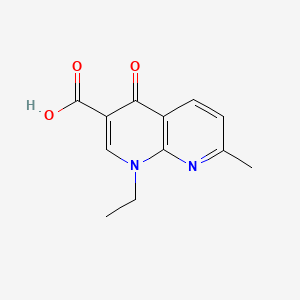
Ácido nalidíxico
Descripción general
Descripción
- El ácido nalidíxico, también conocido por sus nombres comerciales Nevigramon, NegGram, Wintomylon y WIN 18,320, es el primer antibiótico quinolónico sintético.
- Técnicamente, pertenece a la clase de las naftiridonas en lugar de la clase de las quinolonas. Su estructura cíclica es un núcleo de 1,8-naftiridina que contiene dos átomos de nitrógeno, a diferencia de la quinolina, que solo tiene un átomo de nitrógeno .
Mecanismo De Acción
- El ácido nalidíxico inhibe la ADN girasa bacteriana (topoisomerasa II), evitando la replicación y transcripción del ADN.
- Interfiere con la superenrollamiento del ADN, lo que lleva a la muerte celular.
- Los objetivos moleculares del compuesto son las topoisomerasas bacterianas .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Clinical Applications
1.1 Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
Nalidixic acid is primarily used for treating urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible gram-negative microorganisms. It is particularly effective against Escherichia coli, Enterobacter species, and Proteus species. The drug operates effectively across a wide urinary pH range, making it suitable for various patient populations .
1.2 Systemic Infections
In addition to UTIs, nalidixic acid has been administered intravenously for systemic infections, especially those involving the urinary tract . Its bactericidal properties are most potent at concentrations between 50 to 200 µg/ml, effectively inhibiting DNA synthesis in bacteria .
Resistance Patterns
3.1 Emergence of Resistance
Resistance to nalidixic acid has been documented among various bacterial strains. A study indicated that approximately 38.5% of isolated strains from blood samples showed resistance to nalidixic acid . This resistance is concerning as it reflects broader trends in antibiotic resistance among hospital-associated organisms.
3.2 Monitoring Resistance
Monitoring nalidixic acid susceptibility is crucial in understanding resistance patterns to other antibiotics like ciprofloxacin. In regions such as the Indian Subcontinent, nalidixic acid susceptibility testing has served as an effective method for tracking ciprofloxacin resistance among Salmonella strains .
Case Studies and Research Findings
4.1 Clinical Case Reports
A notable case reported transient hyperglycemia and glycosuria following an overdose of nalidixic acid, highlighting potential side effects that clinicians should monitor during treatment .
4.2 Synergistic Effects with Other Antibiotics
Recent research has explored the synergistic effects of nalidixic acid when combined with tetracycline against multi-drug resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii and E. coli. This combination demonstrated enhanced efficacy in both in vitro and in vivo models, suggesting potential therapeutic strategies to combat resistant infections .
Data Tables
| Application Area | Bacterial Targets | Resistance Rates | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urinary Tract Infections | E. coli, Enterobacter, Proteus | 2-14% during treatment | Inhibition of DNA gyrase |
| Systemic Infections | Various gram-negative bacteria | 38.5% resistance noted | Interference with DNA/RNA/protein synthesis |
| Combination Therapy | Multi-drug resistant A. baumannii, E. coli | Varies by strain | Synergistic action with tetracycline |
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Nalidixic acid plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by targeting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes essential for DNA replication and transcription. By inhibiting these enzymes, nalidixic acid prevents the supercoiling and uncoiling of bacterial DNA, thereby halting DNA synthesis. This interaction is specific to bacterial enzymes, making nalidixic acid effective against bacterial infections while having minimal impact on human cells .
Cellular Effects
Nalidixic acid exerts significant effects on various types of cells, particularly bacterial cells. It disrupts cell function by inhibiting DNA synthesis, leading to cell death. In bacterial cells, nalidixic acid affects cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism. The inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV results in the accumulation of DNA breaks, which triggers the bacterial SOS response and ultimately leads to cell death .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of nalidixic acid involves its binding to the A subunit of DNA gyrase and the C subunit of topoisomerase IV. This binding interferes with the enzymes’ ability to introduce negative supercoils into DNA, which is essential for DNA replication and transcription. By stabilizing the DNA-enzyme complex, nalidixic acid prevents the re-ligation of DNA strands, leading to the accumulation of DNA breaks and inhibition of bacterial growth .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of nalidixic acid change over time. Initially, nalidixic acid rapidly inhibits DNA synthesis, leading to a decrease in bacterial growth. Over time, the stability and degradation of nalidixic acid can influence its effectiveness. Studies have shown that nalidixic acid is relatively stable under laboratory conditions, but prolonged exposure can lead to the development of bacterial resistance .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of nalidixic acid vary with different dosages in animal models. At therapeutic doses, nalidixic acid effectively treats bacterial infections without causing significant toxicity. At high doses, nalidixic acid can exhibit toxic effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances and central nervous system toxicity. Threshold effects have been observed, where increasing the dosage beyond a certain point does not significantly enhance its antibacterial activity but increases the risk of adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Nalidixic acid is metabolized in the liver, primarily through hydroxylation to form hydroxynalidixic acid. This metabolite retains antibacterial activity and contributes to the overall effectiveness of nalidixic acid. The metabolic pathways involve enzymes such as cytochrome P450, which facilitate the conversion of nalidixic acid to its active metabolite. The presence of hydroxynalidixic acid in the bloodstream ensures sustained antibacterial activity .
Transport and Distribution
Nalidixic acid is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through passive diffusion. It can cross cell membranes and accumulate in bacterial cells, where it exerts its antibacterial effects. The distribution of nalidixic acid within tissues is influenced by factors such as blood flow and tissue permeability. Transporters and binding proteins may also play a role in the cellular uptake and distribution of nalidixic acid .
Subcellular Localization
Nalidixic acid primarily localizes in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells, where it interacts with DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. The subcellular localization of nalidixic acid is crucial for its antibacterial activity, as it needs to reach its target enzymes to inhibit DNA synthesis. Post-translational modifications and targeting signals may influence the localization and activity of nalidixic acid within bacterial cells .
Métodos De Preparación
- El ácido nalidíxico se sintetiza a partir de 2-metilpiridina para formar 2-amino-5-metilpiridina.
- El último compuesto se condensa luego con formiato de etilo y oxalato de dietilo para producir N-(2-metil-5-amino-piridina)metilen malonato.
- La ciclación a 260-270 °C seguida de hidrólisis con hidróxido de sodio produce ácido 7-metil-1,8-naftiridina-4-hidroxi-3-carboxílico.
- Finalmente, la N-alquilación con bromoetano conduce al ácido nalidíxico .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
- El ácido nalidíxico exhibe actividad antibacteriana contra bacterias gramnegativas y algunas grampositivas.
- Actúa bacteriostáticamente a concentraciones más bajas y bactericidamente a concentraciones más altas.
- Las reacciones comunes incluyen hidrólisis, alquilación y oxidación.
- Los principales productos formados incluyen ácido 7-metil-1,8-naftiridina-4-hidroxi-3-carboxílico y sus derivados .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
- El ácido nalidíxico es único debido a su estructura de naftiridona.
- Compuestos similares incluyen otras quinolonas como ciprofloxacina, levofloxacina y moxifloxacina .
Actividad Biológica
Nalidixic acid, a synthetic antibacterial agent belonging to the quinolone class, was first introduced in the 1960s. It primarily exhibits activity against gram-negative bacteria, making it a critical compound in the treatment of urinary tract infections and other bacterial infections. This article explores its biological activity, mechanisms of action, and relevant case studies, providing a comprehensive overview of its role in antibacterial therapy.
Nalidixic acid acts primarily by inhibiting bacterial DNA synthesis. It targets the enzyme DNA gyrase, which is crucial for DNA replication and transcription in bacteria. The inhibition of DNA gyrase leads to the disruption of DNA supercoiling, a necessary process for proper DNA function.
Key Findings:
- Bactericidal Concentration : Nalidixic acid exhibits optimal bactericidal activity against various gram-negative species at concentrations ranging from 50 to 200 µg/ml. At concentrations above this range, it tends to become bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal .
- Inhibition of Synthesis : Studies have shown that nalidixic acid inhibits deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis without affecting ribonucleic acid (RNA) or protein synthesis at lower concentrations. However, at higher concentrations, it can inhibit both RNA and protein synthesis as well .
In Vitro Studies
Research has demonstrated nalidixic acid's effectiveness against several bacterial strains:
| Bacterial Strain | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) |
|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | 1-4 µg/ml |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 16-32 µg/ml |
| Salmonella typhi | 4-8 µg/ml |
These findings highlight nalidixic acid's potency against enteric pathogens and its role in treating infections caused by these organisms .
Case Studies
- Urinary Tract Infections : A study involving patients with recurrent urinary tract infections revealed that nalidixic acid was effective in reducing bacterial load and improving clinical outcomes. The study reported a significant decrease in Escherichia coli counts post-treatment .
- Resistance Patterns : Recent data indicate a concerning trend in resistance among gram-negative bacteria to nalidixic acid. For instance, a retrospective analysis showed that 38.5% of isolated strains from blood cultures demonstrated resistance to nalidixic acid, suggesting an increasing prevalence of multi-drug-resistant organisms .
Comparative Studies with New Quinolones
Nalidixic acid has been compared with newer quinolone derivatives like ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin:
| Antibiotic | Activity Against Gram-Negative Bacteria | Activity Against Gram-Positive Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Nalidixic Acid | Moderate | Low |
| Ciprofloxacin | High | Moderate |
| Norfloxacin | High | Low |
Newer quinolones exhibit superior antibacterial activity due to their improved pharmacokinetic properties and broader spectrum of action against resistant strains .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
1-ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H12N2O3/c1-3-14-6-9(12(16)17)10(15)8-5-4-7(2)13-11(8)14/h4-6H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,16,17) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MHWLWQUZZRMNGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCN1C=C(C(=O)C2=C1N=C(C=C2)C)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H12N2O3 | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20720 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
3374-05-8 (hydrochloride salt, anhydrous) | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000389082 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID3020912 | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3020912 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
232.23 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Nalidixic acid is a cream-colored powder. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20720 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic Acid | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014917 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 1 mg/mL at 70 °F (NTP, 1992), Soly at 23 °C (mg/ml): chloroform 35; toluene 1.6; methanol 1.3; ethanol 0.6; water 0.1; ether 0.1., PRACTICALLY INSOL IN WATER; SOL IN SOLN OF CARBONATES, 2.30e+00 g/L | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20720 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00779 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3241 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic Acid | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014917 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Evidence exists for Nalidixic acid that its active metabolite, hydroxynalidixic acid, binds strongly, but reversibly, to DNA, interfering with synthesis of RNA and, consequently, with protein synthesis., IT APPEARS TO ACT BY INHIBITING DNA SYNTH. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00779 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3241 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
PALE BUFF, CRYSTALLINE POWDER, WHITE TO SLIGHTLY YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER | |
CAS No. |
389-08-2 | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20720 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=389-08-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000389082 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00779 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757432 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=82174 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3020912 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.006.241 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/3B91HWA56M | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3241 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic Acid | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014917 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
444 to 446 °F (NTP, 1992), 229-230 °C, 229.5 °C | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20720 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic acid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00779 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NALIDIXIC ACID | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3241 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nalidixic Acid | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014917 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details






















Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













