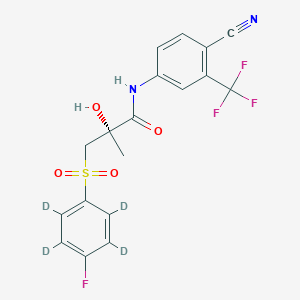
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4
Übersicht
Beschreibung
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 is a deuterated form of (S)-Bicalutamide, a non-steroidal anti-androgen medication primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The deuterium atoms in this compound replace the hydrogen atoms, which can enhance the compound’s metabolic stability and potentially improve its pharmacokinetic properties.
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of (S)-Bicalutamide-d4 involves several steps, starting from commercially available starting materials. The key steps include:
Deuterium Exchange Reaction: This involves the replacement of hydrogen atoms with deuterium atoms using deuterated reagents.
Coupling Reactions: These reactions form the core structure of this compound, typically involving palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions.
Purification: The final product is purified using techniques such as recrystallization or chromatography to ensure high purity.
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process is optimized for efficiency and cost-effectiveness, often involving continuous flow reactors and automated systems to ensure consistent quality and yield.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: This reaction involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen, often using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate.
Reduction: This involves the addition of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen, typically using reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride.
Substitution: This reaction involves the replacement of one functional group with another, often using nucleophilic or electrophilic reagents.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidation: Potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide.
Reduction: Lithium aluminum hydride, sodium borohydride.
Substitution: Halogenating agents, nucleophiles like amines or thiols.
Major Products
The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used. For example, oxidation may yield hydroxylated derivatives, while reduction could produce deuterated alcohols.
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Pharmacological Studies
Mechanism of Action
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 acts as an androgen receptor antagonist, inhibiting the effects of androgens such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. It competes for binding at the androgen receptor sites, thereby blocking androgen-induced gene expression. This mechanism is crucial in understanding prostate cancer's growth dynamics and resistance mechanisms.
Research on Prostate Cancer
Numerous studies utilize this compound to investigate its efficacy in combination therapies for advanced prostate cancer. For instance, it has been shown to enhance the effects of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogs, which suppress serum testosterone levels. Clinical data indicate that patients receiving this compound alongside LHRH therapy exhibit improved outcomes compared to those receiving LHRH alone .
Neurodegenerative Disease Research
Recent studies have explored the potential of this compound in treating neurodegenerative diseases like spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). Research indicates that this compound can enhance autophagic processes, leading to increased degradation of toxic proteins associated with neurodegeneration. In a mouse model of SBMA, administration of this compound resulted in improved motor function and extended survival rates by reducing androgen receptor toxicity .
Case Study: SBMA Model
- Objective : To assess the neuroprotective effects of this compound.
- Methodology : Mice were treated with this compound alongside trehalose, a natural disaccharide known for its protective effects on neurons.
- Results : The combination therapy led to significant improvements in motor behavior and muscle morphology, demonstrating the compound's potential as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative conditions .
Dermatological Applications
This compound has also been investigated for its efficacy in treating hyperandrogenism-related dermatological conditions such as hirsutism and acne. Clinical trials have shown that patients treated with bicalutamide formulations exhibit significant reductions in symptoms associated with excessive androgen levels.
Case Study: Treatment of Female Pattern Hair Loss
- Study Population : 44 women with female pattern hair loss.
- Dosage : 25-50 mg of bicalutamide daily for over six months.
- Outcomes : A mean reduction in hair loss severity was observed, with some patients maintaining or improving their condition without significant side effects .
Comparative Data Table
| Application Area | Compound Used | Study Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate Cancer | This compound | Clinical Trial | Improved outcomes when combined with LHRH analogs |
| Neurodegenerative Disease | This compound | Animal Study | Enhanced motor function and survival in SBMA mice |
| Dermatology | Bicalutamide | Case Series | Significant improvement in symptoms of hyperandrogenism |
Wirkmechanismus
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 exerts its effects by binding to androgen receptors, thereby inhibiting the action of androgens like testosterone. This inhibition prevents the growth and proliferation of androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells. The deuterium atoms in this compound may enhance its binding affinity and metabolic stability, leading to prolonged action.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Similar Compounds
(S)-Bicalutamide: The non-deuterated form, widely used in clinical settings.
Enzalutamide: Another non-steroidal anti-androgen with a different chemical structure but similar therapeutic use.
Apalutamide: Similar to enzalutamide, used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Uniqueness
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 is unique due to its deuterium labeling, which can enhance its metabolic stability and pharmacokinetic properties compared to its non-deuterated counterpart. This can potentially lead to improved therapeutic outcomes and reduced side effects.
Biologische Aktivität
(S)-Bicalutamide-d4 is a deuterated analogue of bicalutamide, a well-known non-steroidal antiandrogen primarily used in the treatment of prostate cancer. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its mechanism of action, efficacy in various cancer models, and potential therapeutic applications.
This compound functions as an androgen receptor (AR) antagonist . It binds to the AR and inhibits its activity, preventing the receptor from translocating to the nucleus where it would typically promote the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation and survival. Research indicates that this compound exhibits a similar mechanism to its parent compound, bicalutamide, by effectively blocking dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from activating the AR pathway .
Prostate Cancer
A significant body of research has focused on the efficacy of this compound in prostate cancer models. In vitro studies have demonstrated that this compound can inhibit cell growth in various prostate cancer cell lines, including LNCaP and DU-145. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values for these cell lines have been reported as follows:
| Cell Line | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| LNCaP | 45.20 |
| DU-145 | 51.61 |
These values indicate that this compound is effective at concentrations comparable to bicalutamide, suggesting potential for similar therapeutic applications .
Breast Cancer
Recent studies have also explored the use of bicalutamide and its analogues in treating androgen receptor-positive breast cancer. A phase II trial involving patients with estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer demonstrated that bicalutamide treatment resulted in a clinical benefit rate (CBR) of 19% among those with AR-positive tumors. Although specific data for this compound in this context is limited, its structural similarity implies potential efficacy against AR-positive breast cancers as well .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
- Phase II Trial in Breast Cancer : A clinical trial evaluated bicalutamide's effectiveness in patients with metastatic breast cancer who were AR-positive. The study found that 12% of screened patients had AR-positive tumors, with a CBR of 19% after treatment with bicalutamide at 150 mg daily .
- Neuronal Cell Model : In studies involving spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), bicalutamide was shown to reduce toxic effects related to mutant AR aggregation. While specific results for this compound were not reported, these findings highlight the potential neuroprotective roles of antiandrogens in conditions associated with AR dysregulation .
Comparative Analysis with Other Compounds
To better understand the biological activity of this compound, it is essential to compare it with other antiandrogens such as enzalutamide and hydroxyflutamide:
| Compound | Mechanism | IC50 Range (µM) | Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| This compound | AR Antagonist | 45.20 - 51.61 | Prostate Cancer |
| Enzalutamide | AR Antagonist | 11.47 - 53.04 | Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer |
| Hydroxyflutamide | AR Antagonist | Not specified | Prostate Cancer |
This table illustrates that while this compound has comparable efficacy to other established antiandrogens, ongoing research may reveal additional benefits or specific applications for this compound.
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
(2S)-N-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-(2,3,5,6-tetradeuterio-4-fluorophenyl)sulfonylpropanamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H14F4N2O4S/c1-17(26,10-29(27,28)14-6-3-12(19)4-7-14)16(25)24-13-5-2-11(9-23)15(8-13)18(20,21)22/h2-8,26H,10H2,1H3,(H,24,25)/t17-/m1/s1/i3D,4D,6D,7D | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
LKJPYSCBVHEWIU-YNWMVSOESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(CS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)F)(C(=O)NC2=CC(=C(C=C2)C#N)C(F)(F)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
[2H]C1=C(C(=C(C(=C1F)[2H])[2H])S(=O)(=O)C[C@](C)(C(=O)NC2=CC(=C(C=C2)C#N)C(F)(F)F)O)[2H] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C18H14F4N2O4S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
434.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details









Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.













