Raltegravir-Kalium
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Raltegravir Potassium: is an antiretroviral medication used primarily for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. It is the potassium salt form of raltegravir, which is an HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitor. This compound was the first of its class to be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2007 . Raltegravir Potassium works by inhibiting the integrase enzyme, which is essential for the viral replication process .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Treatment of HIV Infection
Raltegravir potassium is indicated for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in both adults and pediatric patients. Its use is essential in achieving viral suppression when combined with other antiretroviral agents. The drug's mechanism involves inhibiting the integrase enzyme, which is crucial for viral replication.
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
Significant clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of raltegravir. For instance, in the BENCHMRK studies, patients treated with raltegravir showed a higher percentage of achieving viral loads below 50 copies/mL compared to those receiving placebo. Specifically, at week 156, 51% of patients on raltegravir achieved this milestone versus only 22% in the placebo group . Furthermore, after 240 weeks, the mean increase in CD4 cell counts was notable, indicating robust immune recovery among those treated with raltegravir .
Pharmacokinetics and Dosage
Raltegravir potassium is administered orally, typically at a dosage of 400 mg twice daily. It exhibits a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with peak plasma concentrations reached approximately three hours post-dose. The drug shows dose-proportional absorption and does not significantly prolong the QTc interval, making it a safe option for many patients .
Table: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Raltegravir
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Tmax | ~3 hours |
| AUC (Area Under Curve) | Dose-proportional |
| Cmax | Increases with dose |
Safety Profile and Side Effects
The safety profile of raltegravir potassium has been evaluated extensively. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances and rash; however, severe adverse events are rare. Monitoring for hypersensitivity reactions and liver function is recommended during treatment .
Combination Therapy
Raltegravir is often used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs to enhance treatment efficacy and reduce the risk of resistance development. This combination approach is crucial for achieving sustained virologic suppression.
Case Study: Efficacy in Treatment-Naïve Patients
In a cohort study involving treatment-naïve patients, those receiving a regimen including raltegravir showed significantly improved outcomes compared to traditional therapies. The study reported that after 48 weeks, over 80% of participants achieved undetectable viral loads .
Potential Beyond HIV Treatment
Recent research suggests that raltegravir may have applications beyond HIV treatment. Investigations into its effects on other viral infections and its potential role in cancer therapy are ongoing. For example, studies are exploring how integrase inhibitors like raltegravir may influence cellular mechanisms relevant to oncogenesis .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Raltegravir potassium primarily targets the HIV-1 integrase , a viral enzyme . This enzyme plays a crucial role in the replication of the HIV-1 virus by catalyzing the integration of the viral DNA into the host cell’s genome .
Mode of Action
Raltegravir inhibits the action of the HIV-1 integrase . By doing so, it prevents the integration of the viral genome into the human genome . This inhibition disrupts the replication cycle of the HIV-1 virus, thereby reducing the viral load in the body .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by raltegravir is the HIV-1 replication cycle . By inhibiting the integrase enzyme, raltegravir disrupts the integration of the viral DNA into the host cell’s genome, a key step in the viral replication process . This disruption prevents the production of new viruses, thereby reducing the viral load in the body .
Pharmacokinetics
Raltegravir is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract . It is approximately 83% bound to human plasma protein and is minimally distributed into red blood cells . The compound is primarily metabolized by glucuronidation . The area under the curve (AUC) and concentration © increase in a dose-proportional manner in the dose range 100 to 800 mg in healthy subjects after a single oral dose of raltegravir in the fasted state .
Result of Action
The inhibition of the HIV-1 integrase by raltegravir results in a decrease in the viral load in the body . This can lead to an improvement in the immune response and a reduction in the symptoms of HIV-1 infection .
Action Environment
The efficacy and stability of raltegravir can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, coadministration of raltegravir with drugs that are strong inducers of UGT1A1 may result in reduced plasma concentrations of raltegravir . This could potentially decrease the efficacy of the drug . Therefore, it’s important to consider potential drug interactions when administering raltegravir .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of Raltegravir Potassium involves several steps, including the selective N-methylation of a pyrimidone intermediate. The process typically includes the following steps :
N-alkylation: The pyrimidone intermediate is alkylated using (chloromethyl)dimethylchlorosilane and potassium fluoride.
Amidation: The alkylated product undergoes amidation with an amine.
Desilylation: The final step involves desilylation using potassium fluoride in methanol.
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of Raltegravir Potassium involves dry granulation techniques to prepare compressed tablets. The process includes blending raltegravir with excipients, compressing the mixture to form slugs, sizing the slugs to form granules, and finally compressing the granules into tablets .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Reaktionstypen: Raltegravir-Kalium unterliegt verschiedenen Arten chemischer Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Es kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden.
Reduktion: Es kann unter Verwendung geeigneter Reduktionsmittel reduziert werden.
Substitution: Verschiedene Substitutionsreaktionen können auftreten, insbesondere unter Beteiligung der Fluorphenylgruppe.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid können verwendet werden.
Substitution: Bedingungen für Substitutionsreaktionen beinhalten oft die Verwendung von Katalysatoren und Lösungsmitteln wie Acetonitril.
Hauptprodukte: Die bei diesen Reaktionen gebildeten Hauptprodukte hängen von den verwendeten Reagenzien und Bedingungen ab. Beispielsweise kann Oxidation zu hydroxylierten Derivaten führen, während Reduktion zu deoxygenierten Verbindungen führen kann .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Raltegravir-Kalium wird mit anderen HIV-Integrase-Inhibitoren verglichen, wie z. B.:
- Elvitegravir
- Dolutegravir
- Bictegravir
Einzigartigkeit: this compound war der erste Integrase-Inhibitor, der für die klinische Anwendung zugelassen wurde, und ebnete damit den Weg für nachfolgende Medikamente dieser Klasse. Es ist bekannt für seine schnelle Wirkung und Wirksamkeit bei der Reduzierung der Viruslast .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
- Elvitegravir : Ein weiterer Integrase-Inhibitor mit ähnlichen Mechanismen, aber unterschiedlichen pharmakokinetischen Eigenschaften.
- Dolutegravir : Bekannt für seine höhere Barriere gegen Resistenz im Vergleich zu Raltegravir.
- Bictegravir : Bietet eine einmal tägliche Dosierung und wird oft in Kombinationstherapien eingesetzt .
Biologische Aktivität
Raltegravir potassium is an antiretroviral medication primarily used in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. As the first integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI), it functions by inhibiting the integrase enzyme, which is crucial for the viral replication process. This article explores the biological activity of raltegravir potassium, including its pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, efficacy in clinical studies, and safety profile.
Raltegravir inhibits the strand transfer activity of the HIV integrase enzyme. By doing so, it prevents the integration of viral DNA into the host cell genome, thereby blocking the replication cycle of HIV-1. This mechanism is vital for managing HIV infections, especially in patients with strains resistant to other antiretroviral therapies .
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution:
- Raltegravir is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring approximately 1 to 4 hours post-dose.
- It has a high plasma protein binding rate (approximately 83%) and shows extensive distribution throughout the body, with significant concentrations found in gastrointestinal organs and excretion pathways .
Metabolism:
- The primary metabolic pathway for raltegravir involves glucuronidation, primarily mediated by UGT1A1, with minor contributions from UGT1A9 and UGT1A3. This metabolic pathway results in a major metabolite that is less pharmacologically active than the parent compound .
Excretion:
- Raltegravir is excreted mainly through feces and urine. Studies have shown that it crosses the placenta and is present in breast milk, indicating potential implications for pregnant or lactating individuals .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
Raltegravir has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing viral loads and increasing CD4 cell counts among HIV-infected patients.
Key Findings from Clinical Trials:
- BENCHMRK Studies: In these randomized trials involving treatment-experienced patients, raltegravir showed a significant reduction in viral load compared to placebo. At week 156, 51% of patients on raltegravir achieved viral loads under 50 copies/mL versus only 22% in the placebo group .
| Study Duration | Raltegravir Group (%) | Placebo Group (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Week 156 | 51% < 50 copies/mL | 22% < 50 copies/mL |
| Week 240 | 42% < 50 copies/mL | - |
- Pediatric Studies: In trials involving children aged 2 years and older, raltegravir demonstrated a virologic success rate of approximately 53% at week 24 among treatment-experienced subjects. This indicates its efficacy across different age groups and treatment histories .
Safety Profile
Raltegravir is generally well-tolerated with a low incidence of severe adverse effects. Common side effects include nausea, headache, and fatigue. Importantly, it has a low potential for drug-drug interactions due to its unique metabolic pathway that does not involve cytochrome P450 enzymes .
Toxicity Studies:
Eigenschaften
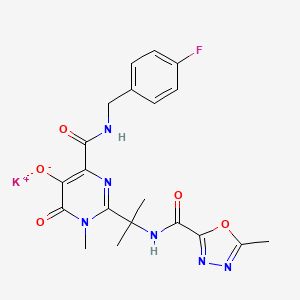
IUPAC Name |
potassium;4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylcarbamoyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-carbonyl)amino]propan-2-yl]-6-oxopyrimidin-5-olate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H21FN6O5.K/c1-10-25-26-17(32-10)16(30)24-20(2,3)19-23-13(14(28)18(31)27(19)4)15(29)22-9-11-5-7-12(21)8-6-11;/h5-8,28H,9H2,1-4H3,(H,22,29)(H,24,30);/q;+1/p-1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
IFUKBHBISRAZTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=NN=C(O1)C(=O)NC(C)(C)C2=NC(=C(C(=O)N2C)[O-])C(=O)NCC3=CC=C(C=C3)F.[K+] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C20H20FKN6O5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID501007339 | |
| Record name | Potassium 4-[{[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]imino}(hydroxy)methyl]-1-methyl-2-{2-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-carbonyl)amino]propan-2-yl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-5-olate | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501007339 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
482.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
871038-72-1 | |
| Record name | Raltegravir potassium [USAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0871038721 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Potassium 4-[{[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]imino}(hydroxy)methyl]-1-methyl-2-{2-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-carbonyl)amino]propan-2-yl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-5-olate | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID501007339 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | potassium;4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylcarbamoyl]-1-methyl-2-[2-[(5 methyl-1,3,4oxadiazole-2-carbonyl)amino]propan-2-yl]-6 oxopyrimidin-5-olate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | RALTEGRAVIR POTASSIUM | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/43Y000U234 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.













