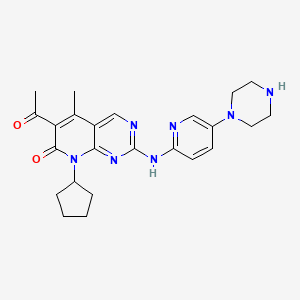
Palbociclib
Overview
Description
Palbociclib is a medication developed by Pfizer for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer . It is a selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6, which play a crucial role in cell cycle regulation . This compound was the first cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor to be approved as a cancer therapy .
Preparation Methods
The preparation of Palbociclib involves several synthetic routes and reaction conditions. One method includes the following steps :
Ring-closing reaction: 2-acetyl-2-butenoic acid methyl ester and malononitrile react under alkaline conditions to generate 1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methoxyl-4-methyl-5-acetyl-6-oxy-3-pyridine carbonitrile.
Substitution reaction: The intermediate product reacts with halogenated cyclopentane under the effect of an acid-binding agent to generate N-cyclopentyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methoxyl-4-methyl-5-acetyl-6-oxy-3-pyridinecarbonitrile.
Condensation reaction: The intermediate product reacts with N-[5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl]guanidine to generate 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5,8-dihydro-5-methyl-2-[5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl]amino-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(6H)-one.
Dehydrogenation reaction: The intermediate product reacts with sodium selenate to prepare this compound.
This method is economical, environmentally friendly, and suitable for industrial production .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Palbociclib undergoes various types of chemical reactions, including substitution reactions, redox reactions, and condensation reactions . Common reagents used in these reactions include thionyl chloride, bromine, cyclopentylamine, and sodium selenate . Major products formed from these reactions include intermediates such as 1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methoxyl-4-methyl-5-acetyl-6-oxy-3-pyridine carbonitrile and 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5,8-dihydro-5-methyl-2-[5-(1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl]amino-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(6H)-one .
Scientific Research Applications
Breast Cancer
The primary indication for palbociclib is in combination with endocrine therapy for advanced breast cancer. Key clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy:
- PALOMA-1 Trial : This Phase 2 study showed that the combination of this compound and letrozole significantly prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) breast cancer. The median PFS was reported at 20.2 months compared to 10.2 months for letrozole alone .
- PALOMA-2 Trial : A Phase 3 trial confirmed these findings, reporting a 44% reduction in the risk of disease progression when this compound was added to letrozole. The trial highlighted an improved median PFS exceeding one year .
Other Cancers
Beyond breast cancer, this compound is being investigated for its potential applications in various malignancies:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) : Preclinical studies indicate that this compound can suppress tumor growth in liver cancer models. It has shown effectiveness in promoting cell cycle arrest and improving survival rates when combined with standard treatments like sorafenib .
- Head and Neck Cancers : Ongoing clinical trials are exploring the use of this compound in treating head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, suggesting a broader application beyond breast cancer .
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) : Research is also underway to evaluate the efficacy of this compound in NSCLC, particularly in cases where traditional therapies have failed .
Case Studies
Several case studies illustrate the real-world applications of this compound:
-
Case Study: ER+ Breast Cancer
A 62-year-old postmenopausal woman with advanced ER+ breast cancer received this compound combined with letrozole after progressing on prior endocrine therapy. The patient achieved a PFS of over 18 months, highlighting the drug's effectiveness even after previous treatments. -
Case Study: Hepatocellular Carcinoma
In a preclinical model, mice treated with this compound alongside sorafenib exhibited a significant reduction in tumor size compared to those receiving sorafenib alone. This suggests that this compound may enhance the efficacy of existing HCC treatments .
Safety and Side Effects
While this compound has shown promising results, it is associated with certain adverse effects, primarily myelosuppression. Clinical trials reported higher rates of neutropenia among patients treated with this compound compared to those receiving placebo or other therapies . Monitoring blood counts is essential during treatment to manage these risks effectively.
Mechanism of Action
Palbociclib exerts its effects by selectively inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 . These kinases are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, particularly the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase . By inhibiting these kinases, this compound prevents the phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein, which is necessary for cell cycle progression . This inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase, thereby preventing cancer cell proliferation .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Other similar compounds in this class include Ribociclib and Abemaciclib . While all three drugs inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6, they have differences in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles . For example, Abemaciclib has three active metabolites with similar potency, whereas the metabolites of Palbociclib and Ribociclib are not of clinical significance . Additionally, Abemaciclib has a clear exposure-efficacy relationship, while such relationships for this compound and Ribociclib remain inconclusive .
Biological Activity
Palbociclib, a selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6), has emerged as a significant therapeutic agent in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer. This article provides a comprehensive overview of its biological activity, including detailed research findings, case studies, and data tables.
This compound functions by inhibiting CDK4 and CDK6, which play crucial roles in cell cycle regulation. By blocking these kinases, this compound prevents the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein (RB1), leading to cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. This action is particularly beneficial in HR+ breast cancer, where dysregulation of the cell cycle is common.
In Vitro Studies
Recent studies have demonstrated that this compound effectively reduces phosphorylated RB1 levels in various breast cancer cell lines. For instance, a comparative study showed that treatment with this compound at doses of 100 nM and 500 nM resulted in significant decreases in p-RB1 levels after 72 hours of exposure. The cytotoxic effects were also assessed using senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining, indicating that both this compound and ribociclib induce cellular senescence at higher concentrations .
| Cell Line | Dose (nM) | p-RB1 Reduction | SA-β-gal Staining |
|---|---|---|---|
| T47D | 100 | Moderate | Increased |
| T47D | 500 | Significant | Highest |
| MCF7 | 100 | Moderate | Increased |
| MCF7 | 500 | Significant | Highest |
Gene Expression Changes
Gene expression profiling revealed that this compound significantly alters the expression of genes associated with various PAM50 intrinsic subtypes. Notably, it increased the Luminal A and Normal-like signatures while decreasing Basal-like and HER2-enriched signatures. This suggests that this compound not only inhibits cell proliferation but also modifies tumor biology towards a less aggressive phenotype .
Clinical Efficacy
This compound's clinical efficacy has been substantiated through pivotal trials such as PALOMA-1 and PALOMA-2. In these studies, this compound combined with letrozole demonstrated a marked improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to letrozole alone. Real-world data further support these findings, showing high clinical benefit rates among patients treated with this compound .
Case Studies
A real-world study involving 162 patients treated with this compound plus letrozole reported a 94% six-month PFS rate. The objective response rate (ORR) was noted at 65%, indicating substantial effectiveness in routine clinical practice .
| Treatment Regimen | 6-Month PFS Rate | Objective Response Rate |
|---|---|---|
| This compound + Letrozole | 94% | 65% |
| This compound + Fulvestrant | 95% | Not specified |
Safety Profile
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, side effects such as neutropenia are common. Monitoring hematologic parameters is essential during treatment to manage potential adverse effects effectively.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. How is palbociclib’s mechanism of action validated in preclinical models of hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer?
- Methodological Answer : Use in vitro assays (e.g., cell cycle arrest via flow cytometry) and in vivo xenograft models to confirm CDK4/6 inhibition. Measure phosphorylation of retinoblastoma (Rb) protein and downstream E2F targets via immunoblotting. Preclinical studies in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) models demonstrated reversible G1 arrest in RB1-proficient cell lines, supporting mechanism validation strategies .
- Key Evidence : this compound induces senescence in RB1-proficient tumors, with resistance linked to RB1 loss .
Q. What statistical methods are recommended for analyzing progression-free survival (PFS) in phase III trials like PALOMA-3?
- Methodological Answer : Employ Cox proportional hazards models with stratification by metastatic site (visceral/nonvisceral), endocrine sensitivity, and menopausal status. Preplanned interim analyses should use independent data monitoring committees to assess efficacy and safety. In PALOMA-3, hazard ratios (HR) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals, and log-rank tests determined significance (P<0.001) .
- Key Evidence : Median PFS improved from 3.8 months (placebo + fulvestrant) to 9.2 months (this compound + fulvestrant) in PALOMA-3 .
Q. How are patient cohorts stratified in trials evaluating this compound combinations?
- Methodological Answer : Stratify by endocrine therapy sensitivity (primary vs. secondary resistance), menopausal status, and presence of visceral metastases. Subgroup analyses in PALOMA-3 revealed stronger overall survival (OS) benefits in endocrine-sensitive populations (HR=0.72; 10-month OS difference) .
- Key Evidence : Patients with prior endocrine sensitivity had a median OS of 39.7 months vs. 29.7 months in the placebo group .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can exposure-response analysis optimize this compound dosing in heterogeneous populations?
- Methodological Answer : Use pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling with average steady-state concentration (Cavg,t) to correlate drug exposure with PFS. In PALOMA-2, patients with Cavg,t below the median had shorter PFS, suggesting exposure-dependent efficacy. Adjust dosing in renal/hepatic impairment using population PK models .
- Key Evidence : Dose reductions did not significantly impact efficacy if Cavg,t remained above threshold levels .
Q. What experimental approaches identify mechanisms of this compound resistance in HR+ breast cancer?
- Methodological Answer : Perform genomic profiling (e.g., whole-exome sequencing) to detect RB1 loss or cyclin E1 amplification. Use in vitro models with long-term this compound exposure to mimic acquired resistance. In HCC models, RB1 loss conferred intrinsic resistance, observed in 30% of tumors .
- Key Evidence : RB1-deficient tumors show no response to CDK4/6 inhibition .
Q. How do real-world studies address limitations of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for this compound?
- Methodological Answer : Apply propensity score matching to balance baseline characteristics (e.g., prior therapies, age) between real-world and RCT cohorts. Retrospective analyses, such as the POLARIS study, validate this compound’s PFS benefit (median 12.4 months in real-world vs. 9.2–24.8 months in trials) despite broader eligibility criteria .
- Key Evidence : Real-world data confirm neutropenia (80% incidence) as the primary toxicity, consistent with RCTs .
Q. What methodologies assess synergism between this compound and PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors?
- Methodological Answer : Use combination index (CI) assays (e.g., Chou-Talalay method) in vitro. In the INAVO120 trial, inavolisib (PI3K inhibitor) + this compound + fulvestrant improved PFS vs. This compound + fulvestrant alone (15.0 vs. 7.3 months; HR=0.43) .
- Key Evidence : Synergistic effects are linked to dual pathway inhibition, delaying compensatory resistance .
Q. How are biomarkers like Rb phosphorylation or Ki-67 integrated into early-phase trial designs?
- Methodological Answer : Include exploratory endpoints using immunohistochemistry (IHC) or RNA sequencing to quantify Rb pathway activity. In PALOMA-1, Rb-positive tumors showed higher response rates to this compound + letrozole .
- Key Evidence : Rb loss or cyclin D1 amplification predicts poor response to CDK4/6 inhibitors .
Q. What pharmacodynamic endpoints are critical for this compound combination trials?
- Methodological Answer : Measure cell cycle arrest (G1 phase fraction) via flow cytometry and senescence markers (e.g., SA-β-galactosidase). In breast cancer models, this compound + EGFR inhibitors increased apoptosis (e.g., 40% apoptotic cells in HCT15 lines) .
- Key Evidence : Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) markers (e.g., IL-6, IL-8) are elevated in resistant tumors .
Q. How do ethnic and sex-specific factors influence this compound pharmacokinetics and efficacy?
- Methodological Answer : Conduct subgroup analyses stratified by ethnicity (e.g., Asian vs. non-Asian) or sex. In Japanese patients, this compound exposure correlated with body weight, necessitating dose adjustments. Male patients showed similar safety profiles to females in real-world studies .
- Key Evidence : FDA approval for male patients was based on real-world data and PK consistency across sexes .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H29N7O2/c1-15-19-14-27-24(28-20-8-7-18(13-26-20)30-11-9-25-10-12-30)29-22(19)31(17-5-3-4-6-17)23(33)21(15)16(2)32/h7-8,13-14,17,25H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27,28,29) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
AHJRHEGDXFFMBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=O)N(C2=NC(=NC=C12)NC3=NC=C(C=C3)N4CCNCC4)C5CCCC5)C(=O)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H29N7O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID40972590 | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40972590 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
447.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Palbociclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor that acts by binding to the ATP pocket with an IC50 in the range of 9-15 nmol/L. It is important to consider that it presents low to absent activity against other kinases. The CDK4/6 kinase is involved, with coregulatory partner cyclin D, in the G1-S transition. Hence, inhibition of this step prevents cell cycle progression in cells in whose this pathway is functioning. This step includes the pathways of the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein and the E2F family of transcription factors. | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09073 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
571190-30-2 | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=571190-30-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Palbociclib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0571190302 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09073 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40972590 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 6-Acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2-[[5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]-8H-pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | PALBOCICLIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/G9ZF61LE7G | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Melting Point |
263-266 ºC | |
| Record name | Palbociclib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09073 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.













