Coluracetam
Übersicht
Beschreibung
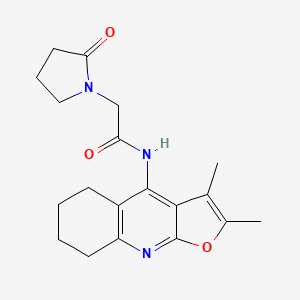
Coluracetam, also known by its chemical name N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b]quinolin-4-yl)-2-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)acetamide, is a member of the racetam family of nootropic compounds. Initially developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, it has since been explored for its potential benefits in enhancing cognitive function, memory, and mood .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Cognitive Disorders
Coluracetam has been explored in various clinical settings for its effects on cognitive disorders:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Initial studies focused on its potential to improve cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients. While promising results were observed in animal models regarding memory restoration, human trials yielded inconclusive results .
- Depression and Anxiety: this compound was investigated in phase II clinical trials for major depressive disorder and anxiety. Although these studies were ultimately discontinued due to failure to meet endpoints, preliminary findings suggested potential anxiolytic effects without impacting serotonin levels .
Case Studies
Several case studies have documented the effects of this compound on cognitive enhancement:
- Visual Perception and Reasoning: A study assessed the impact of this compound on visual perception and abstract reasoning. Participants demonstrated improvements in analytical thinking and spatial orientation after administration .
- Memory Improvement in Impaired Subjects: Research involving rats with chemically induced memory deficits showed significant enhancements in working memory following this compound treatment over an eight-day period .
Summary of Research Findings
The following table summarizes key findings from various studies on this compound:
| Study Focus | Key Findings | Population Studied |
|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Increased acetylcholine levels; inconclusive human trial results | Animal models; human trials |
| Major Depression & Anxiety | Potential anxiolytic effects; discontinued phase II trials | Human subjects |
| Cognitive Enhancement | Improved visual perception, reasoning, and analytical thinking | Case study participants |
| Memory Restoration | Significant improvement in working memory in impaired rats | Animal models |
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
The primary target of Coluracetam is the high-affinity choline uptake (HACU) in neurons . Choline is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which plays a crucial role in cognitive processes such as memory formation, learning, and attention .
Mode of Action
This compound interacts with its target, the high-affinity choline transporter (HACU), which is responsible for transporting choline across the cell membrane and into neurons . By enhancing the efficiency of the choline transport system, this compound promotes the synthesis and release of acetylcholine, ultimately leading to improved cognitive function .
Biochemical Pathways
This compound affects the cholinergic system, specifically the pathway of acetylcholine synthesis . By enhancing high-affinity choline uptake, this compound increases the levels of acetylcholine, a crucial neurotransmitter associated with memory and cognition . This increase can help with memory formation and retention, making the brain work more efficiently and supporting various mental tasks .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound appears to have very rapid kinetics, with a peak in blood at around 30 minutes and on the decline within 3 hours . Due to this, supplementation may be time-dependent in relation to activity . It is fat-soluble, so it needs fats for optimal absorption . It’s usually taken sublingually (under the tongue) or orally . This method enhances its bioavailability .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of this compound’s action are primarily related to its enhancement of acetylcholine synthesis. By increasing the levels of acetylcholine, this compound improves cognitive functions such as memory formation, learning, and attention . It has been shown to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of this compound can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the presence of fats in the environment (i.e., the user’s diet) can affect the absorption of this fat-soluble compound . Furthermore, the timing of supplementation in relation to activity can influence the compound’s effects due to its rapid kinetics .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
The primary mechanism of action for coluracetam is its ability to increase the uptake of choline into neurons . Choline is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which plays a crucial role in cognitive processes such as memory formation, learning, and attention . This compound achieves this by interacting with the high-affinity choline transporter (HACU), which is responsible for transporting choline across the cell membrane and into neurons . By enhancing the efficiency of the choline transport system, this compound promotes the synthesis and release of acetylcholine .
Cellular Effects
This compound works mainly by increasing the levels of acetylcholine, a crucial neurotransmitter, and modulating choline uptake in the brain . Its unique mechanisms make it interesting for cognitive enhancement and potential therapeutic uses . Enhancement of Acetylcholine Synthesis: this compound boosts acetylcholine synthesis . Acetylcholine is vital for learning and memory . The brain uses choline to produce acetylcholine . By enhancing this process, this compound improves cognitive functions .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound enhances high-affinity choline uptake (HACU), which is the rate-limiting step of acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis . Studies have shown this compound to improve learning impairment on a single oral dose given to rats which have been exposed to cholinergic neurotoxins . Subsequent studies have shown that it may induce long-lasting procognitive effects in cholinergic neurotoxin-treated rats by changing the choline transporter regulation system .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
Most of the research on this compound was done on animals rather than humans, so there are no universally accepted dosing guidelines . In a 2010 animal study, this compound improved artificially-induced memory deficits without producing any significant side effects .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is fat-soluble, so it needs fats for optimal absorption . It’s usually taken sublingually (under the tongue) or orally . This method enhances its bioavailability .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely that this compound interacts with neurons in the brain where it enhances the uptake of choline, a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine .
Side effects and long-term safety remain areas requiring more comprehensive research .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Coluracetam wird durch einen mehrstufigen Prozess synthetisiert, der die Reaktion von 2,3-Dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b]chinolin mit 2-Oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamid beinhaltet. Die wichtigsten Schritte umfassen:
Bildung des Chinolinkernes: Dies beinhaltet Cyclisierungsreaktionen unter kontrollierten Bedingungen.
Anlagerung der Pyrrolidinylgruppe: Dieser Schritt erfordert in der Regel die Verwendung von Kupplungsreagenzien und Katalysatoren, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten.
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: Die industrielle Produktion von this compound folgt ähnlichen Synthesewegen, jedoch in größerem Maßstab. Das Verfahren ist auf Effizienz, Kosteneffektivität und Einhaltung der regulatorischen Standards optimiert. Wichtige Überlegungen sind:
Reaktionsskalierbarkeit: Sicherstellung, dass die Reaktionen ohne Einbußen bei Ausbeute oder Reinheit hochskaliert werden können.
Reinigung: Einsatz von Techniken wie Kristallisation und Chromatographie, um die gewünschten Reinheitsgrade zu erreichen.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Coluracetam unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Dies kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten und zur Bildung oxidierter Derivate führen.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können die funktionellen Gruppen modifizieren und die Aktivität der Verbindung möglicherweise verändern.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können verschiedene funktionelle Gruppen einführen, die ihre nootropen Eigenschaften verstärken oder abschwächen können.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidationsmittel: Wie Kaliumpermanganat oder Wasserstoffperoxid.
Reduktionsmittel: Einschließlich Natriumborhydrid oder Lithiumaluminiumhydrid.
Katalysatoren: Häufig in Substitutionsreaktionen eingesetzt, um die Reaktionsraten und Ausbeuten zu erhöhen.
Hauptprodukte: Die Hauptprodukte dieser Reaktionen sind modifizierte Formen von this compound, die unterschiedliche pharmakologische Eigenschaften haben können. Diese Derivate werden häufig untersucht, um Struktur-Wirkungs-Beziehungen zu verstehen.
4. Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound wurde für verschiedene wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen untersucht:
Chemie: Untersucht wegen seiner einzigartigen chemischen Struktur und seines Potenzials zur Bildung neuer Derivate.
Biologie: Untersucht auf seine Auswirkungen auf Neurotransmittersysteme, insbesondere Acetylcholin.
Medizin: Untersucht auf sein Potenzial zur Behandlung kognitiver Störungen, Depressionen und Angstzustände.
Industrie: Wird bei der Entwicklung von Nootropika-Nahrungsergänzungsmitteln eingesetzt, die auf die Verbesserung der kognitiven Funktion und der Stimmung abzielen.
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound verbessert in erster Linie die Aufnahme von Cholin mit hoher Affinität (HACU), der geschwindigkeitsbestimmenden Stufe bei der Synthese von Acetylcholin, einem wichtigen Neurotransmitter für Lernen und Gedächtnis . Durch die Erhöhung der Verfügbarkeit von Cholin steigert this compound die Acetylcholinproduktion und verbessert so die kognitiven Funktionen. Es moduliert auch das Regulationssystem des Cholintransporters und führt zu langanhaltenden prokognitiven Effekten .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Piracetam: Das erste Racetam-Nootropikum, bekannt für seine kognitivsteigernden Effekte.
Aniracetam: Ein weiteres Racetam mit anxiolytischen und kognitiven Vorteilen.
Oxiracetam: Bekannt für seine stimulierenden Effekte und die Steigerung der kognitiven Leistungsfähigkeit.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound: this compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seines spezifischen Mechanismus zur Steigerung der Cholinaufnahme mit hoher Affinität, der bei anderen Racetamen nicht beobachtet wird. Diese besondere Wirkung macht es besonders effektiv bei der Verbesserung von Gedächtnis und Lernen in Situationen, in denen die cholinerge Funktion beeinträchtigt ist .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Piracetam: The first racetam nootropic, known for its cognitive-enhancing effects.
Aniracetam: Another racetam with anxiolytic and cognitive benefits.
Oxiracetam: Known for its stimulating effects and cognitive enhancement.
Uniqueness of Coluracetam: this compound is unique due to its specific mechanism of enhancing high-affinity choline uptake, which is not observed in other racetams. This distinct action makes it particularly effective in improving memory and learning in conditions where cholinergic function is compromised .
Biologische Aktivität
Coluracetam is a synthetic compound originally developed in Japan, primarily recognized for its role as a cognitive enhancer. It belongs to a class of drugs known as racetams and has garnered attention for its potential neuroprotective properties and effects on memory and learning. The compound acts primarily as a high-affinity choline uptake (HACU) enhancer, which is crucial for the synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh), a neurotransmitter associated with memory and cognitive function.
This compound's primary mechanism involves enhancing the uptake of choline in the brain, which is vital for ACh production. This is achieved through its interaction with the choline transporter (CHT1), leading to increased availability of choline for ACh synthesis. Research indicates that this compound may also modulate the efficiency of HACU, thereby enhancing synaptic ACh levels without directly affecting acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, which breaks down ACh in the synapse .
Key Mechanisms:
- High-Affinity Choline Uptake (HACU): this compound enhances HACU activity, facilitating greater choline availability for ACh synthesis .
- Neuroprotective Effects: It has been shown to reverse deficits in ACh levels in animal models, particularly in cases where ACh depletion occurs due to neurotoxic agents .
- Cognitive Enhancement: The compound has demonstrated improvements in various cognitive functions, including memory and learning, particularly in models with induced cognitive deficits .
Observational Studies
This compound has been tested in various animal models to assess its effects on cognitive function. In studies involving rats treated with AF64A (a neurotoxin that induces cholinergic deficits), this compound significantly reversed the decline in ACh levels and improved cognitive performance metrics such as spatial learning and memory retention .
Case Studies
A notable case study examined the effects of this compound on a 36-year-old male participant over three months. The participant reported improvements in visual perception, abstract reasoning, pattern recognition, and analytical thinking, although there was a slight decline in spatial orientation scores. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences between pre- and post-test scores across most cognitive domains, suggesting that while subjective improvements were noted, they may not have been statistically robust .
Summary of Cognitive Effects from Case Study:
| Cognitive Domain | Pretest Score | Posttest Score | Change | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Perception | X | Y | +Δ | NS |
| Abstract Reasoning | X | Y | +Δ | NS |
| Pattern Recognition | X | Y | +Δ | NS |
| Spatial Orientation | X | Y - 5 | -5 | NS |
| Analytical Thinking | X | Y | +Δ | NS |
NS = Not Significant
Pharmacological Studies
Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that this compound enhances cognitive function through its action on the HACU system. In repeated administration studies, it was found that this compound could induce long-lasting pro-cognitive effects by modifying choline transporter regulation systems .
Neurochemical Effects
In rodent studies, administration of this compound resulted in:
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
N-(2,3-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-b]quinolin-4-yl)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H23N3O3/c1-11-12(2)25-19-17(11)18(13-6-3-4-7-14(13)20-19)21-15(23)10-22-9-5-8-16(22)24/h3-10H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21,23) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PSPGQHXMUKWNDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(OC2=NC3=C(CCCC3)C(=C12)NC(=O)CN4CCCC4=O)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C19H23N3O3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60159386 | |
| Record name | Coluracetam | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60159386 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
341.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
135463-81-9 | |
| Record name | Coluracetam | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=135463-81-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Coluracetam [INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0135463819 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Coluracetam | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60159386 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | COLURACETAM | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/V6FL6O5GR7 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.















