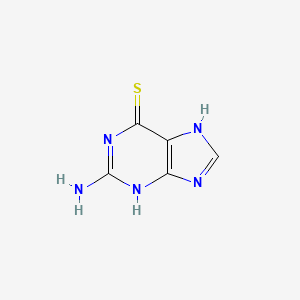
6-tioguanina
Descripción general
Descripción
Mecanismo De Acción
La tioguanina ejerce sus efectos compitiendo con la hipoxantina y la guanina por la enzima hipoxantina-guanina fosforribosiltransferasa (HGPRTasa). Se convierte en ácido 6-tioguanílico, que alcanza altas concentraciones intracelulares a dosis terapéuticas . El compuesto se incorpora al ADN durante la fase de síntesis, lo que lleva a efectos citotóxicos . Además, la tioguanina inhibe la proteína de unión a GTP Rac1, que regula la vía Rac / Vav .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Pharmacological Profile
Mechanism of Action
6-Thioguanine functions as an antimetabolite, primarily inhibiting DNA synthesis by incorporating into nucleic acids, particularly DNA. This incorporation disrupts the replication process, leading to cell death in rapidly dividing tumor cells. Evidence indicates that 6-TG is more effective in younger, rapidly growing tumor populations compared to older ones, highlighting the importance of timing in treatment regimens .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of 6-TG have been extensively studied. It is metabolized by guanase and xanthine oxidase, with higher blood levels observed post-intravenous administration compared to oral dosing. Studies show that repeated doses lead to significant incorporation of 6-TG into DNA, particularly in bone marrow cells .
Clinical Applications
Cancer Treatment
6-Thioguanine has been utilized in various types of cancer, particularly hematological malignancies such as acute leukemia and lymphomas. Its efficacy has been noted in patients with specific genetic profiles, particularly those with homozygous deletions of the methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) gene. These tumors are often resistant to other therapies but may respond favorably to 6-TG when combined with methylthioadenosine (MTA), which protects normal tissues from toxicity while allowing higher doses of 6-TG .
Case Study: Leukemia Treatment
A retrospective study involving 30 patients with Crohn's Disease who failed conventional immunosuppression demonstrated the efficacy of 6-TG as a third-line treatment. The median dose was 40 mg daily over 21.5 months, with an initial clinical response in 60% of patients . This study underscores the drug's potential beyond oncology into inflammatory conditions.
Combination Therapies
Research suggests that combining 6-Thioguanine with other agents can enhance its therapeutic effects. For instance, combinations with methotrexate or pralatrexate have shown promising results against MTAP-deficient tumors. The synergistic effects observed in xenograft models indicate a potential for developing more effective treatment protocols .
Safety and Toxicity
While 6-TG is effective, it is not without risks. Hepatotoxicity remains a concern, particularly in long-term use. In the previously mentioned study on Crohn's Disease patients, some experienced abnormal liver function tests during treatment; however, these were mostly mild and transient . Monitoring liver function during therapy is crucial for patient safety.
Summary Table of Applications
| Application Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Cancer Types | Acute leukemia, lymphomas, solid tumors (e.g., mesothelioma, melanoma) |
| Mechanism | Incorporation into DNA/RNA leading to growth arrest and apoptosis |
| Combination Potential | Enhanced effects when used with MTA or other chemotherapeutics |
| Safety Concerns | Hepatotoxicity; requires monitoring during treatment |
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
6-Thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and is itself converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP), which reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses . It is ribosylated and phosphorylated by the same pathway as natural purine bases .
Cellular Effects
6-Thioguanine has been shown to have cytotoxic effects on cells. It is incorporated into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell cycle, stopping normal development and division . It also inhibits the GTP-binding protein (G protein) Rac1, which regulates the Rac/Vav pathway .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of 6-Thioguanine involves its conversion to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP) via the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase). TGMP is then further metabolized to form 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGN). These 6-TGN are cytotoxic to cells by incorporation into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell and through inhibition of the GTP-binding protein (G protein) Rac1 .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of 6-Thioguanine in laboratory settings can vary over time. For instance, a study showed that mean 6-thioguanine nucleotide levels were higher among patients in clinical remission, with a pooled difference of 63.37 pmol/8 × 10 8 red blood cells .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of 6-Thioguanine can vary with different dosages. A study demonstrated the efficacy of low dose 6-Thioguanine treatment on low-mutation melanoma in a pre-clinical mouse model .
Metabolic Pathways
6-Thioguanine is catabolized via two pathways. One route is through the deamination by the enzyme guanine deaminase to 6-thioxanthine, which has minimal anti-neoplastic activity, then by oxidation by xanthine oxidase of the thioxanthine to thiouric acid .
Transport and Distribution
6-Thioguanine is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It is converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP) by the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of 6-Thioguanine involves its incorporation into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell cycle . This suggests that 6-Thioguanine is localized in the nucleus where DNA replication occurs.
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción
La tioguanina se puede sintetizar utilizando 2,9-diacil guanina o 2-acil guanina como materiales de partida. La reacción implica la sulfuración de estos compuestos con pentóxido de fósforo en una solución de piridina, con un ligero catalizador . Este método ofrece condiciones de reacción suaves, operación simple y un alto rendimiento de hasta el 75% .
Métodos de producción industrial
La producción industrial de tioguanina sigue rutas sintéticas similares, pero a mayor escala. El proceso implica el uso de anhídrido tiofosfórico y solución de piridina, con control cuidadoso de las condiciones de reacción para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones
La tioguanina sufre varias reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Desaminación: La reacción de desaminación de la tioguanina con agua, iones hidróxido y formas protonadas se ha estudiado ampliamente.
Oxidación: La tioguanina se puede oxidar para formar metabolitos tóxicos, lo que contribuye a sus efectos citotóxicos.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes
Desaminación: Los iones hidróxido y el agua son reactivos comunes utilizados en la desaminación de la tioguanina.
Principales productos formados
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La tioguanina es parte de la familia de las tiopurinas, que incluye mercaptopurina y azatioprina . En comparación con estos compuestos, la tioguanina tiene una mayor eficacia y una acción más rápida . su uso está limitado por las preocupaciones sobre la hepatotoxicidad y otros efectos secundarios .
Compuestos similares
Mercaptopurina: Otro análogo de purina utilizado en el tratamiento de la leucemia y otras afecciones.
Azatioprina: Un profármaco de mercaptopurina, utilizado como inmunosupresor en el trasplante de órganos y enfermedades autoinmunes.
Las propiedades únicas de la tioguanina, como su incorporación al ADN y la inhibición de vías moleculares específicas, la convierten en un compuesto valioso tanto en investigación como en entornos clínicos .
Actividad Biológica
6-Thioguanine (6-TG) is a purine analog that has been utilized in the treatment of various hematological malignancies, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Since its approval in the 1960s, research has expanded to explore its biological activity beyond oncology, revealing significant effects in conditions like diabetic retinopathy and psoriasis. This article delves into the biological activity of 6-TG, supported by case studies, data tables, and comprehensive research findings.
6-TG exerts its effects primarily through the inhibition of purine metabolism and DNA synthesis. It gets incorporated into DNA, replacing guanine, which leads to the disruption of DNA replication and ultimately induces apoptosis in rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells and activated lymphocytes. This mechanism is particularly relevant in the treatment of leukemias and autoimmune diseases.
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of DNA synthesis : 6-TG is metabolized to thioguanine nucleotides (TGNs), which interfere with DNA replication.
- Induction of apoptosis : Primarily observed in activated T lymphocytes, where it triggers programmed cell death.
- Immunosuppressive effects : Reduction in peripheral blood lymphocytes and total leukocyte counts.
1. Treatment of Psoriasis
A notable study involving 20 patients with moderate to severe plaque-type psoriasis demonstrated that 6-TG significantly improved disease severity. After six months of treatment:
- 12 patients were completely cleared of disease.
- 6 showed marked improvement .
- 2 did not respond .
Biopsy results indicated a reduction in keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation, correlating with clinical improvement. The therapy also led to a significant decrease in circulating lymphocytes by an average of 42% after two months .
2. Anti-Angiogenic Activity in Diabetic Retinopathy
Recent research highlighted the anti-angiogenic properties of 6-TG in diabetic retinopathy models. In vitro studies with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to high glucose levels showed:
- Marked reduction in tube formation at concentrations as low as 5 µM .
- In vivo studies demonstrated that diabetic mice treated with 6-TG exhibited reduced retinal vascular alterations, as confirmed by fluorescein angiography .
3. Efficacy in Leukemia Treatment
Comparative studies have shown that 6-TG is more effective than its counterpart, 6-mercaptopurine, particularly in reducing the risk of isolated central nervous system relapse. However, it carries a higher risk of severe adverse effects, including veno-occlusive disease .
Toxicity and Side Effects
While 6-TG has demonstrated efficacy across various conditions, its use is associated with several toxicities:
- Risk of infections due to immunosuppression.
- Development of liver complications such as veno-occlusive disease.
- Mutagenic potential leading to G→A mutations .
Summary Table: Clinical Findings
| Condition | Response Rate | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | 90% | Significant reduction in skin lesions |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | N/A | Reduced retinal vascular changes |
| Childhood Leukemia | N/A | Lower CNS relapse risk but higher mortality |
Research Findings
A variety of studies have investigated the pharmacokinetics and biological effects of 6-TG:
- Pharmacokinetics : Blood levels were higher post-intravenous administration compared to oral doses, indicating better bioavailability and incorporation into DNA .
- Mutagenicity Studies : Research indicated that both 6-TG and its metabolites are mutagenic in human cell lines, raising concerns about long-term use .
- Immunological Effects : A decrease in circulating leukocytes was noted alongside clinical improvements in autoimmune conditions .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
2-amino-3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C5H5N5S/c6-5-9-3-2(4(11)10-5)7-1-8-3/h1H,(H4,6,7,8,9,10,11) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WYWHKKSPHMUBEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=NC2=C(N1)C(=S)N=C(N2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C5H5N5S | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
5580-03-0 (hemihydrate), 76078-67-6 (mono-Na salt) | |
| Record name | Thioguanine [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000154427 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6023652 | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6023652 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
167.19 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
6-thioguanine appears as odorless or almost odorless pale yellow crystalline powder. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 1 mg/mL at 73 °F (NTP, 1992), INSOL IN WATER, ALCOHOL, CHLOROFORM; FREELY SOL IN DIL SOLUTIONS OF ALKALI HYDROXIDES, 8.34e-01 g/L, Readily soluble in dilute aqueous alkali. Insoluble in water, alcohol, or chloroform. | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | NCI Investigational Drugs | |
| URL | http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
| Description | An investigational drug is one that is under study but does not have permission from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be legally marketed and sold in the United States. NCI provides the investigational drug to the physicians who are participating in clinical trials or TRC protocols. For more information please visit NCI investigational drug website: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
Mechanism of Action |
Thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase) and is itself converted to 6-thioguanilyic acid (TGMP), which reaches high intracellular concentrations at therapeutic doses. TGMP interferes with the synthesis of guanine nucleotides by its inhibition of purine biosynthesis by pseudofeedback inhibition of glutamine-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase, the first enzyme unique to the de novo pathway of purine ribonucleotide synthesis. TGMP also inhibits the conversion of inosinic acid (IMP) to xanthylic acid (XMP) by competition for the enzyme IMP dehydrogenase. Thioguanine nucleotides are incorporated into both the DNA and the RNA by phosphodiester linkages, and some studies have shown that incorporation of such false bases contributes to the cytotoxicity of thioguanine. Its tumor inhibitory properties may be due to one or more of its effects on feedback inhibition of de novo purine synthesis; inhibition of purine nucleotide interconversions; or incorporation into the DNA and RNA. The overall result of its action is a sequential blockade of the utilization and synthesis of the purine nucleotides., THIOGUANINE, THE 6-THIO ANALOGUE OF GUANINE, IS A PRODRUG THAT IS CONVERTED TO 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE, AN ACTIVE METABOLITE. ... 6-THIOGUANINE-RIBOSE-PHOSPHATE IS A FEEDBACK INHIBITOR OF THE INITIAL (AMIDOTRANSFERASE) STEP IN PURINE BIOSYNTHESIS. THIS METABOLITE ALSO BLOCKS CONVERSIONS OF INOSINIC ACID TO GUANYLIC ACID & OF GUANYLIC ACID TO GDP. THIOGUANINE ALSO IS CONVERTED TO THE DEOXYNUCLEOTIDE TRIPHOSPHATE, WHICH CAN BE INCORPORATED INTO TUMOR CELL DNA. ALTHOUGH SOME INVESTIGATORS BELIEVE THAT THIS IS THE MAJOR MECHANISM OF CYTOTOXICITY, THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF THE VARIOUS SITES OF ACTION HAS NOT BEEN DETERMINED. ... THIOGUANINE IS CELL-CYCLE SPECIFIC FOR THE S PHASE., APPARENTLY, THE METABOLISM OF 6-THIOGUANINE TO 6-THIOGUANOSINE IN SARCOMA 180 & 180/TG CELLS IS MEDIATED BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE & NEWLY SYNTHESIZED 6-THIOGUANOSINE IS READILY EFFLUXED INTO THE CELLULAR ENVIRONMENT. THE FORMATION OF 6-THIOGUANINE, BY PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE, MAY BE IMPORTANT TO THE EXPRESSION OF CELLULAR SENSITIVITY TO 6-THIOGUANINE, IN THAT IT DECR THE AVAIL OF 6-THIOGUANINE FOR DIRECT CONVERSION BY HYPOXANTHINE-GUANINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE TO THE NUCLEOTIDE LEVEL, A PHENOMENON CRITICAL TO THE EXPRESSION OF THE ANTINEOPLASTIC ACTIVITY OF THE 6-THIOPURINES., PHENYL SUBSTITUTION AT C-8 OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE ABOLISHED THE IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTIVITY. THEREFORE, A NONSUBSTITUTED 8 POSITION OF 2-AMINO-6-MERCAPTOPURINE IS ESSENTIAL FOR IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE ACTION., SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES (IN CELL DIVISION IN CULTURES WITHOUT ADDITION OF PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ, PHA) GO THROUGH VARIOUS PHASES OF 1ST DIVISION WITH THE SAME KINETICS AS PHA-STIMULATED CELLS. IN SAMPLES FROM 10 REFERENTS, THE FREQUENCY OF SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING LYMPHOCYTES VARIED FROM 8.9X10-5 TO 9.5X10-3 AS INDICATED WITH AUTORADIOGRAPHY ON CELLS IN (S + G2) PHASE DETERMINED BY FLOW SORTING. IN PHA-STIMULATED SAMPLES FROM THE SAME PERSONS THE FREQUENCY OF 6-THIOGUANINE (TG)-RESISTANT VARIANTS WAS BETWEEN 4X10-7 & 2.6X10-6, WHICH INDICATES THAT MOST OF THE SPONTANEOUSLY CYCLING CELLS WERE TG-SENSITIVE., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for THIOGUANINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
NEEDLES FROM WATER, YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER | |
CAS No. |
154-42-7 | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=154-42-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000154427 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | thioguanine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757348 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=752 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 6-Thioguanine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6023652 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.005.299 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/WIX31ZPX66 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
greater than 680 °F (NTP, 1992), >360 °C, GREATER THAN 360 °C, > 360 °C | |
| Record name | 6-THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21107 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Tioguanine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00352 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | THIOGUANINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2504 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Thioguanine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014496 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















