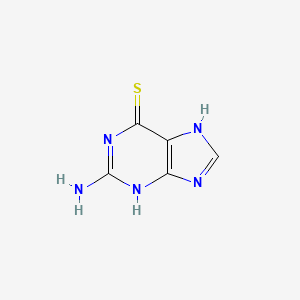
6-Thioguanine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
6-Thioguanine primarily targets the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) . This enzyme plays a crucial role in the purine salvage pathway, which is essential for DNA and RNA synthesis. Additionally, this compound has been found to inhibit the human deubiquitinating protease USP2 , which plays a critical role in tumor cell survival .
Mode of Action
This compound competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for HGPRTase and is converted into 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP) . TGMP reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses . The TGMP, along with its diphosphate (TGDP) and triphosphate (TGTP) forms, are collectively named This compound nucleotides (6-TGN) . These 6-TGNs are cytotoxic to cells by incorporating into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell cycle and inhibiting the GTP-binding protein (G protein) Rac1, which regulates the Rac/Vav pathway .
Biochemical Pathways
The biochemical pathways affected by this compound primarily involve the purine salvage pathway and the Rac/Vav pathway . The incorporation of 6-TGN into DNA disrupts normal DNA synthesis and function, leading to cell death. The inhibition of the G protein Rac1 disrupts the Rac/Vav pathway, further contributing to the cytotoxic effects of this compound .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is administered orally and has a bioavailability of 30% (range 14% to 46%) . It is metabolized intracellularly, and its elimination half-life is approximately 80 minutes (range 25–240 minutes) . The drug is excreted in urine .
Result of Action
The primary result of this compound’s action is the induction of cell death in rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells . This is achieved through the disruption of DNA synthesis and function, as well as the inhibition of the Rac/Vav pathway . These actions make this compound effective in the treatment of various forms of leukemia .
Action Environment
The action of this compound can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the deamination reaction of this compound has been found to be more feasible in the presence of an additional water molecule . Additionally, the drug’s efficacy can be affected by the pH of the stomach, as it is expected that the entire dosages of thioguanine can be dissolved rapidly in the gastric fluids due to the low pH (~ pH 1–2) . Furthermore, the drug’s action can be influenced by genetic factors, as people with a genetic deficiency in thiopurine S-methyltransferase are at higher risk of side effects .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Pharmacological Profile
Mechanism of Action
6-Thioguanine functions as an antimetabolite, primarily inhibiting DNA synthesis by incorporating into nucleic acids, particularly DNA. This incorporation disrupts the replication process, leading to cell death in rapidly dividing tumor cells. Evidence indicates that 6-TG is more effective in younger, rapidly growing tumor populations compared to older ones, highlighting the importance of timing in treatment regimens .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of 6-TG have been extensively studied. It is metabolized by guanase and xanthine oxidase, with higher blood levels observed post-intravenous administration compared to oral dosing. Studies show that repeated doses lead to significant incorporation of 6-TG into DNA, particularly in bone marrow cells .
Clinical Applications
Cancer Treatment
this compound has been utilized in various types of cancer, particularly hematological malignancies such as acute leukemia and lymphomas. Its efficacy has been noted in patients with specific genetic profiles, particularly those with homozygous deletions of the methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) gene. These tumors are often resistant to other therapies but may respond favorably to 6-TG when combined with methylthioadenosine (MTA), which protects normal tissues from toxicity while allowing higher doses of 6-TG .
Case Study: Leukemia Treatment
A retrospective study involving 30 patients with Crohn's Disease who failed conventional immunosuppression demonstrated the efficacy of 6-TG as a third-line treatment. The median dose was 40 mg daily over 21.5 months, with an initial clinical response in 60% of patients . This study underscores the drug's potential beyond oncology into inflammatory conditions.
Combination Therapies
Research suggests that combining this compound with other agents can enhance its therapeutic effects. For instance, combinations with methotrexate or pralatrexate have shown promising results against MTAP-deficient tumors. The synergistic effects observed in xenograft models indicate a potential for developing more effective treatment protocols .
Safety and Toxicity
While 6-TG is effective, it is not without risks. Hepatotoxicity remains a concern, particularly in long-term use. In the previously mentioned study on Crohn's Disease patients, some experienced abnormal liver function tests during treatment; however, these were mostly mild and transient . Monitoring liver function during therapy is crucial for patient safety.
Summary Table of Applications
| Application Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Cancer Types | Acute leukemia, lymphomas, solid tumors (e.g., mesothelioma, melanoma) |
| Mechanism | Incorporation into DNA/RNA leading to growth arrest and apoptosis |
| Combination Potential | Enhanced effects when used with MTA or other chemotherapeutics |
| Safety Concerns | Hepatotoxicity; requires monitoring during treatment |
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
6-Thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and is itself converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP), which reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses . It is ribosylated and phosphorylated by the same pathway as natural purine bases .
Cellular Effects
This compound has been shown to have cytotoxic effects on cells. It is incorporated into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell cycle, stopping normal development and division . It also inhibits the GTP-binding protein (G protein) Rac1, which regulates the Rac/Vav pathway .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its conversion to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP) via the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase). TGMP is then further metabolized to form this compound nucleotides (6-TGN). These 6-TGN are cytotoxic to cells by incorporation into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell and through inhibition of the GTP-binding protein (G protein) Rac1 .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of this compound in laboratory settings can vary over time. For instance, a study showed that mean this compound nucleotide levels were higher among patients in clinical remission, with a pooled difference of 63.37 pmol/8 × 10 8 red blood cells .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of this compound can vary with different dosages. A study demonstrated the efficacy of low dose this compound treatment on low-mutation melanoma in a pre-clinical mouse model .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is catabolized via two pathways. One route is through the deamination by the enzyme guanine deaminase to 6-thioxanthine, which has minimal anti-neoplastic activity, then by oxidation by xanthine oxidase of the thioxanthine to thiouric acid .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It is converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP) by the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound involves its incorporation into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell cycle . This suggests that this compound is localized in the nucleus where DNA replication occurs.
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies synthétiques et conditions réactionnelles
Tioguanine peut être synthétisée en utilisant la 2,9-diacétyl guanine ou la 2-acétyl guanine comme matières de départ. La réaction implique la sulfuration de ces composés avec du pentasulfure de phosphore dans une solution de pyridine, avec un léger catalyseur . Cette méthode offre des conditions de réaction douces, une opération simple et un rendement élevé pouvant atteindre 75 % .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle de la tioguanine suit des voies synthétiques similaires, mais à plus grande échelle. Le procédé implique l'utilisation d'anhydride thiophosphorique et de solution de pyridine, avec un contrôle minutieux des conditions réactionnelles pour assurer un rendement élevé et une pureté .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
Tioguanine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Désamination : La réaction de désamination de la tioguanine avec l'eau, les ions hydroxydes et les formes protonées a été étudiée de manière approfondie.
Oxydation : Tioguanine peut être oxydée pour former des métabolites toxiques, contribuant à ses effets cytotoxiques.
Réactifs et conditions communs
Désamination : Les ions hydroxydes et l'eau sont des réactifs courants utilisés dans la désamination de la tioguanine.
Principaux produits formés
Désamination : La désamination de la tioguanine conduit à la formation de divers intermédiaires et produits, selon les conditions réactionnelles.
Oxydation : L'oxydation de la tioguanine conduit à la formation de métabolites toxiques qui peuvent être incorporés dans l'ADN.
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Tioguanine a plusieurs applications de recherche scientifique, notamment :
Médecine : Principalement utilisé dans le traitement de diverses formes de leucémie.
Industrie : Utilisé dans le développement de nouveaux agents antinéoplasiques et d'autres composés thérapeutiques.
Mécanisme d'action
Tioguanine exerce ses effets en entrant en compétition avec l'hypoxanthine et la guanine pour l'enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransférase (HGPRTase). Elle est convertie en acide 6-thioguanilyique, qui atteint des concentrations intracellulaires élevées à des doses thérapeutiques . Le composé est incorporé dans l'ADN pendant la phase de synthèse, ce qui conduit à des effets cytotoxiques . De plus, la tioguanine inhibe la protéine de liaison au GTP Rac1, qui régule la voie Rac/Vav .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Tioguanine fait partie de la famille des thiopurines, qui comprend la mercaptopurine et l'azathioprine . Comparée à ces composés, la tioguanine a une efficacité plus élevée et une action plus rapide . son utilisation est limitée par des inquiétudes concernant l'hépatotoxicité et d'autres effets secondaires .
Composés similaires
Mercaptopurine : Un autre analogue de la purine utilisé dans le traitement de la leucémie et d'autres affections.
Azathioprine : Un prodrug de la mercaptopurine, utilisé comme immunosuppresseur dans la transplantation d'organes et les maladies auto-immunes.
Les propriétés uniques de la tioguanine, telles que son incorporation dans l'ADN et l'inhibition de voies moléculaires spécifiques, en font un composé précieux dans les milieux de recherche et cliniques .
Activité Biologique
6-Thioguanine (6-TG) is a purine analog that has been utilized in the treatment of various hematological malignancies, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Since its approval in the 1960s, research has expanded to explore its biological activity beyond oncology, revealing significant effects in conditions like diabetic retinopathy and psoriasis. This article delves into the biological activity of 6-TG, supported by case studies, data tables, and comprehensive research findings.
6-TG exerts its effects primarily through the inhibition of purine metabolism and DNA synthesis. It gets incorporated into DNA, replacing guanine, which leads to the disruption of DNA replication and ultimately induces apoptosis in rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells and activated lymphocytes. This mechanism is particularly relevant in the treatment of leukemias and autoimmune diseases.
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of DNA synthesis : 6-TG is metabolized to thioguanine nucleotides (TGNs), which interfere with DNA replication.
- Induction of apoptosis : Primarily observed in activated T lymphocytes, where it triggers programmed cell death.
- Immunosuppressive effects : Reduction in peripheral blood lymphocytes and total leukocyte counts.
1. Treatment of Psoriasis
A notable study involving 20 patients with moderate to severe plaque-type psoriasis demonstrated that 6-TG significantly improved disease severity. After six months of treatment:
- 12 patients were completely cleared of disease.
- 6 showed marked improvement .
- 2 did not respond .
Biopsy results indicated a reduction in keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation, correlating with clinical improvement. The therapy also led to a significant decrease in circulating lymphocytes by an average of 42% after two months .
2. Anti-Angiogenic Activity in Diabetic Retinopathy
Recent research highlighted the anti-angiogenic properties of 6-TG in diabetic retinopathy models. In vitro studies with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to high glucose levels showed:
- Marked reduction in tube formation at concentrations as low as 5 µM .
- In vivo studies demonstrated that diabetic mice treated with 6-TG exhibited reduced retinal vascular alterations, as confirmed by fluorescein angiography .
3. Efficacy in Leukemia Treatment
Comparative studies have shown that 6-TG is more effective than its counterpart, 6-mercaptopurine, particularly in reducing the risk of isolated central nervous system relapse. However, it carries a higher risk of severe adverse effects, including veno-occlusive disease .
Toxicity and Side Effects
While 6-TG has demonstrated efficacy across various conditions, its use is associated with several toxicities:
- Risk of infections due to immunosuppression.
- Development of liver complications such as veno-occlusive disease.
- Mutagenic potential leading to G→A mutations .
Summary Table: Clinical Findings
| Condition | Response Rate | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | 90% | Significant reduction in skin lesions |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | N/A | Reduced retinal vascular changes |
| Childhood Leukemia | N/A | Lower CNS relapse risk but higher mortality |
Research Findings
A variety of studies have investigated the pharmacokinetics and biological effects of 6-TG:
- Pharmacokinetics : Blood levels were higher post-intravenous administration compared to oral doses, indicating better bioavailability and incorporation into DNA .
- Mutagenicity Studies : Research indicated that both 6-TG and its metabolites are mutagenic in human cell lines, raising concerns about long-term use .
- Immunological Effects : A decrease in circulating leukocytes was noted alongside clinical improvements in autoimmune conditions .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
2-amino-3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C5H5N5S/c6-5-9-3-2(4(11)10-5)7-1-8-3/h1H,(H4,6,7,8,9,10,11) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WYWHKKSPHMUBEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=NC2=C(N1)C(=S)N=C(N2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C5H5N5S | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
5580-03-0 (hemihydrate), 76078-67-6 (mono-Na salt) | |
| Record name | Thioguanine [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000154427 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6023652 | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6023652 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
167.19 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
6-thioguanine appears as odorless or almost odorless pale yellow crystalline powder. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 1 mg/mL at 73 °F (NTP, 1992), INSOL IN WATER, ALCOHOL, CHLOROFORM; FREELY SOL IN DIL SOLUTIONS OF ALKALI HYDROXIDES, 8.34e-01 g/L, Readily soluble in dilute aqueous alkali. Insoluble in water, alcohol, or chloroform. | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | NCI Investigational Drugs | |
| URL | http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
| Description | An investigational drug is one that is under study but does not have permission from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be legally marketed and sold in the United States. NCI provides the investigational drug to the physicians who are participating in clinical trials or TRC protocols. For more information please visit NCI investigational drug website: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
Mechanism of Action |
Thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and is itself converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP), which reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses. TGMP interferes with the synthesis of guanine nucleotides by its inhibition of purine biosynthesis by pseudofeedback inhibition of glutamine-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase, the first enzyme unique to the de novo pathway of purine ribonucleotide synthesis. TGMP also inhibits the conversion of inosinic acid (IMP) to xanthylic acid (XMP) by competition for the enzyme IMP dehydrogenase. Thioguanine nucleotides are incorporated into both the DNA and the RNA by phosphodiester linkages, and some studies have shown that incorporation of such false bases contributes to the cytotoxicity of thioguanine. Its tumor inhibitory properties may be due to one or more of its effects on feedback inhibition of de novo purine synthesis; inhibition of purine nucleotide interconversions; or incorporation into the DNA and RNA. The overall result of its action is a sequential blockade of the utilization and synthesis of the purine nucleotides., THIOGUANINE, THE 6-THIO ANALOGUE OF GUANINE, IS A PRODRUG THAT IS CONVERTED TO 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE, AN ACTIVE METABOLITE. ... 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE IS A FEEDBACK INHIBITOR OF THE INITIAL (AMIDOTRANSFERASE) STEP IN PURINE BIOSYNTHESIS. THIS METABOLITE ALSO BLOCKS CONVERSIONS OF INOSINIC ACID TO GUANYLIC ACID & OF GUANYLIC ACID TO GDP. THIOGUANINE ALSO IS CONVERTED TO THE DEOXYNUCLEOTIDE TRIPHOSPHATE, WHICH CAN BE INCORPORATED INTO TUMOR CELL DNA. ALTHOUGH SOME INVESTIGATORS BELIEVE THAT THIS IS THE MAJOR MECHANISM OF CYTOTOXICITY, THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF THE VARIOUS SITES OF ACTION HAS NOT BEEN DETERMINED. ... THIOGUANINE IS CELL-CYCLE SPECIFIC FOR THE S PHASE., APPARENTLY, THE METABOLISM OF 6-THIOGUANINE TO 6-THIOGUANOSINE IN SARCOMA 180 & 180/TG CELLS IS MEDIATED BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE & NEWLY SYNTHESIZED 6-THIOGUANOSINE IS READILY EFFLUXED INTO THE CELLULAR ENVIRONMENT. THE FORMATION OF 6-THIOGUANINE, BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE, MAY BE IMPORTANT TO THE EXPRESSION OF CELLULAR SENSITIVITY TO 6-THIOGUANINE, IN THAT IT DECR THE AVAIL OF 6-THIOGUANINE FOR DIRECT CONVERSION BY HYPOXANTHINE-GUANINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE TO THE NUCLEOTIDE LEVEL, A PHENOMENON CRITICAL TO THE EXPRESSION OF THE ANTINEOPLASTIC ACTIVITY OF THE 6-THIOPURINES., PHENYL SUBSTITUTION AT C-8 OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE ABOLISHED THE IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTIVITY. THEREFORE, A NONSUBSTITUTED 8 POSITION OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE IS ESSENTIAL FOR IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTION., SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES (IN CELL DIVISION IN CULTURES WITHOUT ADDITION OF PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ, PHA) GO THROUGH VARIOUS PHASES OF 1ST DIVISION WITH THE SAME KINETICS AS PHA-STIMULATED CELLS. IN SAMPLES FROM 10 REFERENTS, THE FREQUENCY OF SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES VARIED FROM 8.9X10-5 TO 9.5X10-3 AS INDICATED WITH AUTORADIOGRAPHY ON CELLS IN (S + G2) PHASE DETERMINED BY FLOW SORTING. IN PHA-STIMULATED SAMPLES FROM THE SAME PERSONS THE FREQUENCY OF 6-THIOGUANINE (TG)-RESISTANT VARIANTS WAS BETWEEN 4X10-7 & 2.6X10-6, WHICH INDICATES THAT MOST OF THE SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING CELLS WERE TG-SENSITIVE., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for THIOGUANINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
NEEDLES FROM WATER, YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER | |
CAS No. |
154-42-7 | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=154-42-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000154427 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | thioguanine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757348 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=752 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6023652 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.005.299 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/WIX31ZPX66 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
greater than 680 °F (NTP, 1992), >360 °C, GREATER THAN 360 °C, > 360 °C | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
















