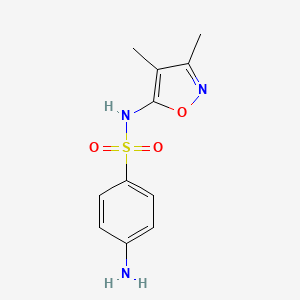
Sulfisoxazole
Overview
Description
Sulfisoxazole is a sulfonamide antibiotic used to prevent and treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. This compound works by inhibiting bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The preparation of sulfisoxazole involves a condensation reaction where 3-aminoisoxazole is reacted with p-acetamido-benzenesulfonyl chloride in the presence of toluene and pyridine. This reaction is typically carried out over 20-24 hours. The resulting product undergoes hydrolysis with liquid caustic soda, followed by a salt-forming reaction to obtain this compound sodium .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process involves careful control of reaction conditions to ensure high yield and purity. The final product is often crystallized and purified to meet pharmaceutical standards .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Sulfisoxazole undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized under specific conditions to form different derivatives.
Reduction: It can also undergo reduction reactions, although these are less common.
Substitution: this compound can participate in substitution reactions, particularly involving the sulfonamide group.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate.
Reduction: Reducing agents such as sodium borohydride can be used.
Substitution: Reagents like alkyl halides and acyl chlorides are often used in substitution reactions.
Major Products: The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used. For example, oxidation can lead to the formation of sulfone derivatives .
Scientific Research Applications
Antitumor Activity
Inhibition of Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEV) Secretion
Recent studies have identified sulfisoxazole as a potent inhibitor of small extracellular vesicle secretion from breast cancer cells. This mechanism is significant because sEVs are known to facilitate cancer progression and metastasis. This compound interferes with the endothelin receptor A (ETA), which is crucial for the biogenesis and secretion of sEVs. In mouse models, this compound demonstrated substantial anti-tumor and anti-metastatic effects, reducing tumor burden without significant toxicity .
- Mechanism of Action :
Immunomodulatory Effects
Reinvigoration of Exhausted T Cells
This compound has shown promise in enhancing the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. It significantly decreases the levels of PD-L1 in exosomes derived from tumors, which is crucial for overcoming immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. When combined with anti-PD-1 antibodies, this compound reinvigorates exhausted CD8+ T cells, thereby eliciting robust antitumor responses .
- Clinical Implications :
- The combination therapy could improve response rates in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, addressing a major limitation in current cancer therapies.
Safety Profile and Adverse Reactions
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is essential to consider its safety profile in clinical settings. A study monitoring hospitalized patients revealed that adverse reactions occurred in approximately 3.1% of cases treated with this compound. Common reactions included skin rashes and eosinophilia; however, serious reactions were rare (0.14%) and often associated with prolonged therapy .
Environmental Applications
Biodegradation Research
This compound has also been studied for its biodegradation properties in environmental contexts. Research indicates that this compound can be relevant in assessing the impact of pharmaceutical contaminants on ecosystems, particularly regarding microbial degradation processes .
Data Table: Summary of Applications
Mechanism of Action
Sulfisoxazole exerts its effects by inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is crucial for the bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, a precursor for nucleic acid synthesis. By preventing the condensation of pteridine with para-aminobenzoic acid, this compound effectively halts bacterial growth and replication .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Sulfamethoxazole: Another sulfonamide antibiotic with a similar mechanism of action but different pharmacokinetics.
Sulfadiazine: Used primarily in the treatment of toxoplasmosis.
Sulfapyridine: Used in the treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis.
Uniqueness: Sulfisoxazole is unique in its short-acting nature and its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacterial species. It is particularly useful in combination therapies to enhance antibacterial efficacy .
Biological Activity
Sulfisoxazole (SFX) is a sulfonamide antibiotic that has garnered attention not only for its antibacterial properties but also for its potential biological activities in cancer therapy and immunomodulation. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its mechanisms of action, effects on cancer cells, and associated research findings.
This compound primarily functions as an antibacterial agent by inhibiting bacterial dihydropteroate synthase, an enzyme critical for folate synthesis. However, recent studies have revealed additional mechanisms through which this compound exerts biological effects:
- Inhibition of Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEV) Secretion : SFX has been identified as an inhibitor of sEV secretion from breast cancer cells. It interferes with the endothelin receptor A (ETA), leading to reduced tumor growth and metastasis in mouse models of breast cancer. This inhibition is linked to decreased expression of proteins involved in sEV biogenesis and enhanced lysosomal degradation of multivesicular endosomes .
- Modulation of Immune Responses : SFX has shown promise in enhancing antitumor immune responses. It decreases the levels of exosomal PD-L1 in blood, which is associated with immune evasion in tumors. By reinvigorating exhausted CD8+ T cells, this compound may improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors like anti-PD-1 antibodies .
Case Studies and Experimental Data
- Anti-Tumor Effects : In a study involving mouse models of breast cancer xenografts, this compound demonstrated significant anti-tumor and anti-metastatic effects. The results indicated that SFX could serve as a potential therapeutic agent targeting cancer progression through its action on ETA and sEV secretion pathways .
- Electrochemical Analysis : Recent electrochemical studies have developed sensitive methods for detecting this compound in biological samples. Using modified glassy carbon electrodes, researchers achieved detection limits as low as 0.4 μM, showcasing the compound's presence in various biological matrices .
- Adverse Reactions : While this compound is generally well-tolerated, adverse reactions have been reported. A study monitoring hospitalized patients revealed that 3.1% experienced severe reactions necessitating discontinuation of therapy, with skin rashes and eosinophilia being the most common manifestations .
Data Table: Summary of Biological Activities
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What is the mechanism of action of sulfisoxazole, and how can researchers validate it experimentally?
this compound inhibits bacterial dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS), a key enzyme in folate biosynthesis. To validate this, researchers can perform in vitro enzyme inhibition assays using purified DHPS, monitor substrate (p-aminobenzoic acid) utilization via spectrophotometry, and compare inhibition kinetics with control compounds. Competitive binding studies using radiolabeled this compound analogs can further confirm target specificity .
Q. What synthetic methodologies are commonly used to produce this compound, and how can purity be ensured?
this compound is synthesized via condensation of 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide with 3,4-dimethyl-5-isoxazolylamine. Post-synthesis, purity is assessed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection (λ = 265 nm) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to confirm structural integrity. Recrystallization in ethanol-water mixtures (70:30 v/v) is recommended to achieve ≥98% purity .
Q. Which analytical techniques are most reliable for quantifying this compound in biological matrices?
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is optimal for quantifying this compound in plasma or tissue homogenates, offering sensitivity down to 0.1 ng/mL. For non-biological samples, UV-Vis spectrophotometry (at 257 nm) or reverse-phase HPLC with C18 columns provides reproducible results. Calibration curves should be validated using spiked samples to account for matrix effects .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can researchers investigate this compound resistance mechanisms in Gram-negative bacteria?
Resistance often arises from mutations in the folP gene (encoding DHPS) or overexpression of efflux pumps. To study this:
- Perform whole-genome sequencing of resistant strains to identify folP mutations.
- Use quantitative PCR (qPCR) to measure efflux pump gene expression (e.g., acrAB-tolC in E. coli).
- Conduct competitive growth assays with and without efflux inhibitors (e.g., phenylalanine-arginine β-naphthylamide) .
Q. What experimental strategies optimize this compound’s pharmacokinetics while minimizing toxicity?
- Structural modification : Introduce hydrophilic groups (e.g., hydroxyl or carboxyl) to enhance solubility and reduce renal crystallinity risk.
- Nanoparticle encapsulation : Use poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles to improve bioavailability and target tissue delivery.
- Toxicity screening : Employ in vitro hepatocyte models (e.g., HepG2 cells) to assess metabolic stability and cytotoxicity .
Q. How can researchers resolve contradictions in reported this compound efficacy across different bacterial strains?
Contradictions may stem from variations in bacterial folate biosynthesis pathways or assay conditions. Mitigate this by:
- Standardizing MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) assays using CLSI guidelines (e.g., Mueller-Hinton broth, pH 7.2–7.4).
- Including positive controls (e.g., trimethoprim) and strain-specific folate pathway annotations .
Q. What methodologies are effective for studying this compound’s synergism with other antibiotics?
Use checkerboard assays to calculate fractional inhibitory concentration indices (FICIs). For example, combining this compound with trimethoprim (targeting DHFR) often shows synergy (FICI ≤0.5). Time-kill curves over 24 hours can further validate synergistic bactericidal activity .
Q. How should researchers design in vivo studies to evaluate this compound’s tissue penetration?
- Animal models : Use neutropenic murine thigh infections for pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling.
- Tissue sampling : Measure drug concentrations in target tissues (e.g., kidneys, lungs) via microdialysis or homogenization followed by LC-MS/MS.
- Data analysis : Apply non-compartmental analysis (NCA) to calculate AUC/MIC ratios .
Q. What experimental approaches assess this compound’s stability under varying physiological conditions?
Conduct forced degradation studies :
- Acidic/alkaline hydrolysis (0.1M HCl/NaOH, 70°C for 24 hours).
- Oxidative stress (3% H₂O₂, 25°C for 6 hours).
- Photostability (ICH Q1B guidelines, 1.2 million lux hours). Analyze degradation products using LC-MS and compare to stability-indicating HPLC methods .
Q. How can predictive modeling improve this compound derivative screening?
Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models trained on existing sulfonamide datasets can predict bioactivity and ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity) profiles. Use molecular docking (e.g., AutoDock Vina) to simulate binding to DHPS active sites, prioritizing derivatives with lower binding energies (ΔG ≤ -8 kcal/mol) .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-(3,4-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)benzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H13N3O3S/c1-7-8(2)13-17-11(7)14-18(15,16)10-5-3-9(12)4-6-10/h3-6,14H,12H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
NHUHCSRWZMLRLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(ON=C1C)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C11H13N3O3S | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
2200-44-4 (mono-hydrochloride salt), 6155-81-3 (mono-lithium salt) | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole [USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000127695 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6021292 | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6021292 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
267.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Sulfisoxazole is an odorless white to yellowish crystalline powder. Slightly bitter taste. Acid to litmus. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>40.1 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 72.5 °F (NTP, 1992), White to off-white, odorless, crystalline powder. Sol in alcohol; freely sol in water. /Diethanolamine salt/, Soluble in alcohol, SOL IN DIETHYL ETHER (1 IN 800); SOL IN 5% AQ SODIUM BICARBONATE (1 IN 30), 1 G IN ABOUT 6700 ML WATER; SOL IN DIL HYDROCHLORIC ACID; 1 G IN ABOUT 10 ML BOILING ALCOHOL, In water, 300 mg/L at 37 °C, pH 4.5, 3.13e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID859862 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfisoxazole is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. It inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by preventing the condensation of the pteridine with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid., The sulfonamides are bacteriostatic agents and the spectrum of activity is similar for all. Sulfonamides inhibit bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by preventing the condensation of the pteridine with aminobenzoic acid through competitive inhibition of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. Resistant strains have altered dihydropteroate synthetase with reduced affinity for sulfonamides or produce increased quantities of aminobenzoic acid., Sulfonamides are usually bacteriostatic in action. Sulfonamides interfere with the utilization of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid (the reduced form of folic acid) cofactors in susceptible bacteria. Sulfonamides are structural analogs of PABA and appear to interfere with PABA utilization by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, which catalyzes the formation of dihydropteroic acid (a precursor of tetrahydrofolic acid) from PABA and pteridine; however, other mechanism(s) affecting the biosynthetic pathway also may be involved. Compounds such as pyrimethamine and trimethoprim, which block later stages in the synthesis of folic acid, act synergistically with sulfonamides. Only microorganisms that synthesize their own folic acid are inhibited by sulfonamides; animal cells and bacteria which are capable of utilizing folic acid precursors or preformed folic acid are not affected by these drugs. The antibacterial activity of the sulfonamides is reportedly decreased in the presence of blood or purulent body exudates. /Sulfonamides/ | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Colorless prisms, White to slightly yellowish crystalline powder | |
CAS No. |
127-69-5 | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=127-69-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole [USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000127695 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757343 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=38588 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=33807 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=13120 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(3,4-dimethyl-5-isoxazolyl)- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6021292 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfafurazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.004.418 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/740T4C525W | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
383 to 388 °F (NTP, 1992), 194 °C, MP: 191 °C, MP: 195-198 °C | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















