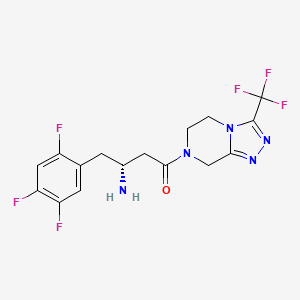
Sitagliptine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
- Notamment, la sitagliptin présente l'avantage d'avoir de bons profils de sécurité, de faibles taux d'hypoglycémie et un gain de poids minime .
Sitagliptin: appartient à la classe des inhibiteurs de la dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Il peut être utilisé seul ou en association avec d'autres médicaments antidiabétiques oraux pour gérer le diabète de type 2.
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Sitagliptin primarily targets the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme . DPP-4 is responsible for the inactivation of incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis .
Mode of Action
Sitagliptin works by inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme, which leads to increased levels of active incretin hormones, GLP-1 and GIP . The effect of this medication leads to glucose-dependent increases in insulin and decreases in glucagon, thereby improving control of blood sugar .
Biochemical Pathways
By inhibiting DPP-4, sitagliptin slows the inactivation of incretins like GLP-1 and GIP . Incretins are released throughout the day and are upregulated in response to meals as part of glucose homeostasis . This results in an increase in insulin secretion and a decrease in glucagon levels in a glucose-dependent manner .
Pharmacokinetics
Sitagliptin has a bioavailability of 87% and is primarily excreted by the kidneys . The apparent terminal half-life of single-dose sitagliptin 100mg in healthy volunteers was 12.4 hours, with renal clearance of ≈350 mL/min . These properties support a once-daily dosing regimen .
Result of Action
Sitagliptin’s action results in improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus . It has been found to promote insulin secretion, inhibit islet β cell apoptosis, and reduce blood glucose levels . Other pharmacological mechanisms, such as improving insulin resistance, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-fibrosis, are still being explored .
Action Environment
Sitagliptin’s action, efficacy, and stability can be influenced by environmental factors. For instance, it is known that no differences in safety and efficacy were observed in geriatric patients compared to younger patients, however caution should be used in this population as they are more likely to have reduced renal function .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Chemistry: Researchers study sitagliptin’s reactivity, stability, and interactions with other compounds.
Biology: In biological research, sitagliptin’s effects on glucose metabolism, insulin secretion, and pancreatic function are investigated.
Medicine: Clinical trials explore its efficacy in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications associated with diabetes.
Industry: Pharmaceutical companies utilize sitagliptin in the development of antidiabetic medications.
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Sitagliptin plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). This inhibition prevents the degradation of incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). By maintaining higher levels of these hormones, sitagliptin enhances insulin secretion and suppresses glucagon release, thereby improving glycemic control .
Cellular Effects
Sitagliptin affects various types of cells and cellular processes. In pancreatic beta cells, it enhances insulin secretion in response to meals, while in alpha cells, it suppresses glucagon release. This dual action helps to regulate blood glucose levels more effectively. Additionally, sitagliptin has been shown to improve beta-cell function and survival, which is crucial for long-term diabetes management .
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, sitagliptin exerts its effects by binding to and inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme. This inhibition prevents the breakdown of incretin hormones, leading to increased levels of GLP-1 and GIP. These hormones then bind to their respective receptors on pancreatic cells, triggering a cascade of signaling pathways that result in increased insulin secretion and decreased glucagon release .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of sitagliptin have been observed to change over time. Studies have shown that sitagliptin remains stable and effective over extended periods, with consistent improvements in glycemic control observed in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Long-term use of sitagliptin has been associated with sustained improvements in HbA1c levels and beta-cell function .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of sitagliptin vary with different dosages. Low to moderate doses of sitagliptin have been shown to improve glycemic control without significant adverse effects. At higher doses, some toxic effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances and renal impairment, have been observed. These findings highlight the importance of optimizing dosage to balance efficacy and safety .
Metabolic Pathways
Sitagliptin is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine, with minimal metabolism occurring in the liver. The minor metabolic pathways involve cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP3A4 and CYP2C8. These pathways result in the formation of inactive metabolites, which are then excreted in the urine and feces .
Transport and Distribution
Sitagliptin is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. It is a substrate for p-glycoprotein, which facilitates its transport across cell membranes. Additionally, sitagliptin has been shown to enhance the translocation of glucose transporter-4 (Glut4) to the cell membrane, improving glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissues .
Subcellular Localization
Sitagliptin’s subcellular localization is primarily within the cytoplasm, where it interacts with the DPP-4 enzyme. This interaction prevents the degradation of incretin hormones, allowing them to exert their effects on insulin and glucagon secretion. The localization of sitagliptin within the cytoplasm is crucial for its inhibitory action on DPP-4 and subsequent regulation of blood glucose levels .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse: La sitagliptin est synthétisée en plusieurs étapes chimiques. Une voie de synthèse courante implique la condensation d'un dérivé d'acide aminé (3-amino-1-adamantanol) avec un dérivé de cyanoacétyle (cyanoguanidine). Cette réaction donne la structure de base de la sitagliptin.
Production industrielle: La production industrielle de la sitagliptin implique une synthèse à grande échelle utilisant des conditions optimisées. Le processus comprend généralement des étapes de purification pour obtenir de la sitagliptin de haute pureté à usage pharmaceutique.
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Réactivité: La sitagliptin subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment des réactions d'oxydation, de réduction et de substitution.
Réactifs et conditions courants: Les réactifs et les conditions spécifiques dépendent de la transformation souhaitée. Par exemple
Produits majeurs: Les principaux produits formés au cours de ces réactions comprennent des intermédiaires et des dérivés finaux de la sitagliptin.
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Chimie: Les chercheurs étudient la réactivité, la stabilité et les interactions de la sitagliptin avec d'autres composés.
Biologie: En recherche biologique, les effets de la sitagliptin sur le métabolisme du glucose, la sécrétion d'insuline et la fonction pancréatique sont étudiés.
Médecine: Des essais cliniques explorent son efficacité dans la gestion des taux de sucre dans le sang et la prévention des complications associées au diabète.
Industrie: Les sociétés pharmaceutiques utilisent la sitagliptin dans le développement de médicaments antidiabétiques.
Mécanisme d'action
Inhibition de la DPP-4: La sitagliptin inhibe la DPP-4, une enzyme qui dégrade rapidement les hormones incrétines telles que le peptide-1 de type glucagon (GLP-1) et le peptide insulinotopique dépendant du glucose (GIP).
Augmentation du GLP-1 et du GIP: En inhibant la DPP-4, la sitagliptin augmente les niveaux de GLP-1 et de GIP actifs. Ces hormones améliorent la libération d'insuline et réduisent la sécrétion de glucagon d'une manière dépendante du glucose.
Effets cliniques: Chez les patients atteints de diabète de type 2, la sitagliptin diminue l'HbA1c, la glycémie à jeun et la glycémie postprandiale.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Unicité: La sitagliptin est unique en tant que premier inhibiteur de la DPP-4 utilisé pour le traitement du diabète de type 2.
Composés similaires: D'autres inhibiteurs de la DPP-4 comprennent la vildagliptine, la saxagliptine et la linagliptine.
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(3R)-3-amino-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-6,8-dihydro-5H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H15F6N5O/c17-10-6-12(19)11(18)4-8(10)3-9(23)5-14(28)26-1-2-27-13(7-26)24-25-15(27)16(20,21)22/h4,6,9H,1-3,5,7,23H2/t9-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MFFMDFFZMYYVKS-SECBINFHSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN2C(=NN=C2C(F)(F)F)CN1C(=O)CC(CC3=CC(=C(C=C3F)F)F)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CN2C(=NN=C2C(F)(F)F)CN1C(=O)C[C@@H](CC3=CC(=C(C=C3F)F)F)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H15F6N5O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID70197572 | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70197572 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
407.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
3.40e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibition of DPP-4 by sitagliptin slows DPP-4 mediated inactivation of incretins like GLP-1 and GIP. Incretins are released throughout the day and upregulated in response to meals as part of glucose homeostasis. Reduced inhibition of incretins increase insulin synthesis and decrease glucagon release in a manner dependant on glucose concentrations. These effects lead to an overall increase in blood glucose control which is demonstrated by reduced glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)., Januvia is a member of a class of oral anti-hyperglycemic agents called dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The improvement in glycemic control observed with this medicinal product may be mediated by enhancing the levels of active incretin hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. Treatment with GLP-1 or with DPP-4 inhibitors in animal models of type 2 diabetes has been demonstrated to improve beta cell responsiveness to glucose and stimulate insulin biosynthesis and release. With higher insulin levels, tissue glucose uptake is enhanced. In addition, GLP-1 lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells. Decreased glucagon concentrations, along with higher insulin levels, lead to reduced hepatic glucose production, resulting in a decrease in blood glucose levels. The effects of GLP-1 and GIP are glucose-dependent such that when blood glucose concentrations are low, stimulation of insulin release and suppression of glucagon secretion by GLP-1 are not observed. For both GLP-1 and GIP, stimulation of insulin release is enhanced as glucose rises above normal concentrations. Further, GLP-1 does not impair the normal glucagon response to hypoglycemia. The activity of GLP-1 and GIP is limited by the DPP-4 enzyme, which rapidly hydrolyzes the incretin hormones to produce inactive products. Sitagliptin prevents the hydrolysis of incretin hormones by DPP-4, thereby increasing plasma concentrations of the active forms of GLP-1 and GIP. By enhancing active incretin levels, sitagliptin increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in a glucose-dependent manner. In patients with type 2 diabetes with hyperglycemia, these changes in insulin and glucagon levels lead to lower hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and lower fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations. The glucose-dependent mechanism of sitagliptin is distinct from the mechanism of sulfonylureas, which increase insulin secretion even when glucose levels are low and can lead to hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and in normal subjects. Sitagliptin is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the enzyme DPP-4 and does not inhibit the closely-related enzymes DPP-8 or DPP-9 at therapeutic concentrations., Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor, which is believed to exert its actions in patients with type 2 diabetes by slowing the inactivation of incretin hormones. Concentrations of the active intact hormones are increased by Januvia, thereby increasing and prolonging the action of these hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. These hormones are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme, DPP-4. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, leading to reduced hepatic glucose production. By increasing and prolonging active incretin levels, Januvia increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in the circulation in a glucose-dependent manner. Sitagliptin demonstrates selectivity for DPP-4 and does not inhibit DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating those from therapeutic doses. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01261 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7516 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Viscous liquid | |
CAS No. |
486460-32-6 | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=486460-32-6 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0486460326 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01261 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70197572 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (3R)-3-amino-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.217.948 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/QFP0P1DV7Z | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7516 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details











Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
![1-(4-{13-Chloro-4-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(15),3,5,7,11,13-hexaen-2-yl}piperazin-1-yl)ethan-1-one](/img/structure/B1680906.png)
![(6aR,13bS)-11-chloro-6,6a,7,8,9,13b-hexahydro-5H-naphtho[1,2-a][3]benzazepin-12-ol](/img/structure/B1680907.png)
![4-[4-[4-[4-[[(3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-pentan-3-yl-1,2,4-triazol-3-one](/img/structure/B1680909.png)
![2-[2-[(6-methoxy-3-methyl-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]quinolin-4-yl)amino]ethoxy]ethanol](/img/structure/B1680910.png)
![7H-Pyrrolo[3,2-f]quinazoline-1,3-diamine, N3-cyclopropyl-7-[[4-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]methyl]-](/img/structure/B1680918.png)
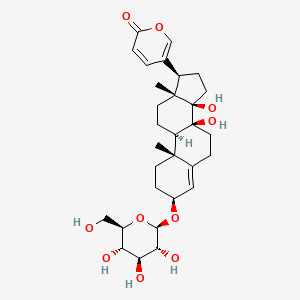
![5-[(3S,8R,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-3-[3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-14-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,3,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pyran-2-one](/img/structure/B1680924.png)