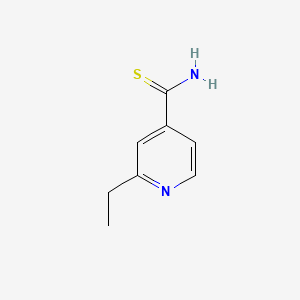
Éthionamide
Vue d'ensemble
Description
L’éthionamide est un antibiotique synthétique utilisé principalement comme traitement de deuxième intention de la tuberculose, en particulier dans les cas où la maladie est résistante aux médicaments de première intention. Il est également parfois utilisé pour traiter la lèpre. L’éthionamide agit en inhibant la synthèse des acides mycoliques, qui sont des composants essentiels des parois cellulaires des mycobactéries .
Mécanisme D'action
L’éthionamide exerce ses effets en inhibant la synthèse des acides mycoliques, qui sont des composants essentiels de la paroi cellulaire des mycobactéries. Il s’agit d’un promédicament qui nécessite une activation par l’enzyme EthA. Une fois activé, il inhibe l’enzyme InhA, ce qui conduit à la perturbation de la synthèse des acides mycoliques et entraîne finalement la mort cellulaire .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Therapeutic Use in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Ethionamide plays a crucial role in treating MDR-TB, particularly in regimens where first-line drugs are ineffective. It is often combined with other agents to enhance treatment efficacy.
Dosage and Administration:
- Recommended dosage: 15–20 mg/kg/day, typically divided into 2 to 3 doses .
- Ethionamide is administered alongside other antitubercular drugs such as isoniazid and rifampicin to optimize treatment outcomes .
Efficacy:
- Studies indicate that ethionamide contributes significantly to sputum conversion rates in patients with MDR-TB .
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Understanding the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of ethionamide is essential for optimizing its use in clinical settings.
Key Findings:
- Ethionamide exhibits a half-life of approximately 3 hours with a clearance rate of 0.06 L/h .
- The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) to minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ratio has been identified as critical for achieving effective bacterial kill rates .
Research Implications:
- Recent studies utilized hollow fiber systems to model tuberculosis and determine optimal dosing strategies for ethionamide, revealing that an AUC/MIC >56.2 is necessary for maximal efficacy .
Mechanisms of Drug Resistance
Resistance to ethionamide poses significant challenges in treating tuberculosis. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for developing effective treatment strategies.
Resistance Mechanisms:
- Genetic mutations in the ethA gene, which encodes the enzyme responsible for ethionamide activation, have been linked to resistance .
- Studies show that approximately 43% of resistant isolates had MIC values ≤ 5 mg/L, complicating susceptibility assessments .
Case Studies:
- A study highlighted the emergence of ethionamide-resistant strains during monotherapy, emphasizing the need for combination therapies to prevent resistance development .
Innovative Research Applications
Recent research has explored novel applications of ethionamide beyond its traditional use as an antitubercular agent.
Stem Cell Research:
- Ethionamide has been investigated for its potential to enhance the proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In vitro studies demonstrated that ethionamide increased MSC proliferation by up to 1.6-fold at higher concentrations, suggesting its utility in regenerative medicine .
Biomimetic Activation Studies:
- Researchers have developed biomimetic methods for activating ethionamide using various oxidants, leading to insights into its metabolic pathways and potential new therapeutic applications .
Data Tables
| Application Area | Description | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| MDR-TB Treatment | Used as part of combination therapy for MDR-TB. | Significant contribution to sputum conversion rates. |
| Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics | AUC/MIC ratios critical for efficacy; half-life ~3 hours. | Optimal dosing strategies identified through modeling. |
| Drug Resistance Mechanisms | Mutations in ethA linked to resistance; resistance complicates treatment outcomes. | High variability in MIC values among resistant strains. |
| Stem Cell Research | Enhances proliferation/migration of MSCs; potential applications in regenerative medicine. | Increased MSC proliferation by up to 1.6-fold observed. |
| Biomimetic Activation Studies | Investigated activation pathways using oxidants; insights into metabolic processes. | Novel activation mechanisms proposed based on findings. |
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies synthétiques et conditions de réaction : L’éthionamide peut être synthétisé par réaction de la 2-éthylpyridine avec du sulfure de carbone et de l’ammoniac, suivie d’une oxydation. Le processus comprend plusieurs étapes :
Formation de la 2-éthylpyridine-4-carbothioamide : Cela est obtenu en faisant réagir la 2-éthylpyridine avec du sulfure de carbone en présence d’ammoniac.
Oxydation : Le composé résultant est ensuite oxydé pour former l’éthionamide.
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle d’éthionamide implique généralement une synthèse à grande échelle utilisant les mêmes réactions chimiques de base, mais optimisées pour l’efficacité et le rendement. Cela comprend un contrôle précis des conditions de réaction telles que la température, la pression et l’utilisation de catalyseurs pour accélérer les réactions .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : L’éthionamide subit plusieurs types de réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : L’éthionamide peut être oxydé pour former le sulfoxyde d’éthionamide, qui est un métabolite actif.
Réduction : L’éthionamide peut être réduit dans certaines conditions, bien que cela soit moins courant.
Substitution : L’éthionamide peut subir des réactions de substitution, en particulier en présence de nucléophiles forts.
Réactifs et conditions courants :
Agents oxydants : Les agents oxydants courants utilisés comprennent le peroxyde d’hydrogène et le permanganate de potassium.
Agents réducteurs : Le borohydrure de sodium et l’hydrure de lithium et d’aluminium sont des agents réducteurs typiques.
Nucléophiles : Des nucléophiles forts tels que le méthylate de sodium peuvent être utilisés pour les réactions de substitution.
Principaux produits :
Sulfoxyde d’éthionamide : Formé par oxydation et est un métabolite actif.
Dérivés substitués : Différents dérivés substitués peuvent être formés en fonction du nucléophile utilisé.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
L’éthionamide est similaire à d’autres antibiotiques thioamides tels que la prothionamide et l’isoniazide. Il possède des propriétés uniques qui le rendent particulièrement utile dans le traitement de la tuberculose multirésistante :
Prothionamide : Structure et fonction similaires, mais propriétés pharmacocinétiques différentes.
Isoniazide : Inhibe également la synthèse des acides mycoliques, mais par une voie d’activation différente.
Pyrazinamide : Autre médicament antituberculeux qui agit par un mécanisme différent, mais est souvent utilisé en association avec l’éthionamide .
La capacité de l’éthionamide à traverser la barrière hémato-encéphalique et son efficacité contre les souches résistantes de mycobactéries en font un médicament précieux dans la lutte contre la tuberculose .
Activité Biologique
Ethionamide (ETH) is a thioamide pro-drug primarily used in the treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Its biological activity is closely linked to its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and interactions with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). This article explores the biological activity of ethionamide, highlighting its pharmacodynamics, mechanisms of resistance, and recent research findings.
Ethionamide is activated by the Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenase EthA, which converts it into its active form. This active compound inhibits InhA, an essential enzyme in the mycolic acid biosynthesis pathway, similar to the action of isoniazid (INH) but through distinct activation pathways . The inhibition of InhA leads to a disruption in the synthesis of mycolic acids, critical components of the Mtb cell wall, thereby exerting bactericidal effects.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Ethionamide exhibits variable pharmacokinetic properties influenced by factors such as dosage and patient characteristics. It is typically administered at a dose of 15–20 mg/kg/day divided into 2 to 3 doses . Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Cmax : Maximum concentration in plasma
- tmax : Time to reach maximum concentration
- t1/2 : Terminal elimination half-life (approximately 3 hours)
- AUC(0-24) : Area under the concentration-time curve over 24 hours
Recent studies have indicated that ethionamide has a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ranging from 1 mg/L to 2.5 mg/L for various strains of Mtb, demonstrating its efficacy against both drug-susceptible and resistant strains .
Efficacy Against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Ethionamide has shown significant microbial kill rates in clinical studies. For instance, in a hollow fiber system model of tuberculosis, ethionamide achieved a maximal kill rate (Emax) of approximately 1.94 log10 CFU/mL for extracellular Mtb and 2.88 log10 CFU/mL for intracellular Mtb . This indicates that ethionamide is effective not only against extracellular bacteria but also within host cells.
Table 1: Ethionamide Efficacy Data
| Study Type | Emax (log10 CFU/mL) | EC50 (times MIC) | MIC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hollow Fiber System Model | Extracellular: 1.94 | 2.64 | 1 |
| Intracellular: 2.88 | 1.01 | 2.5 |
Resistance Mechanisms
Resistance to ethionamide can occur through various mechanisms, including mutations in the ethA gene responsible for its activation and upregulation of efflux pumps that expel the drug from bacterial cells . Additionally, phenotypic resistance has been observed where prior exposure to ethionamide leads to tolerance against other anti-tubercular agents like isoniazid and ethambutol .
Case Study 1: Tanzanian Clinical Study
In a Tanzanian cohort study involving patients with MDR-TB, researchers evaluated the pharmacokinetics of ethionamide alongside levofloxacin-based regimens. The study utilized Monte Carlo simulations to determine optimal dosing strategies that would achieve target exposures in over 10,000 patients. Results indicated that dosing adjustments could significantly enhance treatment outcomes .
Case Study 2: Ethionamide Boosters
Recent research has focused on developing ethionamide boosters that enhance its antibacterial activity. A study identified novel compounds that inhibit EthR, a transcriptional regulator controlling ethionamide bioactivation. These inhibitors demonstrated nanomolar potency and improved solubility and metabolic stability compared to ethionamide alone .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
2-ethylpyridine-4-carbothioamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C8H10N2S/c1-2-7-5-6(8(9)11)3-4-10-7/h3-5H,2H2,1H3,(H2,9,11) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
AEOCXXJPGCBFJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCC1=NC=CC(=C1)C(=S)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C8H10N2S | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20353 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0020577 | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020577 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
166.25 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Ethionamide appears as yellow crystals or canary yellow powder with a faint to moderate sulfide odor. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20353 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014747 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 1 mg/mL at 70 °F (NTP, 1992), Practically insoluble, Very sparingly soluble in ether. Sparingly soluble in methanol, ethanol, propylene glycol. Soluble in hot acetone, dichloroethane. Freely soluble in pyridine., 8.39e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20353 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00609 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7473 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014747 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug attained at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the infecting organism. Ethionamide, like prothionamide and pyrazinamide, is a nicotinic acid derivative related to isoniazid. It is thought that ethionamide undergoes intracellular modification and acts in a similar fashion to isoniazid. Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids, an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. Specifically isoniazid inhibits InhA, the enoyl reductase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, by forming a covalent adduct with the NAD cofactor. It is the INH-NAD adduct that acts as a slow, tight-binding competitive inhibitor of InhA., Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug attained at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the infecting organism. The exact mechanism of action of ethionamide has not been fully elucidated, but the drug appears to inhibit peptide synthesis in susceptible organisms. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00609 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7473 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Yellow crystals from ethanol | |
CAS No. |
536-33-4 | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20353 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=536-33-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000536334 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00609 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ethionamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757028 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | ethionamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=255115 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020577 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.007.846 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/OAY8ORS3CQ | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7473 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014747 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
327 to 331 °F (Decomposes) (NTP, 1992), 164-166 °C (decomposes), 163 °C | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20353 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00609 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ETHIONAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7473 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Ethionamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014747 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
















