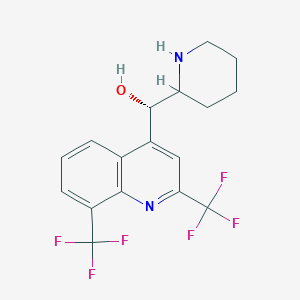
Mefloquine
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Mefloquin ist ein Medikament, das hauptsächlich zur Vorbeugung und Behandlung von Malaria eingesetzt wird, einer schweren Infektion, die durch Plasmodium-Parasiten verursacht und von Mücken übertragen wird . Es wurde in den 1970er Jahren von der US-Armee entwickelt und kam Mitte der 1980er Jahre zum Einsatz . Mefloquin ist wirksam gegen Plasmodium falciparum und Plasmodium vivax, einschließlich Chlorquin-resistenter Stämme . Es wird oral eingenommen und ist bekannt für seine lange Halbwertszeit, die eine wöchentliche Dosierung ermöglicht .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Mefloquin wird in einem mehrstufigen Verfahren synthetisiert, das die Reaktion von 2,8-Bis(trifluormethyl)chinolin mit Piperidin umfasst . Die Syntheseroute umfasst typischerweise:
Bildung des Chinolinrings: Dies beinhaltet die Cyclisierung geeigneter Vorläufer unter sauren Bedingungen.
Einführung von Trifluormethylgruppen: Dieser Schritt wird durch die Verwendung von Trifluormethylierungsmitteln erreicht.
Anbindung des Piperidin-Moleküls: Dies erfolgt über nukleophile Substitutionsreaktionen.
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden beinhalten oft die Optimierung dieser Schritte, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten, wobei großtechnische Reaktoren und strenge Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen eingesetzt werden .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Mefloquin unterliegt verschiedenen Arten von chemischen Reaktionen:
Oxidation: Mefloquin kann zu verschiedenen Metaboliten oxidiert werden, hauptsächlich in der Leber.
Reduktion: Obwohl weniger häufig, können Reduktionsreaktionen unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten.
Substitution: Nukleophile Substitutionsreaktionen werden bei der Synthese verwendet, insbesondere bei der Anbindung des Piperidinrings.
Häufig verwendete Reagenzien in diesen Reaktionen sind Trifluormethylierungsmittel, Säuren zur Cyclisierung und Nukleophile zur Substitution. Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind der pharmazeutische Wirkstoff und seine Metaboliten .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Mefloquine is a drug traditionally used to treat malaria, but research has shown it to have other potential applications, including use as an antibiotic adjuvant, antiviral, and antitumor agent .
Antibiotic Adjuvant
This compound has emerged as a promising antibiotic adjuvant because of its ability to enhance the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics against resistant bacterial strains . this compound exhibits synergistic bacteriostatic effects when combined with antibiotics, including colistin, β-lactams, antituberculosis drugs, quinolones, and linezolid . Potential mechanisms underlying these synergistic effects include the inhibition of antibiotic efflux, disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity, and disturbance of biofilm formation .
Antiviral Effects
This compound has demonstrated antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 by inhibiting the viral entry process after the virus attaches to the cell . Mathematical modeling suggests that this compound administration could reduce viral dynamics in patients, reducing the cumulative viral load and shortening the period until virus elimination in clinical concentration ranges .
Antitumor Effects
This compound has demonstrated antitumor effects against several cancers .
Inhibition of Multiple Membrane Channels
This compound has been shown to inhibit multiple membrane channels . It acts as an antagonist of the cardiac potassium channel, KvLQT1/minK, and slows its activation . this compound also effectively blocks volume-regulated and calcium-activated chloride channels .
Malaria Prophylaxis
This compound is used for malaria prophylaxis in nonimmune travelers . However, atovaquone-proguanil was better tolerated than this compound and similarly effective for malaria .
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms
A case study reported the development of acute neuropsychiatric symptoms in a 10-year-old boy after returning from travel in Africa, where he had taken this compound . A 4-week course of cognitive-behavioral therapy effectively treated this substance-induced anxiety disorder caused by this compound . The study highlights the importance of obtaining travel histories, including exposure to prophylactic medication, when patients present with acute-onset psychiatric symptoms .
Long-term Neurocognitive Effects
Some case studies have reported word-finding, processing speed, verbal learning, auditory and visual memory, motor speed, and motor learning deficits as side effects of this compound use . Other case studies reported neurobehavioral/neurologic symptoms, vestibular dysfunction, and mild impairment in fine motor dexterity and processing speed . One case study reported long-term symptoms of self-reported dizziness, short-term memory, vivid dreams/nightmares, and vestibulopathy persisted .
Prolonged Visual Illusions
Prolonged visual illusions have been reported as a result of this compound use .
Babesiosis
Wirkmechanismus
The exact mechanism of action of mefloquine is not completely understood. it is believed to target the 80S ribosome of Plasmodium falciparum, inhibiting protein synthesis and causing schizonticidal effects . This compound also alters cholinergic synaptic transmission by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, which affects neurotransmission in the brain .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Mefloquin gehört zur Klasse der Chinolin-Methanol-Antimalariamittel. Ähnliche Verbindungen umfassen:
Chlorquin: Ein älteres Antimalariamittel, das gegen nicht-resistente Stämme von Plasmodium wirksam ist.
Hydroxychlorquin: Ähnlich wie Chlorquin, aber mit zusätzlichen Anwendungen bei Autoimmunerkrankungen.
Mefloquin ist einzigartig in seiner langen Halbwertszeit, die eine wöchentliche Dosierung ermöglicht, und seiner Wirksamkeit gegen Chlorquin-resistente Stämme . Es ist auch mit neuropsychiatrischen Nebenwirkungen verbunden, die seinen Einsatz in bestimmten Populationen einschränken .
Biologische Aktivität
Mefloquine is a synthetic antimalarial drug that has garnered attention for its diverse biological activities beyond its primary use in treating malaria. This article delves into the compound's mechanisms of action, its effects on various pathogens, and associated neuropsychiatric outcomes, supported by case studies and research findings.
Chemical Profile
- Chemical Name : (α S)- rel-α-(2 R)-2-Piperidinyl-2,3-bis(trifluoromethyl-4-quinolinemethanol hydrochloride
- Purity : ≥98%
- Molecular Weight : 433.87 g/mol
This compound exhibits multiple biological activities:
- Antimalarial Activity :
- Antischistosomal Activity :
- Antiviral Properties :
- Antifungal Activity :
- Neuropharmacological Effects :
Neuropsychiatric Outcomes
Despite its therapeutic benefits, this compound has been associated with various neuropsychiatric side effects:
- A cohort study indicated that veterans exposed to this compound reported poorer health outcomes and greater neurobehavioral symptoms compared to unexposed individuals .
- Commonly reported symptoms include:
Case Studies
A selection of case studies highlights the complexities surrounding this compound's effects:
- One study documented persistent symptoms such as dizziness and memory issues in a veteran population following this compound exposure, despite overall neuropsychological assessments appearing normal .
- Another case highlighted vestibular dysfunction linked to this compound use, underscoring the need for careful monitoring in patients prescribed this medication .
Comparative Efficacy Against Pathogens
The following table summarizes the comparative efficacy of this compound against various pathogens:
| Pathogen | Mechanism of Action | IC50/MIC Values |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium falciparum | Inhibition of protein synthesis | Not specified |
| Schistosoma mansoni | Disruption of metabolic processes | Not specified |
| Candida auris | Disruption of cell membrane integrity | Improved by 8-64 fold |
| Mycobacterium abscessus | Interference with mycolic acid biosynthesis | MIC = 16 μg/mL |
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
(S)-[2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]-[(2R)-piperidin-2-yl]methanol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H16F6N2O/c18-16(19,20)11-5-3-4-9-10(15(26)12-6-1-2-7-24-12)8-13(17(21,22)23)25-14(9)11/h3-5,8,12,15,24,26H,1-2,6-7H2/t12-,15+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XEEQGYMUWCZPDN-DOMZBBRYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CCNC(C1)C(C2=CC(=NC3=C2C=CC=C3C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CCN[C@H](C1)[C@H](C2=CC(=NC3=C2C=CC=C3C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C17H16F6N2O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4037168, DTXSID101019853 | |
| Record name | Mefloquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4037168 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (-)-Mefloquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID101019853 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
378.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Density |
Crystal density: 1.432 g/cu cm | |
| Record name | MEFLOQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/6853 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Mefloquine, like chloroquine and quinine, is a blood schizonticidal agent and is active against the intraerythrocytic stages of parasite development. Similar to chloroquine and quinine, mefloquine appears to interfere with the parasite's ability to metabolize and utilize erythrocyte hemoglobin. The antimalarial activity of mefloquine may depend on the ability of the drug to form hydrogen bonds with cellular constituents; results of structure-activity studies indicate that the orientation of the hydroxyl and amine groups with respect to each other in the mefloquine molecule may be essential for antimalarial activity. While the precise mechanism of action of mefloquine is unknown, it may involve mechanisms that differ from those proposed for chloroquine., The effects of the antimalarial drug, mefloquine, on the uptake and release of Ca2+ by crude microsomes from dog brain were investigated using a spectrophotometric method. Mefloquine inhibited the inositol-1,4,5-phosphate (IP3)-induced Ca2+ release with an IC50 of 42 uM, but was a weaker inhibitor of the uptake of Ca2+ into the vesicles (IC50: 272 uM). These effects of mefloquine are in contrast to its actions on Ca2+ uptake and release by skeletal muscle microsomes, where its predominant effect was seen to be the inhibition of Ca2+ uptake into the vesicles. Mefloquine was found to be more potent than quinine as a specific inhibitor of Ca2+ release from IP3-sensitive stores in dog brain microsomes. The possibility of the drug affecting cellular IP3-linked signal transduction processes should be considered. | |
| Record name | MEFLOQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/6853 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
51742-87-1, 53230-10-7 | |
| Record name | (+)-Mefloquine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=51742-87-1 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Mefloquine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=53230-10-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | (-)-Mefloquine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0051742871 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Mefloquine [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0053230107 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Mefloquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4037168 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (-)-Mefloquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID101019853 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | MEFLOQUINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/TML814419R | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | MEFLOQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/6853 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
174-176 °C | |
| Record name | MEFLOQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/6853 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
















