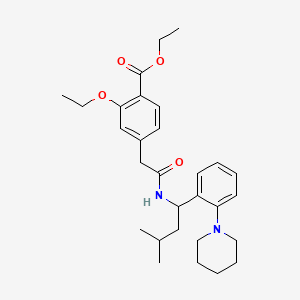
Repaglinide ethyl ester
Descripción general
Descripción
Repaglinide ethyl ester is a chemical compound that serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of repaglinide, a medication used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus. Repaglinide is a non-sulfonylurea insulin secretagogue that helps regulate blood glucose levels by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta cells .
Métodos De Preparación
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
Repaglinide ethyl ester can be synthesized through various synthetic routes. One common method involves the esterification of 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, followed by formylation, oxidation, etherification, and selective hydrolysis . The reaction conditions, such as temperature, time, solvent, and substrate ratios, are optimized to achieve high yields and purity .
Industrial Production Methods
In industrial settings, the production of this compound involves large-scale synthesis using similar reaction steps. The process is designed to be scalable and environmentally friendly, minimizing waste and optimizing resource utilization .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Types of Reactions
Repaglinide ethyl ester undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Conversion of functional groups to higher oxidation states.
Reduction: Conversion of functional groups to lower oxidation states.
Substitution: Replacement of one functional group with another.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate, reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride, and substitution reagents like ethyl bromide . The reactions are typically carried out under controlled conditions to ensure high selectivity and yield.
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from these reactions include various intermediates that are further processed to produce repaglinide .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Repaglinide ethyl ester has several scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of repaglinide and other related compounds.
Medicine: Essential in the development of repaglinide, a drug used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Industry: Utilized in the large-scale production of repaglinide, ensuring consistent quality and supply.
Mecanismo De Acción
Repaglinide ethyl ester itself does not have a direct mechanism of action, as it is an intermediate compound. repaglinide, the final product, exerts its effects by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels in pancreatic beta cells. This inhibition leads to membrane depolarization, opening of calcium channels, and subsequent insulin release .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Similar Compounds
Similar compounds to repaglinide ethyl ester include:
Nateglinide: Another meglitinide class drug used to manage type 2 diabetes.
Mitiglinide: A similar insulin secretagogue with a different chemical structure.
Uniqueness
This compound is unique due to its specific role as an intermediate in the synthesis of repaglinide. Its optimized synthetic route and reaction conditions make it a valuable compound in the pharmaceutical industry .
Propiedades
Fórmula molecular |
C29H40N2O4 |
|---|---|
Peso molecular |
480.6 g/mol |
Nombre IUPAC |
ethyl 2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[3-methyl-1-(2-piperidin-1-ylphenyl)butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H40N2O4/c1-5-34-27-19-22(14-15-24(27)29(33)35-6-2)20-28(32)30-25(18-21(3)4)23-12-8-9-13-26(23)31-16-10-7-11-17-31/h8-9,12-15,19,21,25H,5-7,10-11,16-18,20H2,1-4H3,(H,30,32) |
Clave InChI |
FTCMVLQJMIXDSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES canónico |
CCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)CC(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2N3CCCCC3)C(=O)OCC |
Origen del producto |
United States |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details




Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
![3-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]propanoic acid](/img/structure/B8791354.png)
![Methyl 8-chloroimidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-7-carboxylate](/img/structure/B8791370.png)
![3-(4,4-Dimethyl-2-oxo-2,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[D][1,3]oxazin-6-YL)benzonitrile](/img/structure/B8791411.png)
![4-{[4-(Methanesulfonyl)benzene-1-sulfonyl]amino}benzoic acid](/img/structure/B8791437.png)
