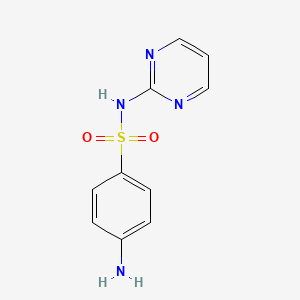
スルファジアジン
概要
説明
スルファジアジンは、さまざまな細菌感染症の治療に広く使用されているスルホンアミド系抗生物質です。 特に尿路感染症、トラコーマ、軟性下疳に効果的です . スルファジアジンは、ピリメタミンと組み合わせて、後天性免疫不全症候群患者におけるトキソプラズマ症の治療や、先天性感染症の新生児の治療にも使用されます . この化合物は、細菌における葉酸合成を阻害する能力で知られており、それにより細菌の増殖と増殖を防ぎます .
科学的研究の応用
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with various applications in medicine, pharmacology, and other scientific fields . It functions by inhibiting bacteria's ability to produce folic acid, which is essential for DNA synthesis, thereby preventing the spread of infection .
Scientific Research Applications
Antibacterial Agent: Sulfadiazine is effective against various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections . It can also be used topically to treat burn and wound infections . The drug inhibits the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, which is crucial for folic acid synthesis .
Treatment of Infections: Sulfadiazine is used in the treatment of several infections, such as trachoma and chancroid . Laboratory studies on animals have indicated that sulfadiazine has less toxicity compared to other drugs like sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole and is highly effective against common pathogens .
Silver Sulfadiazine in Wound Care: Silver sulfadiazine (SSDZ) is a common choice for treating skin burns . It can be integrated into hydrogels for topical wound treatment because hydrogels have minimal toxicity and can sustain the release of pharmaceuticals .
Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), including those incorporating silver sulfadiazine, have demonstrated antimicrobial properties and have contributed to the development of nanotechnology . AgNPs can potentially replace traditional antibiotics due to increasing bacterial resistance .
Combination Therapies: Sulfadiazine can be combined with other substances like hyaluronic acid (HA) to treat conditions such as parastomal skin ulceration . The combination of HA and silver sulfadiazine has shown success in promoting healing and reducing pain in such cases .
Data Table: Properties and Applications of Sulfadiazine
Case Studies
Parastomal Ulcer Healing: A case study demonstrated the successful treatment of chronic parastomal skin ulceration using a combination cream of 0.2% Hyaluronic acid and 1% Silver sulfadiazine . Patients treated with this combination experienced complete healing, reduced pain, and decreased purulent fluid, leading to a reduced cost of treatment compared to standard protocols .
Silver Sulfadiazine Hydrogels for Wound Treatment: Silver sulfadiazine has been integrated into hydrogels for wound treatment due to the hydrogels' low toxicity and capacity for extended pharmaceutical release .
Research Findings and Insights
Efficacy of Silver Sulfadiazine: A systematic review comparing Silver Sulfadiazine with other dressings for burns showed a statistically significant difference in healing time for silver dressings . While some animal studies support the use of Silver Sulfadiazine for partial-thickness burns, others question its effectiveness .
Toxicity and Safety: Laboratory studies on animals suggest that sulfadiazine has lower toxicity compared to sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole .
作用機序
スルファジアジンは、細菌酵素ジヒドロプテロ酸合成酵素を阻害することによって作用します . この酵素は、細菌の増殖と複製に不可欠な葉酸の合成に不可欠です . スルファジアジンは、この酵素を競合的に阻害することにより、細菌が葉酸を合成するのを防ぎ、最終的に細菌を死滅させます .
類似化合物の比較
類似化合物
スルファメトキサゾール: トリメトプリムと組み合わせて、さまざまな細菌感染症の治療に使用される別のスルホンアミド系抗生物質.
スルフィスオキサゾール: 尿路感染症やその他の細菌感染症の治療に使用されます.
スルファジアジン銀: やけどや創傷感染症の治療に使用される局所剤.
独自性
スルファジアジンは、広範囲の抗菌活性と、ピリメタミンなどの他の薬剤と組み合わせて、トキソプラズマ症などの特定の感染症の治療に使用できるという点で独自です . ヒト医学と獣医学の両方におけるその有効性は、その多様性をさらに際立たせています .
準備方法
合成経路と反応条件
スルファジアジンの合成は、通常、アニリン誘導体を無水酢酸を使用してアセチル化してアセタンリド誘導体を得ることから始まります . これらの誘導体は、その後、クロロスルホン酸と反応させて4-アセチルアミノベンゼンスルホニルクロリドを生成します . 並行して、2-アミノピリミジンは、テトラメトキシプロパンをグアニジン塩と反応させて調製されます . 最後の工程は、4-アセチルアミノベンゼンスルホニルクロリドを2-アミノピリミジンと反応させた後、水酸化ナトリウムで加水分解してスルファジアジンを得ることです .
工業的製造方法
スルファジアジンの工業的製造は、同様の合成経路に従いますが、より大規模に行われます。このプロセスには、高い収率と純度を確保するために、反応条件を厳密に制御することが含まれます。 自動反応器と連続フローシステムの使用は、生産の品質と効率の一貫性を維持するのに役立ちます .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類
スルファジアジンは、酸化、還元、置換など、さまざまな化学反応を起こします . この化合物は、芳香族アミンとスルホンアミド基の2つの反応性基を含み、これらの反応に関与します .
一般的な試薬と条件
主な生成物
これらの反応から生成される主な生成物には、スルファジアジンのさまざまな誘導体があり、医薬品用途でさらに使用できます .
科学研究への応用
スルファジアジンは、幅広い科学研究に応用されています。
類似化合物との比較
Similar Compounds
Sulfamethoxazole: Another sulfonamide antibiotic used in combination with trimethoprim to treat various bacterial infections.
Sulfisoxazole: Used to treat urinary tract infections and other bacterial infections.
Silver sulfadiazine: A topical agent used in the treatment of burns and wound infections.
Uniqueness
Sulfadiazine is unique due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and its ability to be used in combination with other drugs like pyrimethamine for the treatment of specific infections like toxoplasmosis . Its effectiveness in both human and veterinary medicine further highlights its versatility .
生物活性
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic that has been widely studied for its biological activity, particularly in the treatment of bacterial infections and its potential applications in various medical fields. This article discusses the compound's mechanisms of action, antimicrobial properties, clinical applications, and recent research findings.
Sulfadiazine functions primarily by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. It acts as a competitive antagonist of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate required for the synthesis of folate in bacteria. By blocking this pathway, sulfadiazine effectively prevents bacterial growth and reproduction, leading to cell death. This mechanism is common among sulfonamides, which have been utilized since their introduction in the 1930s.
Antimicrobial Properties
Sulfadiazine exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. It has been shown to be effective against:
- Gram-positive bacteria : Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative bacteria : Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Fungi : Candida albicans
- Protozoa : Toxoplasma gondii
Comparative Antimicrobial Efficacy
Recent studies have highlighted the enhanced efficacy of sulfadiazine when used in combination with metal complexes. For instance, metal complexes of sulfadiazine have demonstrated superior antibacterial activity compared to the free ligand itself, particularly against resistant strains of bacteria .
| Pathogen | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 32 µg/mL |
| Escherichia coli | 16 µg/mL |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 64 µg/mL |
| Candida albicans | 8 µg/mL |
Clinical Applications
Sulfadiazine is commonly used in clinical settings for treating various infections, including:
- Toxoplasmosis : Often administered in combination with pyrimethamine for effective treatment.
- Burn wounds : Silver sulfadiazine is a topical formulation used extensively for burn management due to its antimicrobial properties .
Case Studies
-
Silver Sulfadiazine in Burn Treatment :
A clinical trial involving children with severe burns demonstrated that silver sulfadiazine significantly reduced infection rates and facilitated wound healing compared to traditional treatments. The study reported no progression to critical infection stages among treated patients . -
Aerosol Formulation for Pressure Ulcers :
A novel aerosol formulation combining silver sulfadiazine with lidocaine and vitamin A showed promising results in treating scalp pressure ulcers in ICU patients. The treatment was associated with improved healing rates and reduced costs compared to conventional dressings .
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have explored the multifaceted biological activities of sulfadiazine beyond its antibacterial properties:
- Anticancer Activity : Research indicates that sulfadiazine exhibits antiproliferative effects on human liver cancer (HepG2) and breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines by inhibiting the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway. The IC50 values were determined to be approximately 245.69 µM for HepG2 cells and 215.68 µM for MCF7 cells .
- Cytotoxic Effects : Sulfadiazine derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines, revealing potential as therapeutic agents in oncology .
特性
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-pyrimidin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H10N4O2S/c11-8-2-4-9(5-3-8)17(15,16)14-10-12-6-1-7-13-10/h1-7H,11H2,(H,12,13,14) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SEEPANYCNGTZFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CN=C(N=C1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H10N4O2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7044130 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
250.28 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
6.01e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is needed for the proper processing of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) which is essential for folic acid synthesis. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
68-35-9 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=68-35-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000068359 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757324 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=35600 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.623 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFADIAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0N7609K889 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。














