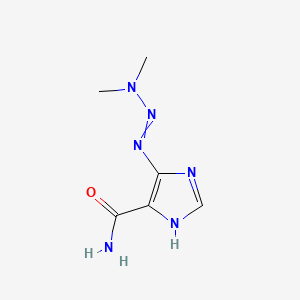
Dacarbazine
Overview
Description
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Dacarbazine is synthesized through a multi-step chemical process. The synthesis begins with the reaction of 5-amino-1H-imidazole-4-carboxamide with nitrous acid to form 5-diazoimidazole-4-carboxamide. This intermediate is then reacted with dimethylamine to yield this compound .
Industrial Production Methods: In industrial settings, this compound is produced in vials containing 100 and 200 milligrams of the drug along with anhydrous citric acid and mannitol. The vials are reconstituted with sterile water for injection to yield solutions containing 10 milligrams per milliliter of this compound . The reconstituted solutions are stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature and up to 96 hours under refrigeration when protected from light .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Dacarbazine undergoes various chemical reactions, including photodegradation, which is influenced by environmental pH . The drug is highly photosensitive, and its photodegradation products can cause adverse reactions such as pain at the injection site, nausea, vomiting, and hepatic toxicity .
Common Reagents and Conditions: The photodegradation of this compound is monitored using UV-Vis absorbance spectra recorded during irradiation by an artificial lighting source. The reaction is influenced by pH levels ranging from 2 to 12 .
Major Products Formed: The major photodegradation product of this compound is 2-azahypoxanthine . Other photoproducts may form depending on the pH and experimental conditions .
Scientific Research Applications
Nanoparticle Delivery Systems
Recent studies have investigated the encapsulation of dacarbazine within solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and other nanocarriers to improve drug delivery specifically to tumor sites while minimizing systemic toxicity.
- Solid Lipid Nanoparticles : A study demonstrated that this compound-loaded SLNs could effectively target melanoma cells with reduced side effects. The SLNs were characterized for their size, stability, and drug release profiles, showing promising results for localized treatment .
- Topical Nanoparticle Formulations : Another approach involved developing a topical formulation using this compound-laden nanoparticles. This method aimed to enhance skin permeation for treating melanoma directly at the site of the tumor .
Clinical Applications
This compound has been evaluated in various clinical settings, demonstrating efficacy in several types of tumors.
- Pancreatic Islet Cell Tumors : A Phase II trial revealed a response rate of 33% among patients with advanced pancreatic islet cell tumors treated with this compound at a dosage of 850 mg/m² every four weeks. The median overall survival was reported at 19.3 months .
- Solitary Fibrous Tumors : A case series involving eight patients treated with this compound indicated its antitumor activity in solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs). Patients received 1,200 mg/m² every three weeks, with positive outcomes observed in tumor volume reduction .
Comparative Effectiveness
Recent analyses have compared this compound to newer agents in terms of cost-effectiveness and clinical outcomes.
- Eribulin vs. This compound : A cost-effectiveness analysis found that eribulin demonstrated longer overall survival compared to this compound in patients with advanced liposarcoma, suggesting it may be a more favorable option despite higher costs .
Safety Profile and Toxicity
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with several adverse effects, including hematological toxicities and gastrointestinal symptoms like vomiting. In clinical trials, severe toxicities were noted but were manageable with appropriate monitoring .
Case Studies and Research Findings
The following table summarizes key findings from notable studies involving this compound:
| Study Focus | Patient Population | Treatment Regimen | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Pancreatic Islet Cells | 50 patients | 850 mg/m² IV every 4 weeks | 33% response rate; median survival 19.3 months |
| Solitary Fibrous Tumors | 8 patients | 1,200 mg/m² every 3 weeks | Demonstrated antitumor activity |
| Nanoparticle Delivery | Melanoma models | This compound-loaded SLNs | Enhanced targeting with reduced side effects |
Mechanism of Action
Dacarbazine is often compared to other alkylating agents such as procarbazine, which has similar chemistry and is used in the treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma . Unlike procarbazine, this compound does not have teratogenic effects, making it a safer option for pediatric patients . Other similar compounds include temozolomide and carmustine, which are also used in cancer therapy but have different mechanisms of action and side effect profiles .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
- Procarbazine
- Temozolomide
- Carmustine
Dacarbazine’s unique properties, such as its specific mechanism of action and reduced teratogenic effects, make it a valuable chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of various cancers.
Biological Activity
Dacarbazine (DTIC) is a chemotherapeutic agent primarily used in the treatment of metastatic melanoma and certain types of lymphoma. Its mechanism of action involves metabolic activation, leading to the formation of reactive metabolites that exert cytotoxic effects on cancer cells. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its mechanisms, efficacy, and potential applications in combination therapies, supported by data tables and relevant case studies.
This compound is an alkylating agent that requires metabolic activation to exert its antitumor effects. The primary metabolic pathway involves cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP2E1, which convert DTIC into its active form. This active metabolite interacts with DNA, leading to cross-linking and subsequent induction of apoptosis in cancer cells .
Efficacy in Cancer Treatment
This compound is FDA-approved for treating melanoma and is often used in combination with other agents. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in various clinical settings:
- Monotherapy : this compound has shown effectiveness as a single agent in treating metastatic melanoma, with response rates around 15-20% .
- Combination Therapy : Studies have indicated that combining this compound with other agents can enhance its therapeutic efficacy. For instance, the combination of this compound with oxyresveratrol exhibited synergistic effects against malignant melanoma cell lines, suggesting a potential for improved outcomes when used together .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Several studies highlight the biological activity and therapeutic potential of this compound:
- This compound-Encapsulated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles : A study investigated the use of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) for delivering this compound to skin melanoma cells. The results indicated enhanced skin permeation and reduced adverse effects compared to conventional formulations. The SLNs demonstrated significant anticancer activity in vivo using a DMBA-induced tumor model .
- Drug Combination Studies : Research on drug combinations involving this compound revealed that pairing it with compounds like imexon can produce additive effects in vitro. However, these effects were not replicated in vivo, highlighting the complexity of drug interactions .
- Metabolic Activation Studies : Investigations into the metabolic pathways of this compound have shown that its activation is crucial for its anticancer effects. The study quantified the activities of various cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in this compound metabolism, providing insights into individual variability in drug response among patients .
Data Tables
The following table summarizes key findings from studies on this compound's biological activity:
| Study Type | Findings |
|---|---|
| Monotherapy Efficacy | Response rates in metastatic melanoma: 15-20% |
| SLN Delivery System | Enhanced skin permeation; significant anticancer activity in DMBA-induced tumor model |
| Drug Combination (Imexon) | Additive effects observed in vitro; no significant effect in vivo |
| Metabolic Pathway Analysis | Key cytochrome P450 enzymes involved: CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2E1; individual variability noted |
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What safety protocols are critical when handling Dacarbazine in preclinical studies?
this compound is classified as a carcinogen (Category 1B) and mutagen (Category 1B) with acute oral toxicity (LD50 ≤ 500 mg/kg). Key protocols include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use impermeable gloves, lab coats, and respiratory protection (e.g., NIOSH-approved masks) to avoid inhalation or dermal exposure .
- Ventilation: Ensure local exhaust ventilation in handling areas to minimize airborne particles .
- Waste Disposal: Follow EPA guidelines for cytotoxic waste, including segregated containers for contaminated materials .
- Long-Term Risks: Rodent studies show carcinogenicity (e.g., breast, lung tumors) after prolonged exposure, necessitating strict institutional biosafety committee oversight .
Q. How does this compound’s monotherapy efficacy in melanoma compare to newer immunotherapies?
In phase III trials, this compound monotherapy achieved a 15–20% response rate in metastatic melanoma, with median overall survival (OS) of 7–9 months . However, newer agents like nivolumab (anti-PD-1) demonstrated superior OS (72.9% vs. 42.1% at 1 year) and progression-free survival (PFS: 5.1 vs. 2.2 months) in BRAF wild-type melanoma . Methodologically, cross-trial comparisons require adjusting for prognostic factors (e.g., PD-L1 status, prior therapies) to contextualize historical controls .
Q. What pharmacokinetic considerations differentiate this compound from its analog temozolomide?
Temozolomide, an oral analog, provides higher systemic exposure to the active metabolite MTIC (AUC 1.5× higher than this compound) due to improved bioavailability. Despite similar median OS (7.7 vs. 6.4 months), temozolomide showed better PFS (1.9 vs. 1.5 months) and quality-of-life metrics in melanoma trials, supporting its use for CNS metastases .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can conflicting OS and PFS outcomes in this compound combination trials be reconciled?
Discrepancies arise from trial design and endpoint selection. For example:
- Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) + this compound: Improved OS (11.2 vs. 9.1 months) despite no PFS benefit, likely due to delayed immune activation .
- Vemurafenib (BRAF inhibitor) vs. This compound: Superior OS (84% vs. 64% at 6 months) correlated with rapid tumor response, but PFS gains were offset by resistance mechanisms .
Methodological solutions include using weighted statistical models (e.g., hazard ratio adjustments) and preplanned subgroup analyses for biomarker-stratified populations .
Q. What methodological frameworks optimize this compound combination therapy trials in sarcoma?
In advanced liposarcoma/leiomyosarcoma, trabectedin outperformed this compound in PFS (4.2 vs. 1.5 months) but not OS (12.4 vs. 12.9 months), highlighting disease control as a clinically relevant endpoint. Trial design should:
- Prioritize PFS or time-to-treatment failure (TTF) for early efficacy signals.
- Include patient-reported outcomes (e.g., symptom burden) to capture clinical benefit beyond survival .
- Use adaptive designs to permit crossover after interim analyses, as seen in vemurafenib trials .
Q. How can biomarkers improve patient stratification for this compound-based therapies?
- BRAF Mutation Status: this compound is ineffective in BRAF V600E melanoma compared to vemurafenib (OS HR: 0.37; P < 0.001) .
- Immune Signatures: Tumors with high tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) may respond better to this compound + ipilimumab, as CTLA-4 blockade enhances T-cell activity .
- Methylation Status: MGMT promoter methylation predicts temozolomide sensitivity but not this compound, necessitating separate biomarker panels .
Q. What experimental models best recapitulate this compound resistance mechanisms?
- In Vivo Models: Syngeneic mouse melanoma (e.g., B16-F10) with BRAF WT status for testing immune checkpoint combinations .
- 3D Tumor Spheroids: Mimic hypoxic microenvironments that upregulate DNA repair enzymes (e.g., O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase), reducing alkylating agent efficacy .
- Patient-Derived Xenografts (PDXs): Capture interpatient heterogeneity in drug metabolism and resistance pathways .
Q. How should RECIST criteria be adapted for this compound combination therapies?
Immune-related response patterns (e.g., pseudoprogression) require modified criteria:
- iRECIST: Incorporates confirmation scans ≥4 weeks post-initial progression to distinguish pseudoprogression from true resistance .
- Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs): Grade 3/4 irAEs (e.g., colitis, hepatitis) in 10–15% of ipilimumab + this compound trials necessitate parallel safety monitoring .
Q. Methodological Resources
- Trial Design: Use factorial designs (e.g., 2×2 for combination testing) with preplanned interim analyses for early stopping .
- Data Analysis: Apply inverse probability weighting to adjust for cross-trial differences in patient populations .
- Safety Reporting: Align with NIH Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 for standardized toxicity grading .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
4-(dimethylaminodiazenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H10N6O/c1-12(2)11-10-6-4(5(7)13)8-3-9-6/h3H,1-2H3,(H2,7,13)(H,8,9) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FDKXTQMXEQVLRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)N=NC1=C(NC=N1)C(=O)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C6H10N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0020369 | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020369 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
182.18 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Dacarbazine appears as white to ivory microcrystals or off-white crystalline solid. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Details | National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 0.1 mg/mL at 59 °F (NTP, 1992), Water: (1 mg/ml at room temp), 1.36e+00 g/L | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Dacarbazine functions as an alkylating agent after metabolic activation in the liver. It appears to inhibit the synthesis of RNA and protein more than it inhibits the synthesis of DNA. It kills cells slowly, and there appears to be no phase of the cell cycle in which sensitivity is increased ... ., ...FOR CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC EFFECTIVENESS, DACARBAZINE REQUIRES INITIAL ACTIVATION BY CYTOCHROME P450 SYSTEM OF LIVER THROUGH N-DEMETHYLATION REACTION. IN TARGET CELL...OCCURS SPONTANEOUS CLEAVAGE LIBERATING AIC /5-AMINOIMIDAZOLE-4-CARBOXAMIDE/ & ALKYLATING MOIETY, PRESUMABLY DIAZOMETHANE..., Although the mechanism of action of dacarbazine is not known in detail, it is demethylated by liver microsomal enzymes to form an unstable monoalkyl derivative which can decompose spontaneously into alkylating moieties. In light, dacarbazine can also rapidly undergo chemical decomposition to form 4-diazoimidazole-5-carboxamide, which is highly toxic but which has no antitumor activity in vivo ... . | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 209 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
IVORY MICROCRYSTALINE SUBSTANCE | |
CAS No. |
4342-03-4 | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=4342-03-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020369 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.022.179 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
482 to 491 °F (explosively decomposes) (NTP, 1992), 205 °C, Melting point: 250-255 °C (explosive decomposition) | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















