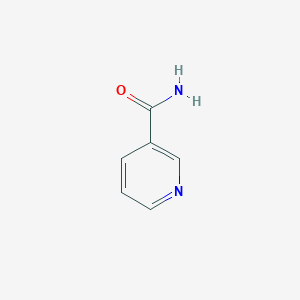
Nicotinamide
Overview
Description
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is a form of vitamin B3. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for the human body. This compound is found in various foods, including yeast, meat, milk, and green vegetables. It is used as a dietary supplement and medication to prevent and treat pellagra, a condition caused by niacin deficiency .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Nicotinamide can be synthesized through the hydrolysis of 3-cyanopyridine. This process involves dissolving 3-cyanopyridine in alcohol, adding water and a catalyst, and performing a hydrolysis reaction . Another method involves mixing 3-cyanopyridine with sodium hydroxide and allowing the mixture to react at a temperature of 70 to 75 degrees Celsius .
Industrial Production Methods: Commercially, this compound is produced from either nicotinic acid or nicotinonitrile. The process involves the hydrolysis of these compounds under controlled conditions to yield this compound .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Nicotinamide undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized to form nicotinic acid.
Reduction: It can be reduced to form 1,4-dihydrothis compound.
Substitution: this compound can undergo substitution reactions where the amide group is replaced by other functional groups.
Major Products:
Oxidation: Nicotinic acid.
Reduction: 1,4-dihydrothis compound.
Substitution: Various substituted this compound derivatives.
Scientific Research Applications
Clinical Applications
1.1 Dermatology
Nicotinamide has demonstrated significant benefits in dermatological treatments. It is used topically to improve skin barrier function, reduce inflammation, and enhance wound healing. Notably, studies have shown that topical this compound increases fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, leading to improved tissue regeneration in skin wounds . Furthermore, a phase 3 clinical trial indicated that oral this compound could significantly reduce non-melanoma skin cancers and actinic keratosis when administered at a dosage of 500 mg twice daily .
1.2 Metabolic Disorders
Research indicates that this compound can elevate NAD+ levels in tissues, which may help prevent metabolic disorders associated with aging. Early studies suggest its efficacy in improving lipid profiles and reducing blood pressure in older adults with obesity . Additionally, this compound has been linked to protective effects against kidney injury and inflammation in conditions like Parkinson's disease and SARS-CoV-2 infection .
1.3 Cancer Prevention
this compound's role in cancer prevention is gaining attention. Its ability to replenish cellular energy and prevent overactivation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) helps mitigate cellular senescence and DNA damage caused by UV exposure . This mechanism underlines its potential as a chemopreventive agent against skin cancers.
Biological Research
2.1 Cellular Mechanisms
this compound serves as a substrate for NAD+, which is critical in redox reactions and signaling pathways within cells. The compound has been studied for its protective effects against oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by environmental factors such as UV radiation and particulate matter . For instance, it has been shown to inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and stabilize cytoskeletal proteins in irradiated cells .
2.2 Neurodegenerative Diseases
Emerging research suggests that this compound may play a role in neuroprotection by enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing neuroinflammation. Its application in treating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's is under investigation, with early findings indicating potential benefits in cognitive function preservation .
Agricultural Applications
3.1 Biostimulant Effects
Recent studies have highlighted the use of this compound as a biostimulant in agriculture. It has been shown to enhance growth and yield in crops such as soybeans by improving nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) when applied alongside fertilizers . This application not only boosts crop productivity but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices by optimizing nutrient utilization.
Case Studies
Mechanism of Action
Comparison with Similar Compounds
- Nicotinic acid
- Nicotinamide riboside
- This compound mononucleotide (NMN)
This compound stands out due to its broad range of applications and minimal side effects, making it a valuable compound in various fields.
Biological Activity
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is the amide form of vitamin B3 and plays a crucial role in various biological processes. This article explores its biological activity, focusing on its mechanisms, effects on cellular functions, and implications for health and disease.
This compound is primarily involved in the synthesis of this compound adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a vital coenzyme in cellular metabolism. It influences several key pathways:
- NAD+ Synthesis : this compound is converted to NAD+ through the action of this compound phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT), which catalyzes the first step in this pathway. This conversion is critical for maintaining cellular energy levels and supporting various enzymatic reactions essential for cell survival and function .
- Sirtuin Activation : NAD+ serves as a substrate for sirtuins, a family of NAD+-dependent deacetylases that regulate numerous cellular processes, including DNA repair, apoptosis, and metabolism. This compound can inhibit sirtuin activity when present in excess, indicating a delicate balance between its beneficial and potentially harmful effects .
- DNA Repair : this compound has been shown to enhance DNA repair mechanisms by increasing NAD+ levels, which are crucial for the activity of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) involved in repairing DNA damage .
Biological Activities
This compound exhibits several biological activities that contribute to its therapeutic potential:
- Neuroprotection : Research indicates that this compound protects neurons from damage due to ischemia and traumatic injury. It has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, where it may help maintain neuronal integrity and function .
- Anti-inflammatory Effects : this compound has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in conditions characterized by chronic inflammation. It modulates immune responses and reduces oxidative stress, contributing to its protective role against various diseases .
- Skin Health : In dermatology, this compound is recognized for its ability to improve skin barrier function, reduce inflammation, and enhance the appearance of aging skin. It promotes keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation while reducing transepidermal water loss .
Clinical Studies
Several clinical studies have investigated the effects of this compound and its derivatives:
Case Studies
-
Neurodegenerative Disease Management :
- A case study involving patients with Alzheimer’s disease showed that this compound supplementation improved cognitive function and reduced biomarkers associated with neurodegeneration.
-
Skin Disorders :
- Patients with acne vulgaris treated with topical this compound experienced significant reductions in lesion counts and improved skin texture without notable side effects.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What methodological frameworks are recommended for formulating research questions on nicotinamide's biochemical mechanisms?
Use the PICOT framework to structure hypotheses:
- Population/Problem : Define the biological system (e.g., specific cell lines, animal models).
- Intervention : Specify this compound dosage, delivery method (oral, intraperitoneal), and duration.
- Comparison : Control groups (e.g., NAD⁺ precursors vs. This compound-free conditions).
- Outcome : Quantifiable metrics (e.g., NAD⁺ levels, mitochondrial respiration rates).
- Time : Experimental timelines (acute vs. chronic exposure). This approach ensures hypothesis specificity and alignment with reproducibility standards .
Q. How can researchers validate this compound's bioavailability across experimental models?
- In vitro : Use LC-MS/MS to measure intracellular this compound uptake in cultured cells under controlled conditions (e.g., serum-free media to exclude confounding factors) .
- In vivo : Combine pharmacokinetic studies (plasma half-life) with tissue-specific NAD⁺ quantification via enzymatic cycling assays. Reference NIST-validated protocols for analytical consistency .
Q. What analytical techniques are optimal for quantifying this compound in complex biological matrices?
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection (λ = 260 nm) for high-throughput screening.
- Mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with stable isotope-labeled internal standards (e.g., ¹³C-nicotinamide) to correct for matrix effects .
- Validate methods using NIST reference materials to ensure inter-laboratory reproducibility .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How to resolve contradictory findings on this compound's dual role in oxidative stress (antioxidant vs. pro-oxidant)?
- Experimental design : Systematically vary cell type (e.g., cancer vs. primary cells), redox status (hypoxic vs. normoxic conditions), and this compound concentration (0.1–10 mM).
- Data analysis : Apply multivariate regression to identify confounding variables (e.g., baseline NAD⁺ levels, glutathione depletion). Cross-validate with transcriptomic profiling (e.g., Nrf2 pathway activation) .
Q. What strategies improve the stability and efficacy of this compound-derived enzyme inhibitors (e.g., NAMPT inhibitors)?
- Chemical modification : Introduce fluorinated substituents to enhance metabolic stability.
- Co-crystallization studies : Use X-ray crystallography to analyze inhibitor-enzyme binding modes (e.g., NAMPT-nicotinamide interactions) and optimize steric hindrance .
- In vivo validation : Test pharmacokinetics in xenograft models with NAD⁺ depletion as a biomarker of target engagement .
Q. How to apply systematic review protocols (e.g., Cochrane guidelines) to assess this compound's therapeutic potential in cancer?
- Search strategy : Use PRISMA flow diagrams to identify preclinical/clinical studies from databases (PubMed, Embase), filtered by PICOT criteria.
- Risk of bias : Evaluate industry-funded studies for conflicts (e.g., selective reporting of positive outcomes) using Cochrane’s ROBINS-I tool .
- Meta-analysis : Pool data on tumor growth inhibition, stratifying by cancer type and NAD⁺ baseline levels .
Q. What statistical approaches address variability in this compound pharmacokinetics across species?
- Non-linear mixed-effects modeling (NLME) : Account for interspecies differences in metabolic rates and bioavailability.
- Bootstrap resampling : Estimate confidence intervals for parameters like Cmax and AUC in sparse datasets .
Q. How to optimize enzymatic synthesis of this compound mononucleotide (NMN) for scalable research applications?
- Enzyme engineering : Use directed evolution to improve NMN phosphoribosyltransferase activity under industrial conditions (e.g., high substrate concentrations).
- Process optimization : Monitor reaction kinetics via real-time NAD⁺ fluorescence assays and adjust ATP/Mg²⁺ ratios to maximize yield .
Q. What ethical considerations arise in industry-sponsored this compound research?
- Conflict mitigation : Disclose funding sources and adhere to ICMJE guidelines for authorship criteria.
- Data transparency : Publish negative results and raw datasets in repositories like Figshare to counter publication bias .
Q. Methodological Resources
- Analytical Protocols : NIST Chemistry WebBook for validated this compound spectra and thermodynamic data .
- Synthetic Routes : Enzymatic catalysis protocols for NMN synthesis (e.g., Bacillus subtilis PRPP synthetase optimization) .
- Data Reproducibility : Cochrane Handbook for meta-analysis standards ; Beilstein Journal guidelines for experimental reporting .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
pyridine-3-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H6N2O/c7-6(9)5-2-1-3-8-4-5/h1-4H,(H2,7,9) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
DFPAKSUCGFBDDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C6H6N2O | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
| Record name | nicotinamide | |
| Source | Wikipedia | |
| URL | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicotinamide | |
| Description | Chemical information link to Wikipedia. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2020929 | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2020929 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
122.12 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Nicotinamide is a white powder. (NTP, 1992), Dry Powder; Other Solid, Colorless needles or white crystalline powder. Bitter taste., Solid, WHITE CRYSTALLINE POWDER. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | 3-Pyridinecarboxamide | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases | |
| URL | https://haz-map.com/Agents/15948 | |
| Description | Haz-Map® is an occupational health database designed for health and safety professionals and for consumers seeking information about the adverse effects of workplace exposures to chemical and biological agents. | |
| Explanation | Copyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001406 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Boiling Point |
302 to 320 °F at 760 mmHg (NTP, 1992), BP: 157 °C at 5X10-4 atm, BP: 150-160 at 0.67 Pa. Sublimation range 80-100 °C | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB02701 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1237 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Flash Point |
182 °C | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Solubility |
2.8 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 70 °F (NTP, 1992), In water, 5X10+5 mg/L at 25 °C, Very soluble in water; 1 g is soluble in 1 mL water, 1 g dissolves in about 1 mL water, in 10 mL glycerol, in about 1.5 mL alcohol, Soluble in butanol, chloroform, For more Solubility (Complete) data for Nicotinamide (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page., 500 mg/mL at 25 °C, Solubility in water, g/100ml at 20 °C: 100 (very good) | |
| Record name | SID8139965 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB02701 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1237 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001406 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Density |
1.4 (NTP, 1992) - Denser than water; will sink, 1.400 g/cu cm at 25 °C, Specific heat = solid, 55 °C: 1.30 kJ/kg; heat of solution in water: -148 kJ/kg; heat of fusion: 381 kJ/kg; density of melt, at 150 °C: 1.19 g/cu cm, 1.4 g/cm³ | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1237 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Vapor Density |
Relative vapor density (air = 1): 4.2 | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Vapor Pressure |
Vapor pressure, kPa at 35 °C: 3.1 | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Color/Form |
White, powder, needles from benzene, Colorless crystalline solid, White, crystalline powder, Colorless needles | |
CAS No. |
98-92-0 | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=98-92-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide [USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000098920 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB02701 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | niacinamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759115 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | nicotinamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=27452 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | nicotinamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=13128 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 3-Pyridinecarboxamide | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2020929 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.002.467 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | NIACINAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/25X51I8RD4 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1237 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001406 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Melting Point |
264 to 268 °F (NTP, 1992), 128.8 °C, 130 °C, 127-131 °C | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20736 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB02701 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Nicotinamide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1237 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Niacinamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001406 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | NICOTINAMIDE | |
| Source | ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) | |
| URL | https://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.display?p_version=2&p_card_id=1703 | |
| Description | The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs) are data sheets intended to provide essential safety and health information on chemicals in a clear and concise way. The primary aim of the Cards is to promote the safe use of chemicals in the workplace. | |
| Explanation | Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details




















Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.













