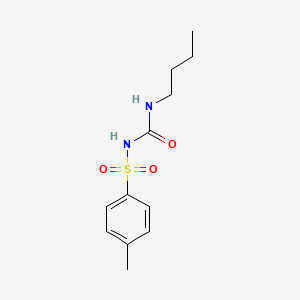
Tolbutamide
Overview
Description
Tolbutamide is a first-generation sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medication used primarily in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It was discovered in 1956 and functions by stimulating the secretion of insulin from the pancreas, thereby reducing blood glucose levels . Despite its efficacy, this compound is not routinely used today due to the availability of newer, second-generation sulfonylureas with fewer adverse effects .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Tolbutamide can be synthesized through the reaction of p-toluene sulfonamide with butyl isocyanate in the presence of triethylamine and tetrahydrofuran . Another method involves dissolving a specified carbamate derivative in hot toluene, adding butylamine slowly, and refluxing for four hours .
Industrial Production Methods: In industrial settings, this compound particles can be prepared by mixing the bulk drug with a supercritical fluid to form a supercritical mixture, which is then expanded to obtain the this compound particles . This method is particularly useful for producing this compound micro-particles.
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Tolbutamide undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution reactions.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized using strong oxidizing agents.
Reduction: Reduction reactions typically involve the use of reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur in the presence of nucleophiles or electrophiles under appropriate conditions.
Major Products: The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific reagents and conditions used. For example, oxidation may yield sulfonic acid derivatives, while reduction could produce amine derivatives.
Scientific Research Applications
Clinical Applications
-
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus :
- Tolbutamide is primarily prescribed for patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It is often used in conjunction with dietary modifications to improve glycemic control .
- A study involving 1,030 diabetic patients highlighted that this compound effectively maintained glycemic control in those with a lower insulin requirement and later-onset diabetes .
-
Research Applications :
- Animal Studies : Research has shown that this compound can reduce the incidence of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. In one study, treatment with this compound significantly decreased the cumulative incidence of diabetes compared to controls .
- Insulin Release Studies : Investigations into the effects of this compound on insulin release from isolated rat islets demonstrated that it stimulates insulin secretion in a dose-dependent manner, particularly at low glucose concentrations .
- Pharmacogenetics and Adverse Drug Reactions :
Case Studies
- Long-term Use and Efficacy : A long-term study indicated that this compound was effective in maintaining blood glucose levels in a significant number of patients over extended periods. Factors such as age at onset and insulin requirements were identified as critical determinants of treatment success .
- Comparative Effectiveness : In comparative studies against other antidiabetic agents, this compound has been shown to have a favorable profile concerning weight gain and hypoglycemia risk compared to newer agents like GLP-1 receptor agonists .
Data Table: Summary of Clinical Findings
Mechanism of Action
Tolbutamide exerts its hypoglycemic effects by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells. It achieves this by binding to and inhibiting the ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the beta cells, leading to cell depolarization and subsequent insulin release . Additionally, this compound reduces glucose output from the liver and increases insulin sensitivity at peripheral target sites .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
- Acetohexamide
- Chlorpropamide
- Tolazamide
Tolbutamide’s uniqueness lies in its rapid metabolism and short duration of action, making it suitable for use in older individuals .
Biological Activity
Tolbutamide is a first-generation sulfonylurea commonly used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its primary mechanism of action involves stimulating insulin release from pancreatic β-cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, supported by various studies and case analyses.
This compound operates by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channels in pancreatic β-cells. This inhibition causes depolarization of the cell membrane, leading to the opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels and an influx of calcium ions, which triggers insulin secretion. The effects are dose-dependent and vary with glucose concentrations.
- At low glucose levels (75 mg/dl), this compound enhances insulin release in a dose-dependent manner, but high concentrations can lead to a monophasic release pattern due to prolonged depolarization that inactivates calcium channels .
- In contrast, at higher glucose levels (150 mg/dl), this compound can reduce the insulin-releasing effect of glucose, indicating a complex interaction between these substances .
Pharmacokinetics and Interactions
Recent studies have highlighted interactions between this compound and other substances, such as pomegranate juice (PJ). The combination of PJ and this compound significantly improved outcomes in diabetic complications compared to this compound alone. The pharmacokinetic profile showed that PJ enhances the bioavailability and half-life of this compound while reducing its clearance .
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
A comparative study involving glipizide and this compound demonstrated that while both drugs effectively lower fasting serum glucose levels, glipizide showed superior results in terms of postprandial glucose control and insulin secretion during therapy . Specifically, glipizide resulted in a 25% reduction in fasting glucose compared to 17% with this compound over six months.
Case Studies
- University Group Diabetes Program (UGDP) :
- Hypoglycemia Diagnostic Test :
Effects on Glucose Metabolism
This compound has been shown to alter glucose transport and metabolism across various tissues:
- In embryonic heart tissues, exposure to this compound increased glucose uptake and glycolysis while upregulating glucose transporter proteins (GLUT-1) and hexokinase I (HKI) levels .
- This suggests that this compound not only affects pancreatic function but also has significant impacts on peripheral tissues involved in glucose metabolism.
Summary of Research Findings
Q & A
Basic Research Question
Q. Q1. What experimental approaches are recommended to elucidate Tolbutamide’s mechanism of action in pancreatic β-cells?
Methodological Answer:
- Step 1 : Use in vitro electrophysiology (e.g., patch-clamp techniques) to confirm this compound’s binding to sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) and subsequent ATP-sensitive potassium (K) channel inhibition .
- Step 2 : Measure insulin secretion in isolated islets via ELISA under varying glucose concentrations to correlate channel inhibition with hormonal output.
- Step 3 : Validate findings in animal models (e.g., streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats) to assess glucose-lowering efficacy and tissue specificity .
Basic Research Question
Q. Q2. How does CYP2C9 polymorphism influence this compound pharmacokinetics, and what experimental designs address this variability?
Methodological Answer:
- Approach : Conduct in vitro metabolism assays using recombinant CYP2C9 isoforms (e.g., CYP2C92 and CYP2C93) to quantify 4-hydroxythis compound formation rates .
- Clinical Validation : Perform pharmacokinetic studies in genotyped cohorts, measuring plasma concentration-time profiles (AUC, C, t) using HPLC-UV (mobile phase: 10 mM sodium acetate buffer [pH 4.4]/acetonitrile, 25:75 v/v) .
- Statistical Analysis : Apply ANOVA to compare metabolic clearance between genotypes, adjusting for covariates like age and liver function .
Advanced Research Question
Q. Q3. How can physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling resolve contradictions in this compound-drug interaction studies?
Methodological Answer:
- Model Development : Integrate in vitro CYP2C9 inhibition constants (K) and clinical PK data into software (e.g., Simcyp®) to simulate this compound exposure with inhibitors (e.g., sulfaphenazole) .
- Verification : Compare simulated AUC ratios (e.g., 2.5–3.5-fold increase with sulfaphenazole) against clinical observations to validate model accuracy .
- Application : Predict interactions with novel CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g., tasisulam) to guide dose adjustments in cancer patients .
Advanced Research Question
Q. Q4. How should researchers address contradictory efficacy data for this compound across patient subpopulations?
Methodological Answer:
- Meta-Analysis : Pool data from RCTs (e.g., 53-patient cohorts ) to stratify outcomes by covariates (age, BMI, prior insulin use).
- Confounder Adjustment : Use multivariate regression to isolate this compound’s effect from dietary adherence or comorbid conditions .
- In Silico Screening : Apply machine learning to EHR datasets to identify subpopulations with optimal HbA1c reduction .
Q. Methodological Guidance
Q. Q5. What quality control measures ensure reproducibility in this compound batch preparation for preclinical studies?
Methodological Answer:
- Analytical QC :
- HPLC-UV : Monitor purity (>98%) and stability under storage conditions (e.g., 4°C vs. room temperature) .
- Mass Spectrometry : Confirm molecular identity (m/z 271.2 for this compound; m/z 287.2 for 4-hydroxythis compound) .
- Batch Consistency :
- Table 1 : Example QC Parameters
| Parameter | Specification | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | ≥98% | HPLC-UV |
| Residual Solvents | <0.1% (ICH Q3C guidelines) | GC-MS |
| Water Content | <0.5% | Karl Fischer Titration |
Advanced Research Question
Q. Q6. How can researchers reconcile in vitro CYP2C9 inhibition data with in vivo this compound interaction outcomes?
Methodological Answer:
- Step 1 : Measure unbound inhibitor concentrations in vivo to adjust in vitro K values for protein binding .
- Step 2 : Use static models (e.g., [I]/K >0.1 threshold) to predict clinical relevance of in vitro findings .
- Step 3 : Validate with dynamic PBPK models incorporating hepatic blood flow and enzyme saturation .
Basic Research Question
Q. Q7. What criteria should guide patient selection for this compound trials to minimize confounding variables?
Methodological Answer:
- Inclusion Criteria :
- Mild type 2 diabetes (HbA1c 6.5–8.0%) .
- Naïve to insulin therapy, responsive to dietary control .
- Exclusion Criteria :
- Hepatic impairment (alters CYP2C9 activity) .
- Concomitant CYP2C9 inhibitors/inducers .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
1-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H18N2O3S/c1-3-4-9-13-12(15)14-18(16,17)11-7-5-10(2)6-8-11/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
JLRGJRBPOGGCBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H18N2O3S | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID8021359 | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8021359 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
270.35 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Tolbutamide appears as white crystals. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>40.6 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 61 °F (NTP, 1992), SOL IN ALC & CHLOROFORM; FREELY SOL IN WATER; VERY SLIGHTLY SOL IN ETHER /SODIUM SALT/, DISSOLVES READILY IN AQ NAOH TO FORM SODIUM DERIV, SOL IN ETHANOL, CHLOROFORM; FREELY IN DIMETHYL CARBONATE; INSOL IN WATER, Sol in ethanol, ethyl ether, and chloroform., In water, 109 mg/l @ 37 °C, 2.02e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855782 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01124 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3393 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Density |
1.245 at 77 °F (NTP, 1992) - Denser than water; will sink, 1.245 g/cu cm @ 25 °C | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3393 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in patients with NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor (receptor 1) on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP-potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin-containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose., SULFONYLUREAS STIMULATE ISLET TISSUE TO SECRETE INSULIN. ... SULFONYLUREAS CAUSE DEGRANULATION OF BETA CELLS, A PHENOMENON ASSOC WITH INCR RATE OF SECRETION OF INSULIN. /SULFONYLUREAS/, ALTHOUGH MOLECULAR MECHANISM...NOT UNDERSTOOD, SEVERAL PERTINENT OBSERVATIONS HAVE BEEN MADE. ...TOLBUTAMIDE IS RESTRICTED IN ITS ACTION TO EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & DOES NOT NEED TO ENTER BETA CELL. INVOKED RELEASE OF INSULIN IS IMMEDIATE & INTIMATELY RELATED TO ACTION OF GLUCOSE...MAY SENSITIZE CELL TO NORMAL SECRETAGOGUE., Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/ | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01124 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3393 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
WHITE OR PRACTICALLY WHITE CRYSTALLINE POWDER, Crystals | |
CAS No. |
64-77-7 | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=64-77-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000064777 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01124 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | tolbutamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757354 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | tolbutamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=23813 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, N-[(butylamino)carbonyl]-4-methyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8021359 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.541 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/982XCM1FOI | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3393 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
262 to 264 °F (NTP, 1992), 128.5-129.5 °C, MP: 41-43 °C; when anhyd, mp range is 130-133 °C /Sodium salt tetrahydrate/, 128.5 °C | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21120 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01124 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | TOLBUTAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3393 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Tolbutamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















