicación bacterianos . Al inhibir competitivamente esta enzima, la this compound evita que las bacterias sinteticen ácido fólico, lo que lleva a su muerte eventual .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción
La síntesis de sulfadiazina generalmente comienza con la acetilación de derivados de anilina utilizando anhídrido acético para formar derivados de acetanilida . Estos derivados se hacen reaccionar luego con ácido clorosulfónico para producir cloruro de 4-acetilaminobencenosulfonilo . En paralelo, la 2-aminopirimidina se prepara haciendo reaccionar tetrametoxipropano con una sal de guanidina . El paso final implica hacer reaccionar cloruro de 4-acetilaminobencenosulfonilo con 2-aminopirimidina, seguido de hidrólisis con hidróxido de sodio para producir this compound .
Métodos de producción industrial
La producción industrial de this compound sigue rutas sintéticas similares pero a mayor escala. El proceso implica un control estricto de las condiciones de reacción para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza. El uso de reactores automatizados y sistemas de flujo continuo ayuda a mantener la calidad y la eficiencia consistentes en la producción .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones
La sulfadiazina experimenta diversas reacciones químicas, incluidas la oxidación, la reducción y la sustitución . El compuesto contiene dos grupos reactivos: una amina aromática y un grupo sulfonamida, que participan en estas reacciones .
Reactivos y condiciones comunes
Reducción: La reducción de this compound se puede lograr utilizando agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio.
Productos principales
Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen diversos derivados de this compound, que pueden utilizarse posteriormente en aplicaciones farmacéuticas .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Compuestos similares
Sulfametoxazol: Otro antibiótico sulfonamida utilizado en combinación con trimetoprima para tratar diversas infecciones bacterianas.
Sulfisoxazol: Utilizado para tratar infecciones del tracto urinario y otras infecciones bacterianas.
Sulfadiazina de plata: Un agente tópico utilizado en el tratamiento de quemaduras e infecciones de heridas.
Unicidad
La this compound es única debido a su actividad antibacteriana de amplio espectro y su capacidad para utilizarse en combinación con otros fármacos como la pirimetamina para el tratamiento de infecciones específicas como la toxoplasmosis . Su eficacia tanto en la medicina humana como veterinaria destaca aún más su versatilidad .
Actividad Biológica
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic that has been widely studied for its biological activity, particularly in the treatment of bacterial infections and its potential applications in various medical fields. This article discusses the compound's mechanisms of action, antimicrobial properties, clinical applications, and recent research findings.
Sulfadiazine functions primarily by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. It acts as a competitive antagonist of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate required for the synthesis of folate in bacteria. By blocking this pathway, sulfadiazine effectively prevents bacterial growth and reproduction, leading to cell death. This mechanism is common among sulfonamides, which have been utilized since their introduction in the 1930s.
Antimicrobial Properties
Sulfadiazine exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. It has been shown to be effective against:
- Gram-positive bacteria : Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative bacteria : Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Fungi : Candida albicans
- Protozoa : Toxoplasma gondii
Comparative Antimicrobial Efficacy
Recent studies have highlighted the enhanced efficacy of sulfadiazine when used in combination with metal complexes. For instance, metal complexes of sulfadiazine have demonstrated superior antibacterial activity compared to the free ligand itself, particularly against resistant strains of bacteria .
| Pathogen | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 32 µg/mL |
| Escherichia coli | 16 µg/mL |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 64 µg/mL |
| Candida albicans | 8 µg/mL |
Clinical Applications
Sulfadiazine is commonly used in clinical settings for treating various infections, including:
- Toxoplasmosis : Often administered in combination with pyrimethamine for effective treatment.
- Burn wounds : Silver sulfadiazine is a topical formulation used extensively for burn management due to its antimicrobial properties .
Case Studies
-
Silver Sulfadiazine in Burn Treatment :
A clinical trial involving children with severe burns demonstrated that silver sulfadiazine significantly reduced infection rates and facilitated wound healing compared to traditional treatments. The study reported no progression to critical infection stages among treated patients . -
Aerosol Formulation for Pressure Ulcers :
A novel aerosol formulation combining silver sulfadiazine with lidocaine and vitamin A showed promising results in treating scalp pressure ulcers in ICU patients. The treatment was associated with improved healing rates and reduced costs compared to conventional dressings .
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have explored the multifaceted biological activities of sulfadiazine beyond its antibacterial properties:
- Anticancer Activity : Research indicates that sulfadiazine exhibits antiproliferative effects on human liver cancer (HepG2) and breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines by inhibiting the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway. The IC50 values were determined to be approximately 245.69 µM for HepG2 cells and 215.68 µM for MCF7 cells .
- Cytotoxic Effects : Sulfadiazine derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines, revealing potential as therapeutic agents in oncology .
Propiedades
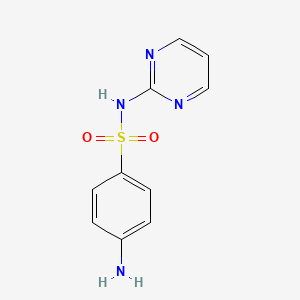
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-pyrimidin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H10N4O2S/c11-8-2-4-9(5-3-8)17(15,16)14-10-12-6-1-7-13-10/h1-7H,11H2,(H,12,13,14) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SEEPANYCNGTZFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CN=C(N=C1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H10N4O2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7044130 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
250.28 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
6.01e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is needed for the proper processing of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) which is essential for folic acid synthesis. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
68-35-9 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=68-35-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000068359 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757324 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=35600 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.623 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFADIAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0N7609K889 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.














