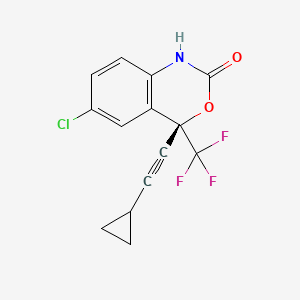
Efavirenz
Overview
Description
Efavirenz is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used primarily in the treatment and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 infection . It is marketed under brand names such as Sustiva and Stocrin . This compound works by inhibiting the activity of reverse transcriptase, an enzyme crucial for the replication of HIV .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: One of the key synthetic routes for efavirenz involves the ortho-lithiation reaction of N-Boc-4-chloroaniline using n-butyllithium . This reaction is performed at a temperature of -45°C and yields a key intermediate, which is then subjected to trifluoroacetylation . Another method involves the reaction of an this compound intermediate with phosgene in solvents such as heptane, toluene, or tetrahydrofuran .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound often employs continuous flow chemistry to improve the selectivity and safety of the reactions . This method allows for the efficient scale-up of the process, making it suitable for large-scale production.
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Efavirenz undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized under specific conditions to form different metabolites.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can modify the functional groups present in this compound.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur at the chloro or trifluoromethyl groups in the molecule.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate.
Reduction: Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride can be used.
Substitution: Reagents like sodium hydroxide or other strong bases can facilitate substitution reactions.
Major Products Formed: The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used. For example, oxidation can lead to the formation of hydroxylated metabolites, while reduction can yield dechlorinated or defluorinated products.
Scientific Research Applications
Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV
Efficacy in Treatment Regimens
Efavirenz has been a cornerstone in the evolution of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Its effectiveness has been demonstrated in numerous clinical trials, establishing it as a preferred option for treating HIV infection, especially in treatment-naive patients. A notable study, the ACTG A5142 trial, showed that this compound combined with two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors resulted in superior virological outcomes compared to boosted protease inhibitors like lopinavir .
Table 1: Summary of Key Clinical Trials Involving this compound
Off-Label Uses
HIV Prevention
This compound is sometimes utilized off-label for HIV prevention in specific contexts, such as occupational exposure or perinatal transmission. Its mechanism involves inhibiting the reverse transcriptase enzyme, thereby disrupting viral replication .
Potential Cancer Treatment
Recent studies have suggested that this compound may have anti-cancer properties. Research indicates that this compound can slow the growth of various cancer cell lines in vitro, suggesting a potential role in oncology . Further investigation into this application is ongoing.
Neuropsychiatric Effects
While this compound is effective in treating HIV, it is associated with central nervous system side effects including depression, vivid dreams, and sleep disturbances. These adverse effects can significantly impact patient adherence to treatment regimens . Understanding these effects is crucial for optimizing patient care and managing potential discontinuation of therapy.
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions
This compound exhibits complex pharmacokinetics influenced by genetic polymorphisms affecting drug metabolism (e.g., CYP2B6). This variability necessitates careful monitoring and potential dose adjustments to mitigate adverse effects while ensuring therapeutic efficacy .
Table 2: Pharmacokinetic Properties of this compound
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Half-life | Approximately 40-55 hours |
| Bioavailability | ~40% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2B6) |
Case Studies
Case Study: Efficacy in Advanced HIV Infection
A longitudinal study involving patients with advanced HIV infection demonstrated that those treated with this compound-based regimens had significant improvements in both virological and immunological responses over a seven-year period. The study highlighted the importance of this compound as a third agent in combination therapies .
Case Study: Neuropsychiatric Outcomes
A cohort study assessed the neuropsychiatric side effects of this compound among patients starting ART. Results indicated that nearly half experienced adverse effects severe enough to impact adherence, emphasizing the need for monitoring and support strategies for affected individuals .
Mechanism of Action
Efavirenz exerts its effects by binding to the reverse transcriptase enzyme of HIV-1 . This binding inhibits the enzyme’s activity, preventing the conversion of viral RNA into DNA, which is a crucial step in the replication cycle of the virus . Unlike nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, this compound does not require intracellular phosphorylation for its activity .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Nevirapine: Another non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in HIV treatment.
Delavirdine: Similar to efavirenz, it inhibits reverse transcriptase but has different pharmacokinetic properties.
Etravirine: A newer non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a broader resistance profile.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique due to its high potency and long half-life, which allows for once-daily dosing . It has been a primary first-line antiviral drug for over 15 years and is known for its effectiveness in combination therapy . its use is sometimes limited by side effects such as central nervous system symptoms .
Biological Activity
Efavirenz is a widely used non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, metabolism, efficacy, and potential adverse effects. This article reviews various studies and findings related to the biological activity of this compound, including data tables and case studies.
This compound inhibits the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which is crucial for the replication of HIV. The drug acts by binding to the enzyme and preventing the conversion of viral RNA into DNA, thus inhibiting viral replication. The active form of this compound is triphosphorylated within cells, and its efficacy is dependent on this conversion process .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits significant variability in pharmacokinetics among individuals, influenced by genetic factors such as polymorphisms in cytochrome P450 enzymes. The primary metabolic pathway for this compound involves hydroxylation and subsequent glucuronidation, primarily mediated by CYP2B6. This metabolism results in inactive metabolites, with 8-hydroxy-efavirenz being the predominant form detected in urine .
Key Pharmacokinetic Parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Half-life | 40-55 hours |
| Protein binding | 99.5-99.75% |
| Metabolism | Cytochrome P450 system |
| Route of elimination | Urinary excretion (metabolites) |
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of this compound in various treatment regimens for HIV. In randomized trials, this compound has shown superior virological outcomes compared to other antiretroviral agents like nevirapine and boosted protease inhibitors .
Efficacy Data from Clinical Trials:
| Study | Treatment Regimen | Efficacy (VL < 50 copies/mL) | CD4 Recovery (cells/mm³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTG A5142 | EFV + 2 NRTIs | 66% | +200 |
| Swiss HIV Cohort Study | EFV + 2 NRTIs | 70% | +150 |
| EfaVIP 2 | EFV + 2 NRTIs | 65% | +180 |
Adverse Effects
Despite its efficacy, this compound is associated with several adverse effects, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms. A case study reported a male patient who developed significant neuropsychiatric issues after six years on an this compound-based regimen. Symptoms included difficulty sleeping and memory loss, which resolved after switching to nevirapine .
Common Adverse Effects:
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms (e.g., insomnia, vivid dreams)
- Rash
- Hepatotoxicity
- Ataxia and encephalopathy in rare cases
Genetic Variability and Drug Response
Genetic polymorphisms significantly affect this compound metabolism and therapeutic outcomes. For instance, individuals with the homozygous G516T genotype of CYP2B6 may experience higher plasma levels of this compound, leading to increased risk of adverse effects without compromising virological success .
Case Studies
A notable case series identified women experiencing severe ataxia linked to long-term this compound use. The study highlighted that these symptoms could arise years after initiation of therapy, particularly in patients with genetic slow metabolizer profiles .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
(4S)-6-chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H9ClF3NO2/c15-9-3-4-11-10(7-9)13(14(16,17)18,21-12(20)19-11)6-5-8-1-2-8/h3-4,7-8H,1-2H2,(H,19,20)/t13-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XPOQHMRABVBWPR-ZDUSSCGKSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1C#CC2(C3=C(C=CC(=C3)Cl)NC(=O)O2)C(F)(F)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CC1C#C[C@]2(C3=C(C=CC(=C3)Cl)NC(=O)O2)C(F)(F)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H9ClF3NO2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9046029 | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9046029 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
315.67 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014763 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble in water (less than 10 mg/L), 8.55e-03 g/L | |
| Record name | EFAVIRENZ | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7163 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014763 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Similar to zidovudine, efavirenz inhibits the activity of viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase (i.e., reverse transcriptase). Antiviral activity of efavirenz is dependent on intracellular conversion to the active triphosphorylated form. The rate of efavirenz phosphorylation varies, depending on cell type. It is believed that inhibition of reverse transcriptase interferes with the generation of DNA copies of viral RNA, which, in turn, are necessary for synthesis of new virions. Intracellular enzymes subsequently eliminate the HIV particle that previously had been uncoated, and left unprotected, during entry into the host cell. Thus, reverse transcriptase inhibitors are virustatic and do not eliminate HIV from the body. Even though human DNA polymerase is less susceptible to the pharmacologic effects of triphosphorylated efavirenz, this action may nevertheless account for some of the drug's toxicity., Efavirenz diffuses into the cell where it binds adjacent to the active site of reverse transcriptase. This produces a conformational change in the enzyme that inhibits function. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00625 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | EFAVIRENZ | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7163 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from toluene:heptane, White to slightly pink crystalline powder | |
CAS No. |
154598-52-4 | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=154598-52-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz [USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0154598524 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00625 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | 154598-52-4 | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=742403 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9046029 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (4S)-6-chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2,4-dihydro-1H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | EFAVIRENZ | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/JE6H2O27P8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | EFAVIRENZ | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7163 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014763 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
139-141 °C, 139 - 141 °C | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00625 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | EFAVIRENZ | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7163 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Efavirenz | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014763 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.
















