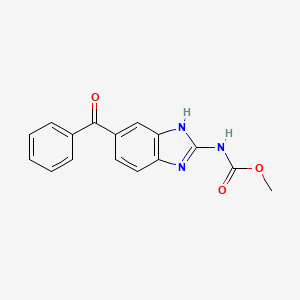
Mebendazole
Overview
Description
Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic compound used to treat various parasitic worm infestations. It was developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica in Belgium and came into use in 1971 . This compound is effective against a range of nematode infestations, including roundworm, hookworm, whipworm, and pinworm . It is poorly absorbed into the bloodstream, making it particularly effective for treating intestinal parasites .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The preparation of mebendazole involves an acylation reaction followed by a Friedel-Crafts reaction. In the acylation reaction, trichlorotoluene is heated to 50-90°C, and a zinc chloride aqueous solution is added dropwise. After the reaction, reduced pressure distillation is carried out to obtain benzoyl chloride . In the Friedel-Crafts reaction, carbendazim, a solvent, and anhydrous aluminum chloride are mixed and stirred. Benzoyl chloride is then added dropwise, followed by continuous stirring and heat preservation reaction. Reduced pressure distillation is conducted to obtain this compound .
Industrial Production Methods
The industrial production of this compound typically follows the same synthetic route as described above. The process is optimized for high yield and efficiency, with a focus on simple flow, mild conditions, and high atom utilization rate .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions
Mebendazole undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution reactions.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate can be used.
Reduction: Reducing agents like palladium-on-charcoal catalyst in the presence of hydrogen can be employed.
Substitution: Substitution reactions often involve the use of halogenating agents or nucleophiles.
Major Products
The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific reagents and conditions used. For example, reduction of 4-amino-3-nitrobenzophenone with palladium-on-charcoal catalyst yields 3,4-diaminobenzophenone .
Scientific Research Applications
Mebendazole has been repurposed for various scientific research applications beyond its original use as an anthelmintic. It has shown promise in the treatment of brain cancers, including glioma, by inhibiting malignant progression and increasing the sensitivity of glioma cells to conventional chemotherapy or radiotherapy . Additionally, this compound has been explored for its anticancer properties in multiple cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia, breast cancer, and gastrointestinal cancer .
Mechanism of Action
Mebendazole works by inhibiting the polymerization of tubulin in parasites, disrupting microtubule formation and interfering with glucose uptake . This ultimately leads to the death of the parasite. The compound targets critical pathways involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion/migration .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Similar Compounds
Albendazole: Another benzimidazole anthelmintic used to treat a variety of parasitic worm infestations.
Pyrantel: An anthelmintic used to treat pinworm, hookworm, and roundworm infections.
Uniqueness
Mebendazole is unique in its ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, making it particularly effective for treating brain tumors . Its broad-spectrum activity and relatively low toxicity also distinguish it from other similar compounds .
Biological Activity
Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic drug primarily used to treat parasitic infections. However, recent studies have unveiled its potential in oncology, particularly its biological activity against various cancer types. This article delves into the biological mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, and clinical applications of this compound, supported by data tables and case studies.
Antiparasitic Activity
this compound works by inhibiting the polymerization of tubulin, which is essential for microtubule formation in parasites. This disruption leads to impaired glucose uptake and energy depletion in the parasites, ultimately resulting in their death.
Antitumor Activity
Recent research highlights this compound's potential as an anticancer agent. It has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells through several mechanisms:
- Bcl-2 Inactivation : this compound induces apoptosis in melanoma cells by phosphorylating Bcl-2, which prevents its interaction with the pro-apoptotic protein Bax, thus promoting cell death .
- Cell Cycle Arrest : It has been observed to cause cell cycle arrest in various cancer cell lines, including ovarian and colorectal cancers .
- Inhibition of Tumor Angiogenesis : this compound reduces angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGFR2 kinase activity, leading to decreased microvessel density in tumors .
Table 1: Biological Activities of this compound
| Activity | Mechanism | Cancer Type |
|---|---|---|
| Apoptosis induction | Bcl-2 phosphorylation | Melanoma |
| Cell cycle arrest | Inhibition of tubulin polymerization | Ovarian cancer |
| Angiogenesis inhibition | VEGFR2 kinase inhibition | Colorectal cancer |
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits variable pharmacokinetic properties influenced by dosage and formulation. Studies indicate that plasma levels increase with higher doses, and the drug achieves a maximum concentration within hours post-administration.
Table 2: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of this compound
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | Approximately 50% |
| Peak plasma concentration | 590 nM (after standard dosing) |
| Half-life | 3-6 hours |
Case Study: this compound in Glioblastoma Treatment
A phase II clinical trial investigated the combination of this compound with temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade glioma. The study enrolled 24 patients, revealing promising results regarding safety and overall survival:
- Median Overall Survival (OS) : 21 months.
- Progression-Free Survival (PFS) : 13.1 months for patients receiving more than one month of treatment .
Table 3: Clinical Outcomes from Glioblastoma Study
| Outcome Measure | Result |
|---|---|
| Median OS | 21 months |
| Median PFS | 13.1 months |
| Adverse Events | Elevated ALT/AST at higher doses |
Case Study: this compound for COVID-19
A recent randomized controlled trial indicated that this compound therapy improved innate immunity and reduced inflammation markers in COVID-19 outpatients compared to a placebo group. Significant reductions in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were noted within three days of treatment .
Q & A
Basic Research Question: What experimental design considerations are critical for evaluating mebendazole’s pharmacokinetics in heterogeneous populations?
Methodological Answer:
To assess pharmacokinetics (PK) in diverse populations, researchers should:
- Define subpopulations (e.g., neonates, immunocompromised individuals) based on metabolic or physiological differences .
- Use population PK modeling to account for variability in drug absorption, distribution, and clearance. For example, sparse sampling in pediatric cohorts can reduce ethical and logistical challenges .
- Validate assays (e.g., HPLC, differential pulse polarography) to ensure sensitivity in detecting low plasma concentrations .
- Data sharing protocols must comply with ethical standards, including anonymization and controlled access to sensitive datasets .
Advanced Research Question: How can conflicting efficacy data for this compound in repurposed oncology studies be reconciled?
Methodological Answer:
Conflicting results often arise from:
- Variability in experimental models : Compare outcomes across cell lines (e.g., LNCaP vs. DU145 prostate cancer cells) and in vivo models (e.g., xenografts vs. genetically engineered mice) .
- Dose-response discordance : Use dose-ranging studies to identify therapeutic thresholds. For example, this compound’s anti-cancer effects in PDE4D7-knockdown LNCaPs occur at lower doses than in wild-type cells .
- Mechanistic heterogeneity : Conduct transcriptomic or proteomic analyses to map pathways (e.g., cAMP dynamics, microtubule disruption) influenced by tumor microenvironment factors .
- Meta-analysis frameworks : Apply PRISMA guidelines to aggregate preclinical data and identify bias sources (e.g., publication bias, model selection) .
Basic Research Question: What validated analytical methods are recommended for quantifying this compound in pharmaceutical formulations?
Methodological Answer:
- Electrochemical techniques : Differential pulse polarography (DPP) offers sensitivity at µg/mL levels, validated in pH 7.4 buffers to mimic physiological conditions .
- Chromatography : HPLC with UV detection (λ = 254 nm) provides reproducibility, but requires column optimization to separate this compound from excipients .
- Quality control : Cross-validate results with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to confirm specificity, especially in complex matrices like serum .
Advanced Research Question: What strategies address this compound’s solubility limitations in preclinical testing?
Methodological Answer:
- Co-solvent systems : Test biocompatible solvents (e.g., PEG-400) to enhance aqueous solubility while monitoring cytotoxicity in vitro .
- Nanoformulation : Develop liposomal or polymeric nanoparticles to improve bioavailability. Characterize particle size (DLS) and encapsulation efficiency (UV-Vis) .
- In silico modeling : Use tools like COSMO-RS to predict solubility in simulated biological fluids and guide formulation design .
Basic Research Question: How should researchers design studies to evaluate this compound resistance in helminthic parasites?
Methodological Answer:
- Longitudinal sampling : Collect parasite isolates pre- and post-treatment to track β-tubulin mutations linked to resistance .
- Phenotypic assays : Measure IC50 shifts in larval motility or egg hatching inhibition assays across multiple generations .
- Genomic sequencing : Identify SNPs in β-tubulin isotype-1 genes and correlate with clinical failure rates .
Advanced Research Question: What methodologies optimize this compound combination therapies for synergistic anti-helminthic effects?
Methodological Answer:
- Checkerboard assays : Determine fractional inhibitory concentration indices (FICI) for this compound paired with albendazole or ivermectin .
- Mechanistic synergy : Use RNAi or CRISPR to validate target pathways (e.g., dual β-tubulin and glutamate-gated chloride channel disruption) .
- In vivo validation : Employ factorial design experiments in rodent models to assess efficacy-toxicity trade-offs .
Basic Research Question: How to ensure reproducibility in this compound’s in vitro cytotoxicity assays?
Methodological Answer:
- Standardize cell lines : Use authenticated stocks (e.g., ATCC-certified DU145) and control for passage number .
- Culture conditions : Maintain consistent O2 levels (5% CO2) and serum concentrations (10% FBS) to minimize batch effects .
- Endpoint validation : Combine MTT assays with live-cell imaging to confirm apoptosis vs. necrosis .
Advanced Research Question: How can computational models predict this compound’s off-target effects in repurposing studies?
Methodological Answer:
- Docking simulations : Use AutoDock Vina to screen this compound against human kinases or GPCRs implicated in side effects .
- Network pharmacology : Construct protein-protein interaction networks to identify secondary targets (e.g., PDE4D7 in prostate cancer) .
- Toxicogenomics : Apply LINCS database queries to predict gene expression changes in non-target tissues .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-(6-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H13N3O3/c1-22-16(21)19-15-17-12-8-7-11(9-13(12)18-15)14(20)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-9H,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,21) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
OPXLLQIJSORQAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
COC(=O)NC1=NC2=C(N1)C=C(C=C2)C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H13N3O3 | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20586 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4040682 | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4040682 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
295.29 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Mebendazole is a white to slightly yellow powder. Pleasant taste. Practically water insoluble. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20586 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014781 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble (NTP, 1992), Soluble in formic acid. Practically insoluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, In water, 7.13X10+1 mg/L at 25 °C, 3.87e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20586 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00643 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3232 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014781 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Mebendazole causes degenerative alterations in the tegument and intestinal cells of the worm by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin, thus inhibiting its polymerization or assembly into microtubules. The loss of the cytoplasmic microtubules leads to impaired uptake of glucose by the larval and adult stages of the susceptible parasites, and depletes their glycogen stores. Degenerative changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria of the germinal layer, and the subsequent release of lysosomes result in decreased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy required for the survival of the helminth. Due to diminished energy production, the parasite is immobilized and eventually dies., Although the exact mechanism of anthelmintic activity of mebendazole has not been fully elucidated, the drug appears to cause selective and irreversible inhibition of the uptake of glucose and other low molecular weight nutrients in susceptible helminths; inhibition of glucose uptake appears to result in endogenous depletion of glycogen stores in the helminth. Mebendazole does not inhibit glucose uptake in mammals. Mebendazole appears to cause degenerative changes in the intestine of nematodes and in the absorptive cells of cestodes. The principal anthelmintic effect of the drug appears to be degeneration of cytoplasmic microtubules within these intestinal and absorptive cells. Microtubular deterioration results in inhibition of organelle movement and interferes with the absorptive and secretory function. As a result of excessive accumulation of intracellular transport secretory granules, hydrolytic and proteolytic enzymes are released and cause cellular autolysis. This irreversible damage leads to death of the parasite., Vermicidal; may also be ovicidal for ova or most helminths; mebendazole causes degeneration of parasite's cytoplasmic microtubules and thereby selectively and irreversibly blocks glucose uptake in susceptible adult intestine-dwelling helminths and their tissue-dwelling larvae; inhibition of glucose uptake apparently results in depletion of the parasite's glycogen stores; this, in turn, results in reduced formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) required for survival and reproduction of the helminth; corresponding energy levels are gradually reduced until death of the parasite ensues; mebendazole does not appear to affect serum glucose concentrations in humans, however., Benzimidazoles produce many biochemical changes in susceptible nematodes, eg, inhibition of mitochondrial fumarate reductase, reduced glucose transport, and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation ... /but/ the primary action ... /should be/ to inhibit microtubule polymerization by binding to beta-tubulin. The selective toxicity of these agents derives from the fact that specific, high-affinity binding to parasite beta-tubulin occurs at much lower concn than does binding to the mammalian protein ... Benzimidazole-resistant Haemonchus contortus display reduced high-affinity drug binding to beta-tubulin and alterations in beta-tubulin isotype gene expression that correlate with drug resistance ... Two identified mechanisms of drug resistance in nematodes involve both a progressive loss of "susceptible" beta-tubulin gene isotypes together with emergence of a "resistant" isotype with a conserved point mutation that encodes a tyrosine instead of phenylalanine at position 200 of beta-tubulin. While this mutation may not be required for benzimidazole resistance in all parasites, eg, Giardia lamblia, benzimidazole resistance in parasitic nematodes is unlikely to be overcome by novel benzimidazole analogs, because tyrosine also is present at position 200 of human beta-tubulin. /Benzimidazoles/ | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00643 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3232 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Off-white amorphous powder, Crystals from acetic acid and methanol | |
CAS No. |
31431-39-7 | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20586 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=31431-39-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0031431397 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00643 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | mebendazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757838 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | mebendazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=184849 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4040682 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.046.017 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/81G6I5V05I | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3232 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014781 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
551.3 °F (NTP, 1992), 288.5 °C | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20586 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00643 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MEBENDAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3232 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mebendazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014781 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















