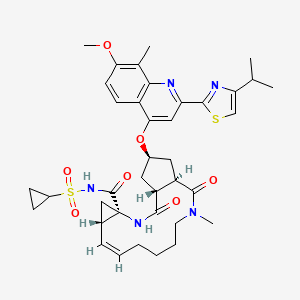
Simeprevir
Descripción general
Descripción
TMC435, también conocido como simeprevir, es un potente inhibidor de la proteasa NS3/4A del virus de la hepatitis C, no covalente, oral y de una sola vez al día. Se utiliza en combinación con interferón pegilado y ribavirina para el tratamiento de la infección crónica por el virus de la hepatitis C del genotipo 1. Este compuesto ha sido aprobado para su uso en varios países, incluidos Japón, Canadá, Estados Unidos, Rusia, la Unión Europea, México y Australia .
Mecanismo De Acción
TMC435 ejerce sus efectos inhibiendo la proteasa de serina NS3/4A del virus de la hepatitis C. Esta proteasa es esencial para la replicación del virus. Al inhibir esta enzima, TMC435 evita que el virus se replique y se propague dentro del huésped. Los objetivos moleculares de TMC435 incluyen residuos específicos dentro de la proteasa NS3/4A, que son críticos para su actividad enzimática .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Clinical Efficacy in Hepatitis C Treatment
Simeprevir has demonstrated significant efficacy in treating chronic hepatitis C, particularly in genotype 1 infections. The following key studies highlight its clinical applications:
- PROMISE Study : In this pivotal Phase 3 study, this compound was administered to treatment-experienced patients, resulting in a sustained virologic response (SVR12) rate of 79%, compared to only 37% in the placebo group. This study established this compound's effectiveness when combined with pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
- QUEST Studies : A pooled analysis from the QUEST-1 and QUEST-2 trials showed that 80% of treatment-naïve patients achieved SVR12 when treated with this compound plus pegylated interferon and ribavirin. This was a significant improvement over historical controls .
- This compound Plus Sofosbuvir : A study evaluating this compound combined with sofosbuvir for 12 weeks reported superior SVR12 rates compared to historical controls for both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients .
Patient Subpopulations
This compound's effectiveness varies among different patient demographics and conditions:
- Cirrhosis Patients : In patients with cirrhosis, SVR12 rates were reported at 83% for those treated with this compound plus sofosbuvir. This indicates that even patients with advanced liver disease can benefit significantly from this combination therapy .
- IL28B Genotype Impact : The efficacy of this compound also correlates with the IL28B genotype. In the PROMISE study, SVR12 rates varied significantly based on genotype, highlighting the importance of genetic factors in treatment outcomes .
Safety Profile
This compound is generally well-tolerated, with manageable side effects. The PROMISE study reported on-treatment failure rates of 3% and relapse rates of 19% among patients treated with this compound, which were significantly lower than those observed in the placebo group . Adverse reactions are relatively infrequent and do not exacerbate anemia, a common side effect associated with other treatments like pegylated interferon .
Future Research Directions
Ongoing studies continue to explore the potential applications of this compound beyond its current indications:
- Combination Therapies : Research is being conducted on the use of this compound in combination with newer antiviral agents to enhance efficacy and reduce treatment duration for various HCV genotypes .
- Drug Repositioning : Preliminary investigations suggest that this compound may have applications beyond hepatitis C, including potential effects on other viral infections or conditions due to its mechanism of action targeting viral proteases .
Summary Table of Clinical Trials Involving this compound
| Study Name | Patient Population | Treatment Duration | SVR12 Rate (%) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROMISE | Treatment-experienced | 12 weeks | 79 | Significant improvement over placebo |
| QUEST-1 & QUEST-2 | Treatment-naïve | 12 weeks | 80 | High efficacy in naïve patients |
| OPTIMIST | Patients with cirrhosis | 8-12 weeks | 83 | Effective even in advanced liver disease |
| This compound + Sofosbuvir | Mixed population | 12 weeks | Variable | Superior SVR12 rates compared to historical control |
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Simeprevir plays a crucial role in inhibiting the replication of the hepatitis C virus by targeting the NS3/4A protease, an enzyme essential for the viral life cycle. The compound binds non-covalently to the NS3/4A protease, resulting in a fast association and slow dissociation rate . This interaction prevents the protease from cleaving the HCV polyprotein into functional viral proteins, thereby inhibiting viral replication. This compound also interacts with other biomolecules, such as the cofactor N4A subunit, which is part of the NS3/4A heterodimeric complex .
Cellular Effects
This compound exerts significant effects on various types of cells, particularly hepatocytes, where it accumulates after uptake via organic anion-transporting polypeptides OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 . In hepatocytes, this compound inhibits the NS3/4A protease, leading to a reduction in viral replication. This inhibition affects cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism by preventing the production of viral proteins necessary for the virus’s life cycle . Additionally, this compound has been shown to display synergistic effects with interferon-α and HCV NS5B inhibitors, further enhancing its antiviral activity .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its binding to the NS3/4A protease, a critical enzyme for the hepatitis C virus. By inhibiting this protease, this compound prevents the cleavage of the HCV polyprotein into individual viral proteins, thereby blocking viral replication . This compound’s binding interactions with the NS3/4A protease are highly specific and potent, making it an effective antiviral agent. Additionally, this compound’s resistance profile differs from first-generation protease inhibitors, as it is less effective against certain polymorphic variants of the NS3 protease .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound have been observed to change over time. The compound is relatively stable, with a half-life of approximately 41 hours in individuals with HCV . Over time, this compound’s antiviral activity can be influenced by factors such as drug degradation and the development of viral resistance. Long-term studies have shown that this compound maintains its efficacy in reducing viral load and achieving sustained virological response (SVR) when used in combination with other antiviral agents .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. Studies have shown that higher doses of this compound result in more significant reductions in viral replication and improved treatment outcomes . At very high doses, this compound may exhibit toxic or adverse effects, such as hepatotoxicity. It is essential to determine the optimal dosage that maximizes antiviral efficacy while minimizing potential side effects .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4, with minor contributions from CYP2C8 and CYP2C19 . The metabolic pathways of this compound involve its conversion into various metabolites, which are then excreted from the body. The compound’s interaction with these enzymes can affect metabolic flux and metabolite levels, influencing its overall efficacy and safety profile .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through specific transporters and binding proteins. The compound is taken up into hepatocytes via organic anion-transporting polypeptides OATP1B1 and OATP1B3, where it accumulates and exerts its antiviral effects . This compound’s localization within hepatocytes is crucial for its activity, as it needs to reach the NS3/4A protease to inhibit viral replication effectively .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound is primarily within the cytoplasm of hepatocytes, where it interacts with the NS3/4A protease . The compound’s activity and function are influenced by its localization, as it needs to be in proximity to the viral protease to exert its inhibitory effects. Post-translational modifications and targeting signals may also play a role in directing this compound to specific compartments within the cell .
Métodos De Preparación
La preparación de TMC435 implica varias rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción. Uno de los intermediarios clave en la síntesis es una lactona amida bicíclica. El método de preparación para este intermediario implica múltiples pasos, incluida la formación de un compuesto macrocíclico . La producción industrial de TMC435 generalmente implica la cristalización del compuesto para obtener una forma estable y pura adecuada para uso farmacéutico .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
TMC435 sufre varias reacciones químicas, incluida la oxidación, la reducción y la sustitución. Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen solventes orgánicos, ácidos y bases. Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones son típicamente derivados del compuesto original, que pueden tener diferentes propiedades farmacológicas .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
TMC435 es similar a otros inhibidores de la proteasa NS3/4A del virus de la hepatitis C, como telaprevir y boceprevir. TMC435 tiene varias características únicas que lo distinguen de estos compuestos. Por ejemplo, TMC435 tiene un perfil de resistencia más favorable y es efectivo contra una gama más amplia de genotipos del virus de la hepatitis C. Además, se ha demostrado que TMC435 tiene un mejor perfil de seguridad y tolerabilidad en comparación con otros inhibidores de la proteasa .
Compuestos similares
- Telaprevir
- Boceprevir
- Grazoprevir
- Paritaprevir
Propiedades
Número CAS |
923604-59-5 |
|---|---|
Fórmula molecular |
C38H47N5O7S2 |
Peso molecular |
749.9 g/mol |
Nombre IUPAC |
(4S)-N-cyclopropylsulfonyl-17-[7-methoxy-8-methyl-2-(4-propan-2-yl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)quinolin-4-yl]oxy-13-methyl-2,14-dioxo-3,13-diazatricyclo[13.3.0.04,6]octadec-7-ene-4-carboxamide |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C38H47N5O7S2/c1-21(2)30-20-51-35(40-30)29-18-32(26-13-14-31(49-5)22(3)33(26)39-29)50-24-16-27-28(17-24)36(45)43(4)15-9-7-6-8-10-23-19-38(23,41-34(27)44)37(46)42-52(47,48)25-11-12-25/h8,10,13-14,18,20-21,23-25,27-28H,6-7,9,11-12,15-17,19H2,1-5H3,(H,41,44)(H,42,46)/t23?,24?,27?,28?,38-/m0/s1 |
Clave InChI |
JTZZSQYMACOLNN-ZMKZURCUSA-N |
SMILES |
CC1=C(C=CC2=C1N=C(C=C2OC3CC4C(C3)C(=O)N(CCCCC=CC5CC5(NC4=O)C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C6CC6)C)C7=NC(=CS7)C(C)C)OC |
SMILES isomérico |
CC1=C(C=CC2=C1N=C(C=C2OC3CC4C(C3)C(=O)N(CCCCC=CC5C[C@@]5(NC4=O)C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C6CC6)C)C7=NC(=CS7)C(C)C)OC |
SMILES canónico |
CC1=C(C=CC2=C1N=C(C=C2OC3CC4C(C3)C(=O)N(CCCCC=CC5CC5(NC4=O)C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C6CC6)C)C7=NC(=CS7)C(C)C)OC |
Color/Form |
White to almost white powder |
Pictogramas |
Irritant; Environmental Hazard |
Solubilidad |
Insoluble Practically insoluble in water over a wide pH range Practically insoluble in propylene glycol; very slightly soluble in ethanol; slightly soluble in acetone. Soluble in dichloromethane; freely soluble in some organic solvents |
Sinónimos |
435, TMC 435350, TMC N-(17-(2-(4-isopropylthiazole-2-yl)-7-methoxy-8-methylquinolin-4-yloxy)-13-methyl-2,14-dioxo-3,13-diazatricyclo(13.3.0.04,6)octadec-7-ene-4-carbonyl)(cyclopropyl)sulfonamide Olysio simeprevir TMC 435 TMC 435350 TMC-435 TMC-435350 TMC435 TMC435350 |
Presión de vapor |
5.9X10-27 mm Hg at 25 °C (est) |
Origen del producto |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















