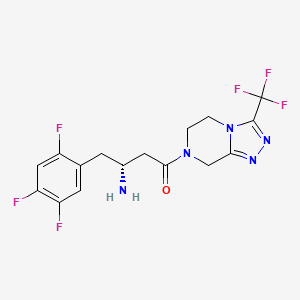
Sitagliptin
Descripción general
Descripción
- Cabe destacar que la sitagliptina tiene la ventaja de tener buenos perfiles de seguridad, bajas tasas de hipoglucemia y un aumento mínimo de peso .
Sitagliptina: pertenece a la clase de los inhibidores de la dipeptidil peptidasa-4 (DPP-4). Se puede utilizar solo o en combinación con otros fármacos antidiabéticos orales para controlar la diabetes tipo 2.
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas: La sitagliptina se sintetiza a través de varias etapas químicas. Una ruta sintética común implica la condensación de un derivado de aminoácido (3-amino-1-adamantanol) con un derivado cianoacetilo (cianoguanidina). Esta reacción produce la estructura central de la sitagliptina.
Producción industrial: La producción industrial de sitagliptina implica la síntesis a gran escala utilizando condiciones optimizadas. El proceso suele incluir pasos de purificación para obtener sitagliptina de alta pureza para uso farmacéutico.
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Reactividad: La sitagliptina sufre varias reacciones químicas, incluidas reacciones de oxidación, reducción y sustitución.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes: Los reactivos y condiciones específicos dependen de la transformación deseada. Por ejemplo
Productos principales: Los productos principales formados durante estas reacciones incluyen intermedios y derivados finales de la sitagliptina.
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Sitagliptin enhances glycemic control by increasing incretin levels, which leads to improved insulin secretion and reduced glucagon levels. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in lowering fasting plasma glucose and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels.
Clinical Trial Findings
- A study involving older adults showed significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose (−27.2 mg/dL) and HbA1c (−0.61%) after 12 months of this compound treatment compared to control groups .
- In another trial, this compound combined with metformin resulted in better glycemic control than either agent alone .
| Study | Population | Duration | HbA1c Reduction | FPG Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Older adults (≥70 years) | 12 months | −0.61% | −27.2 mg/dL | |
| Type 2 diabetes patients | Varies | Significant improvement vs. monotherapy | Not specified |
Cardiovascular Safety
The cardiovascular safety profile of this compound has been extensively studied, particularly through the TECOS trial, which assessed cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes patients.
Key Findings from TECOS Trial
- This compound was found to be non-inferior to placebo concerning major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), with no significant increase in hospitalization for heart failure or all-cause mortality .
- The trial involved over 14,000 patients and concluded that this compound does not adversely affect cardiovascular health .
Renal Function Impact
This compound's effects on renal function have also been a focus of research, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal conditions.
Research Insights
- A study indicated that while there was a slight reduction in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), it was comparable between this compound and placebo groups over a 48-month period .
- Another investigation highlighted that this compound could be safely used in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment, making it a versatile option for managing diabetes in this population .
Applications Beyond Diabetes Management
Emerging research suggests potential applications of this compound beyond glycemic control:
- Weight Management : Studies indicate that this compound may contribute to weight neutrality or modest weight loss, which is beneficial for overweight patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Combination Therapy : this compound is often used in combination with other antidiabetic agents to enhance overall treatment efficacy. For instance, its combination with metformin has shown synergistic effects on glycemic control .
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
Several case studies have documented the real-world effectiveness of this compound:
- A case involving an elderly patient with multiple comorbidities demonstrated significant improvements in glycemic control without serious adverse effects after initiating this compound therapy.
- Another case highlighted the successful use of this compound in a patient with type 2 diabetes who experienced intolerable side effects from other medications, showcasing its tolerability profile.
Mecanismo De Acción
Inhibición de la DPP-4: La sitagliptina inhibe la DPP-4, una enzima que degrada rápidamente las hormonas incretinas, como el péptido similar al glucagón-1 (GLP-1) y el péptido insulinotrópico dependiente de la glucosa (GIP).
Aumento del GLP-1 y el GIP: Al inhibir la DPP-4, la sitagliptina aumenta los niveles de GLP-1 y GIP activos. Estas hormonas potencian la liberación de insulina y reducen la secreción de glucagón de forma dependiente de la glucosa.
Efectos clínicos: En pacientes con diabetes tipo 2, la sitagliptina reduce los niveles de HbA1c, glucosa en ayunas y glucosa posprandial.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Singularidad: La sitagliptina es única al ser el primer inhibidor de la DPP-4 utilizado para el tratamiento de la diabetes tipo 2.
Compuestos similares: Otros inhibidores de la DPP-4 incluyen vildagliptina, saxagliptina y linagliptina.
Actividad Biológica
Sitagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor widely used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its primary mechanism involves the inhibition of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades incretin hormones, thereby enhancing the levels of active glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP). This article explores the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its effects on glucose metabolism, beta-cell function, and its broader implications in diabetes management.
This compound's primary action is to increase the levels of incretin hormones, which play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis. By inhibiting DPP-4, this compound leads to:
- Increased GLP-1 and GIP Levels : this compound enhances the secretion of GLP-1 and GIP, which stimulate insulin release in response to meals and suppress glucagon secretion .
- Improved Beta-Cell Function : Studies indicate that this compound may enhance beta-cell function and mass in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Animal models have shown that treatment with this compound analogs resulted in increased insulin-positive cells and improved glycemic control .
Clinical Efficacy
Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of this compound in reducing blood glucose levels and improving glycemic control. Key findings include:
Direct Effects on Intestinal L Cells
Recent research has uncovered DPP-IV-independent effects of this compound on intestinal L cells. This compound has been shown to activate cAMP and ERK1/2 signaling pathways, leading to increased GLP-1 secretion from these cells. In vitro studies using murine GLUTag and human hNCI-H716 cells revealed that this compound significantly stimulated GLP-1 secretion without feedback inhibition from GLP-1 itself .
Safety Profile
This compound is generally well-tolerated among patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse effects, with no significant hypoglycemic events when used as directed. The long-term safety profile continues to be assessed through ongoing clinical trials.
Case Studies
- Case Study on Cardiovascular Safety : A pooled analysis of 20 clinical trials involving saxagliptin (a related DPP-4 inhibitor) indicated no increased risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) when compared to placebo or other treatments . This finding supports the cardiovascular safety profile of DPP-4 inhibitors like this compound.
- Beta Cell Function Improvement : In a study evaluating the effects of this compound versus sulfonylurea intensification, results showed that patients receiving this compound had better preservation of beta-cell function over time compared to those receiving traditional therapies .
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What experimental design considerations are critical for evaluating Sitagliptin's cardiovascular safety in randomized controlled trials (RCTs)?
- Methodological Answer : Non-inferiority trials with large sample sizes (e.g., >14,000 participants) are essential, using composite endpoints like cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or unstable angina hospitalization. Key parameters include:
- Non-inferiority margin : A relative risk threshold (e.g., ≤1.3) .
- Glycemic control monitoring : Track HbA1c differences (e.g., -0.29% vs. placebo) to isolate cardiovascular effects from glucose-lowering benefits .
- Longitudinal follow-up : Median 3-year follow-up ensures detection of delayed cardiovascular outcomes .
Q. How do researchers address conflicting results between preclinical models and clinical trial data for this compound's efficacy?
- Methodological Answer : Validate predictive models using standardized tools like the ISPOR-AMCP-NPC questionnaire to identify discrepancies in assumptions (e.g., QALY rankings or cardiovascular risk projections). For example:
- Model comparison : CDC/RTI and ARCHeS models showed divergent QALY rankings for this compound vs. exenatide due to differing data inputs and discount rates .
- Sensitivity analysis : Test model robustness by varying parameters like cardiovascular event incidence (49.8% vs. 44.7% across models) .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can researchers reconcile discrepancies in cardiovascular risk predictions between observational studies and RCTs for this compound?
- Methodological Answer : Apply the UKPDS Risk Engine in real-world observational studies to standardize risk estimation. Key steps include:
- Covariate adjustment : Use ANCOVA to control for baseline differences (e.g., HbA1c, age) .
- Long-term risk evolution : Track risk reductions over ≥48 months, with statistical validation via t-tests (e.g., p<0.0001 for gender differences) .
- Log-transformation : Normalize skewed risk factor distributions (e.g., log10 transformation of UKPDS risk scores) .
Q. What statistical approaches are optimal for analyzing this compound's heterogeneous effects in subpopulations (e.g., T1D with nephropathy)?
- Methodological Answer : Stratify analyses using parametric/non-parametric tests based on data distribution:
- Normality testing : Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to determine appropriate statistical methods (e.g., paired t-tests vs. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests) .
- Covariate-adjusted models : Use ANCOVA to isolate treatment effects from confounders like baseline HbA1c .
Q. How should researchers design studies to assess this compound's pancreatic safety profile given contradictory preclinical signals?
- Methodological Answer : Pooled safety analyses from phase 2B/3 trials with standardized adverse event (AE) reporting:
- AE harmonization : Compare pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer rates using Fisher’s exact test (e.g., p=0.07 for pancreatitis) .
- Post-hoc adjustments : Control for exposure duration and concomitant medications (e.g., metformin or sulfonylureas) .
Q. Data Analysis & Interpretation
Q. What methods resolve contradictions in this compound's cost-effectiveness across health economic models?
- Methodological Answer : Conduct cross-model validation using domain-specific questionnaires (e.g., ISPOR-AMCP-NPC) to identify methodological divergences:
- Parameter alignment : Compare discount rates (e.g., 3% vs. 5%) and time horizons (e.g., 15-year projections) .
- Scenario testing : Rank-order therapies under varying assumptions (e.g., QALY differences between this compound and glyburide) .
Q. How can meta-analyses address heterogeneity in this compound's glycemic outcomes across trials?
- Methodological Answer : Use random-effects models to account for variability in study populations and designs:
- Subgroup analysis : Stratify by diabetes duration, baseline HbA1c, or comedications (e.g., metformin vs. sulfonylureas) .
- Publication bias assessment : Funnel plots and Egger’s regression to detect selective reporting .
Q. Research Ethics & Reporting
Q. What guidelines ensure reproducibility of this compound pharmacokinetic studies?
- Methodological Answer : Adhere to journal-specific protocols for experimental reporting:
- Detailed synthesis : Provide full characterization data for reference standards (e.g., Oxo this compound’s regulatory-compliant profiles) .
- Data transparency : Deposit raw datasets in repositories like Dryad or Figshare, with metadata on analytical conditions .
Q. How should researchers frame hypotheses to avoid commercial bias in this compound studies?
- Methodological Answer : Formulate PICOT-structured questions emphasizing mechanistic or comparative outcomes:
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(3R)-3-amino-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-6,8-dihydro-5H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H15F6N5O/c17-10-6-12(19)11(18)4-8(10)3-9(23)5-14(28)26-1-2-27-13(7-26)24-25-15(27)16(20,21)22/h4,6,9H,1-3,5,7,23H2/t9-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MFFMDFFZMYYVKS-SECBINFHSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN2C(=NN=C2C(F)(F)F)CN1C(=O)CC(CC3=CC(=C(C=C3F)F)F)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CN2C(=NN=C2C(F)(F)F)CN1C(=O)C[C@@H](CC3=CC(=C(C=C3F)F)F)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H15F6N5O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID70197572 | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70197572 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
407.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
3.40e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibition of DPP-4 by sitagliptin slows DPP-4 mediated inactivation of incretins like GLP-1 and GIP. Incretins are released throughout the day and upregulated in response to meals as part of glucose homeostasis. Reduced inhibition of incretins increase insulin synthesis and decrease glucagon release in a manner dependant on glucose concentrations. These effects lead to an overall increase in blood glucose control which is demonstrated by reduced glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)., Januvia is a member of a class of oral anti-hyperglycemic agents called dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The improvement in glycemic control observed with this medicinal product may be mediated by enhancing the levels of active incretin hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. Treatment with GLP-1 or with DPP-4 inhibitors in animal models of type 2 diabetes has been demonstrated to improve beta cell responsiveness to glucose and stimulate insulin biosynthesis and release. With higher insulin levels, tissue glucose uptake is enhanced. In addition, GLP-1 lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells. Decreased glucagon concentrations, along with higher insulin levels, lead to reduced hepatic glucose production, resulting in a decrease in blood glucose levels. The effects of GLP-1 and GIP are glucose-dependent such that when blood glucose concentrations are low, stimulation of insulin release and suppression of glucagon secretion by GLP-1 are not observed. For both GLP-1 and GIP, stimulation of insulin release is enhanced as glucose rises above normal concentrations. Further, GLP-1 does not impair the normal glucagon response to hypoglycemia. The activity of GLP-1 and GIP is limited by the DPP-4 enzyme, which rapidly hydrolyzes the incretin hormones to produce inactive products. Sitagliptin prevents the hydrolysis of incretin hormones by DPP-4, thereby increasing plasma concentrations of the active forms of GLP-1 and GIP. By enhancing active incretin levels, sitagliptin increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in a glucose-dependent manner. In patients with type 2 diabetes with hyperglycemia, these changes in insulin and glucagon levels lead to lower hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and lower fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations. The glucose-dependent mechanism of sitagliptin is distinct from the mechanism of sulfonylureas, which increase insulin secretion even when glucose levels are low and can lead to hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and in normal subjects. Sitagliptin is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the enzyme DPP-4 and does not inhibit the closely-related enzymes DPP-8 or DPP-9 at therapeutic concentrations., Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor, which is believed to exert its actions in patients with type 2 diabetes by slowing the inactivation of incretin hormones. Concentrations of the active intact hormones are increased by Januvia, thereby increasing and prolonging the action of these hormones. Incretin hormones, including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. These hormones are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme, DPP-4. The incretins are part of an endogenous system involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin synthesis and release from pancreatic beta cells by intracellular signaling pathways involving cyclic AMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, leading to reduced hepatic glucose production. By increasing and prolonging active incretin levels, Januvia increases insulin release and decreases glucagon levels in the circulation in a glucose-dependent manner. Sitagliptin demonstrates selectivity for DPP-4 and does not inhibit DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating those from therapeutic doses. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01261 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7516 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Viscous liquid | |
CAS No. |
486460-32-6 | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=486460-32-6 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0486460326 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01261 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70197572 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (3R)-3-amino-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.217.948 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/QFP0P1DV7Z | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | SITAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7516 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sitagliptin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015390 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details











Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













