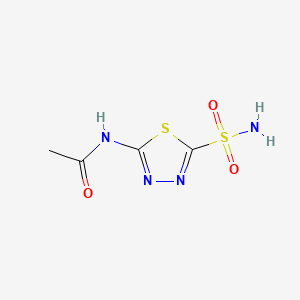
Acetazolamide
Overview
Description
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor widely used in the medical field. It is known for its applications in treating glaucoma, epilepsy, acute mountain sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and heart failure. The compound is also used to alkalinize urine . This compound was first introduced in 1952 and is available as a generic medication .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of acetazolamide involves the oxidation of a thiol derivative to form a sulfonyl chloride intermediate. This intermediate then reacts with various amines, hydrazones, and bis-amine precursors to create new sulfonamide derivatives . The oxidation process can be enhanced by substituting chlorine gas with sodium hypochlorite (commercial bleach), which improves safety and environmental conditions .
Industrial Production Methods: In industrial settings, this compound is produced by mixing this compound with lactose, cornstarch, pregelatinized starch, PVP, sucrose, and carboxymethyl starch sodium. The mixture is then pelletized, dried, and tabletted to obtain this compound tablets .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Acetazolamide undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution. The compound is known for its inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase, which leads to a decrease in the formation of hydrogen ions and bicarbonate from carbon dioxide and water .
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Sodium hypochlorite (commercial bleach) is used as an oxidizing agent.
Reduction and Substitution: Various amines, hydrazones, and bis-amine precursors are used in the synthesis of new sulfonamide derivatives.
Major Products Formed: The major products formed from these reactions include novel sulfonamide derivatives with enhanced antibacterial and antioxidant properties .
Scientific Research Applications
FDA-Approved Indications
Acetazolamide is approved for several medical conditions:
- Glaucoma : Reduces intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous humor production.
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) : Lowers cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) production, thus reducing intracranial pressure.
- Altitude Sickness : Alleviates symptoms by promoting respiratory compensation and diuresis.
- Congestive Heart Failure : Enhances diuretic efficacy when used in conjunction with loop diuretics.
- Periodic Paralysis : Manages symptoms associated with this condition.
- Epilepsy : Acts as an adjunctive treatment for certain types of seizures.
Non-FDA-Approved Indications
In addition to its approved uses, this compound has been explored for several non-FDA-approved applications:
- Central Sleep Apnea : Investigated for its potential benefits in managing sleep-related breathing disorders.
- Marfan Syndrome : Used in some cases to manage symptoms.
- Prevention of High-Dose Methotrexate Nephrotoxicity : Explored as a protective agent against kidney damage during chemotherapy.
- Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy : Studied for its role in protecting renal function during imaging procedures.
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
A study reported significant reductions in intracranial pressure among patients treated with this compound. The drug was effective in managing symptoms and preventing complications like vision loss .
Acute Mountain Sickness
In a clinical trial involving patients with acute mountain sickness, this compound demonstrated efficacy in reducing symptoms such as headache and nausea, attributed to its effects on respiration and fluid balance .
Hydrocephalus Management
In pediatric patients with shunt-dependent hydrocephalus, this compound led to a dramatic reduction in CSF output, allowing clinicians to manage shunt function more effectively .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is well absorbed orally, with a plasma half-life ranging from 6 to 9 hours. It is primarily excreted through the kidneys without undergoing significant metabolic alteration .
Summary Table of Applications
| Application | FDA Approved | Mechanism of Action | Notable Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glaucoma | Yes | Decreases aqueous humor production | Effective in lowering intraocular pressure |
| Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension | Yes | Reduces CSF production | Significant reduction in intracranial pressure |
| Altitude Sickness | Yes | Enhances respiration; promotes diuresis | Alleviates symptoms effectively |
| Congestive Heart Failure | Yes | Enhances diuretic efficacy | Improves decongestion when combined with loop diuretics |
| Periodic Paralysis | Yes | Modulates muscle excitability | Effective for specific genetic mutations |
| Epilepsy | Yes | Inhibits abnormal neuronal discharge | Acts as an adjunctive treatment |
| Central Sleep Apnea | No | Potential respiratory stimulant | Limited evidence; further studies needed |
| Prevention of Nephrotoxicity | No | Protective renal effects | Emerging research; not widely adopted |
Mechanism of Action
Acetazolamide works by inhibiting the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which decreases the formation of hydrogen ions and bicarbonate from carbon dioxide and water . This inhibition leads to a reduction in the reabsorption of bicarbonate, sodium, and chloride ions in the proximal tubule of the kidney, resulting in increased excretion of these ions along with excess water . This mechanism helps lower blood pressure, intracranial pressure, and intraocular pressure .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Sulfanilamide: An earlier discovered compound with similar enzymatic inhibitory activity but much less potent than acetazolamide.
Other Sulfonamide Derivatives: Various diuretics and anticonvulsants with minor to moderate carbonic anhydrase activity.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound stands out due to its potent inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase, making it highly effective in treating a wide range of medical conditions. Its ability to act as a diuretic, anticonvulsant, and glaucoma medication highlights its versatility and importance in both clinical and research settings .
Biological Activity
Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that has garnered attention for its diverse biological activities and therapeutic applications. This article explores the mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects, and clinical implications of this compound, supported by case studies and research findings.
This compound primarily functions by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction between carbon dioxide (CO2) and bicarbonate (HCO3−), leading to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3). This inhibition results in:
- Increased Acidity : The accumulation of carbonic acid lowers blood pH, promoting increased acidity in the bloodstream.
- Altered Electrolyte Excretion : Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the proximal tubule of the nephron leads to increased excretion of sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride, resulting in diuresis and natriuresis .
- Neuronal Effects : In epilepsy management, this compound modulates neuronal excitability by affecting GABA-A receptor signaling and calcium ion kinetics, which may help in controlling seizure activity .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic properties:
- Absorption : It is well absorbed when administered orally.
- Distribution : The drug has a high volume of distribution and is found in red blood cells at higher concentrations in elderly patients compared to younger individuals .
- Elimination : this compound is primarily excreted unchanged in urine, with minimal metabolism occurring .
1. Glaucoma Management
This compound is used to lower intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma. By decreasing aqueous humor production through carbonic anhydrase inhibition, it helps manage this condition effectively .
2. Treatment of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
A multicenter study demonstrated that this compound significantly improved visual function and reduced papilledema in patients with IIH. Participants receiving this compound showed greater improvements in perimetric mean deviation compared to placebo .
3. Heart Failure
Recent literature reviews indicate that this compound can enhance diuretic efficacy in heart failure patients experiencing fluid overload. Studies suggest it improves decongestion and natriuresis when used alongside loop diuretics, although limitations such as small sample sizes warrant further investigation .
4. Antibacterial Activity
Emerging research highlights this compound's potential as an antibacterial agent against enterococci. It has shown effectiveness at clinically achievable concentrations, suggesting a new therapeutic avenue for treating infections caused by resistant strains .
Study on Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
A phase I clinical trial evaluated the safety and efficacy of this compound combined with temozolomide in GBM patients. Results indicated that the combination was well tolerated, with median overall survival reaching 30.1 months, suggesting a promising role for this compound in enhancing treatment outcomes for this aggressive cancer .
| Parameter | This compound + Temozolomide | Historical Data |
|---|---|---|
| Median Overall Survival | 30.1 months | Varies by study |
| Median Progression-Free Survival | 16.0 months | Varies by study |
| 2-Year Overall Survival Rate | 60.9% | Varies by study |
Research Findings
- Diuretic Efficacy : A systematic review found that this compound significantly improved outcomes related to fluid retention in heart failure patients when combined with standard diuretics .
- Epilepsy Control : this compound's role in managing epilepsy was supported by its ability to modulate neuronal excitability through various pathways, including GABA-A signaling modulation .
- Bone Health : Chronic use of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors like this compound has been studied for their effects on bone mineral density, indicating potential implications for long-term therapy .
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What evidence supports the efficacy of different acetazolamide dosages in preventing acute mountain sickness (AMS), and how are optimal doses determined in clinical trials?
- Methodological Answer: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses comparing dosages (e.g., 250 mg vs. 750 mg daily) are critical. For example, a meta-analysis stratified outcomes by dose and used pooled risk ratios to assess AMS incidence reduction. Trials typically employ double-blind, placebo-controlled designs with endpoints like Lake Louise Scores . Dose selection prioritizes balancing efficacy (e.g., 250 mg reduces AMS incidence by 48%) with adverse effects like metabolic acidosis.
Q. How does this compound synergize with dietary sodium restriction in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), and which outcome metrics best capture therapeutic benefits?
- Methodological Answer: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) combine this compound with low-sodium diets, using perimetric mean deviation (PMD) to quantify visual field improvements. Secondary outcomes include papilledema grade (Frisén scale) and quality-of-life surveys (e.g., VFQ-25). For instance, this compound + diet improved PMD by 0.71 dB more than diet alone, with statistical significance (95% CI: 0–1.43 dB; P = 0.05) .
Q. What pharmacokinetic properties of this compound are critical for designing bioavailability studies?
- Methodological Answer: Key parameters include renal excretion (90% unchanged), plasma half-life (~6–9 hours), and protein binding (70–90%). Bioavailability studies use LC-MS/MS to quantify urinary concentrations, as this compound is excreted unmetabolized. Protocols often reference validated assays, such as GC-NICI-MS for derivatized sulfonamides in urine .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can researchers mitigate confounding from prophylactic this compound use in observational studies of hypoxia-induced gene expression?
- Methodological Answer: Confounding is addressed via sensitivity analyses excluding this compound users or multivariable regression adjusting for drug exposure. For example, in genomic studies of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1), post hoc stratification by this compound use clarifies gene expression patterns . Ethical constraints (e.g., withholding prophylaxis) necessitate transparent reporting of confounding in limitations.
Q. What trial design considerations optimize assessments of this compound’s diuretic efficiency in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF)?
- Methodological Answer: The ADVOR trial used stratified randomization by ejection fraction and defined "successful decongestion" as absence of edema/ascites within 72 hours. Primary endpoints combined clinical signs and biomarker thresholds (NT-proBNP >1000 pg/mL). Mixed linear models evaluated urine output and natriuresis, showing this compound increased decongestion success (42.2% vs. 30.5%; RR: 1.46) .
Q. What statistical methods handle missing data in this compound trials, such as studies on obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in high-altitude populations?
- Methodological Answer: Intention-to-treat (ITT) analyses with multiple imputation (e.g., chained equations) preserve randomization integrity. Per-protocol analyses supplement ITT by excluding protocol violators. For example, OSA trials use mixed linear regression to compare treatment effects (this compound vs. placebo) on apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) changes, with sensitivity analyses for missing data .
Q. How does this compound’s thermal instability influence compatibility studies with excipients during formulation development?
- Methodological Answer: Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) identify decomposition temperatures (~260°C for this compound). Compatibility studies with excipients (e.g., chitosan) compare thermograms to detect interactions. For instance, amorphous phase formation post-melting necessitates stability testing under accelerated conditions (40°C/75% RH) .
Q. Data Contradiction & Synthesis
Q. How should conflicting results on this compound’s neuropsychiatric effects (e.g., bipolar disorder) be reconciled in scoping reviews?
- Methodological Answer: PRISMA-guided reviews categorize evidence by study design (RCTs vs. case reports) and outcomes (e.g., affective symptoms vs. cognitive function). For bipolar disorder, data extraction tables highlight dose-response relationships and safety profiles, noting gaps like absent long-term tolerability data .
Q. What explains disparities in this compound’s efficacy across conditions like AMS, IIH, and ADHF?
- Methodological Answer: Mechanistic heterogeneity—carbonic anhydrase inhibition affects distinct pathways (e.g., cerebral blood flow in AMS vs. renal bicarbonate excretion in ADHF). Cross-disciplinary synthesis links pharmacokinetics (e.g., CSF penetration in IIH) to condition-specific outcome measures .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C4H6N4O3S2/c1-2(9)6-3-7-8-4(12-3)13(5,10)11/h1H3,(H2,5,10,11)(H,6,7,9) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BZKPWHYZMXOIDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=NN=C(S1)S(=O)(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C4H6N4O3S2 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
1424-27-7 (mono-hydrochloride salt) | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000059665 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7022544 | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022544 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
222.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Acetazolamide appears as white to yellowish-white fine crystalline powder. No odor or taste. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>33.3 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 72 °F (NTP, 1992), SPARINGLY SOL IN COLD WATER, SLIGHTLY SOL IN ALCOHOL, INSOL IN CHLOROFORM, DIETHYL ETHER, CARBON TETRACHLORIDE; SLIGHTLY SOL IN ACETONE, Readily soluble in 1 N sodium carbonate solution., In water= 980 mg/l at 30 °C., 2.79e+00 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855900 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension. The diuretic effect depends on the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, causing a reduction in the availability of hydrogen ions for active transport in the renal tubule lumen. This leads to alkaline urine and an increase in the excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water., Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors potently inhibit (IC50 for acetazolamide is 10 nM) both the membrane bound and cytoplasmic forms of carbonic anhydrase, resulting in nearly complete abolition of NaHCO3 reabsorption in the proximal tubule. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, Although the proximal tubule is the major site of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase also is involved in secretion of titratable acid in the collecting duct system (a process which involves a proton pump), and therefore the collecting duct system is a secondary site of action for this class of drugs. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, Acetazolamide frequently causes paresthesias and somnolence, suggesting an action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the CNS. The efficacy of acetazolamide in epilepsy is in part due to the production of metabolic acidosis; however, direct actions of acetazolamide in the CNS also contribute to its anticonvulsant action., ... Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase decreases the rate of formation of aqueous humor and consequently reduce intraocular pressure. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
CRYSTALS FROM WATER, WHITE TO FAINTLY YELLOWISH WHITE, CRYSTALLINE, POWDER | |
CAS No. |
59-66-5 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59-66-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000059665 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | acetazolamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=755854 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | acetazolamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=145177 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Acetamide, N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022544 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.400 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/O3FX965V0I | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
496 to 498 °F (effervescence) (NTP, 1992), 258-259 °C (EFFERVESCENCE), 260.5 °C | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details








Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.













