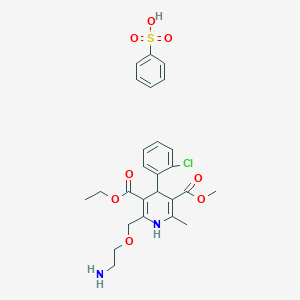
Amlodipino besilato
Descripción general
Descripción
El amlodipino besilato es un bloqueador de los canales de calcio que se utiliza principalmente para tratar la presión arterial alta y la angina de pecho. Es un antagonista de los canales de calcio de tipo dihidropiridina de acción prolongada que funciona relajando los vasos sanguíneos, lo que permite que la sangre fluya más fácilmente. Este compuesto se prescribe ampliamente debido a su eficacia y su perfil de efectos secundarios relativamente leve .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
El amlodipino besilato tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Medicina: Se ha investigado ampliamente por sus efectos terapéuticos en el tratamiento de la hipertensión y la angina.
Industria: Se utiliza en la formulación de varios productos farmacéuticos debido a su estabilidad y eficacia.
Mecanismo De Acción
El amlodipino besilato ejerce sus efectos inhibiendo la entrada transmembrana de iones calcio en el músculo liso vascular y el músculo cardíaco. Esta inhibición se produce mediante el bloqueo de los canales de calcio de tipo L, lo que lleva a la vasodilatación y la reducción de la presión arterial . Los objetivos moleculares incluyen los canales de calcio de tipo L, y las vías involucradas están relacionadas principalmente con la señalización de calcio y la relajación del músculo liso vascular .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Amlodipine besylate interacts with calcium channels in the small arterioles, leading to arterial dilation . It has antioxidant properties and an ability to enhance the production of nitric oxide (NO), an important vasodilator that decreases blood pressure .
Cellular Effects
Amlodipine besylate has a dilating effect on peripheral arterioles, reducing the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the cardiac muscle functions . This reduced work of the heart decreases both myocardial energy use and oxygen requirements .
Molecular Mechanism
Amlodipine besylate is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle . This inhibition of calcium influx leads to arterial dilation, reducing blood pressure .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Amlodipine besylate has been shown to have good efficacy and safety, with strong evidence from large randomized controlled trials for cardiovascular event reduction . The effects of amlodipine besylate are long-lasting, with the option for single daily dosing .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, amlodipine besylate has been shown to have various side effects. In cats, these may include vomiting, diarrhea, lack of appetite, or sleepiness. In dogs, side effects may include gingival (gum) overgrowth .
Metabolic Pathways
Amlodipine besylate is metabolized in the liver, primarily via dehydrogenation of its dihydropyridine moiety to a pyridine derivative . This metabolism is thought to be mediated by CYP3A4/5 .
Transport and Distribution
Amlodipine besylate is well absorbed after oral administration and is highly protein-bound (93%) . It is distributed widely in the body due to its lipophilic nature .
Subcellular Localization
Amlodipine besylate readily penetrates the plasma membrane and accumulates in the intracellular vesicles . Its visible emission and photostability allow for confocal time-lapse imaging and the monitoring of drug uptake .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas de síntesis y condiciones de reacción
La síntesis de amlodipino besilato implica varios pasos. El intermedio clave, amlodipina, se sintetiza a través de un proceso de varios pasos que comienza con el 2-clorobenzaldehído. El paso final implica la reacción de amlodipina con ácido bencensulfónico para formar this compound .
Paso 1: Condensación de 2-clorobenzaldehído con acetoacetato de etilo en presencia de amoníaco para formar 2-clorobencilideno acetoacetato de etilo.
Paso 2: Ciclación del intermedio con metilamina para formar 2-clorofenil-1,4-dihidropiridina.
Paso 3: Alquilación de la dihidropiridina con 2-(2-aminoetoxi)etanol para formar amlodipina.
Paso 4: Reacción de amlodipina con ácido bencensulfónico para formar this compound
Métodos de producción industrial
La producción industrial de this compound sigue rutas sintéticas similares, pero se optimiza para la producción a gran escala. El proceso implica el uso de granuladores de mezcla de alta eficiencia y técnicas de granulación en seco para asegurar un alto rendimiento y pureza .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
El amlodipino besilato se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción son menos comunes, pero se pueden realizar en condiciones específicas.
Sustitución: El this compound puede sufrir reacciones de sustitución, particularmente en el anillo aromático.
Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen peróxido de hidrógeno para la oxidación y borohidruro de sodio para la reducción. Los principales productos formados dependen de las condiciones de reacción específicas, pero a menudo incluyen varios derivados de amlodipina .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
El amlodipino besilato a menudo se compara con otros bloqueadores de los canales de calcio como la nifedipina, la felodipina y el verapamilo.
Nifedipina: Similar en su mecanismo de acción, pero tiene una vida media más corta y requiere dosis más frecuentes
Felodipina: También es un bloqueador de los canales de calcio de tipo dihidropiridina, pero difiere en su perfil farmacocinético y su perfil de efectos secundarios
Verapamilo: Un bloqueador de los canales de calcio no dihidropiridina que afecta tanto al músculo liso vascular como al músculo cardíaco, lo que lleva a una gama más amplia de efectos terapéuticos, pero también a más efectos secundarios potenciales
El this compound es único debido a su larga vida media, lo que permite una dosis única diaria, y su perfil de efectos secundarios relativamente leve .
Actividad Biológica
Amlodipine besylate is a widely used third-generation dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker primarily indicated for the treatment of hypertension and angina. This article explores its biological activity, pharmacokinetics, efficacy in clinical settings, and potential therapeutic applications based on diverse research findings.
Pharmacokinetics
Amlodipine is characterized by its slow absorption and prolonged half-life, which contributes to its effectiveness in managing blood pressure. Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Bioavailability : Approximately 64-90% .
- Peak Plasma Concentration (C_max) : Achieved 6-12 hours post-administration .
- Volume of Distribution : 21 L/kg .
- Protein Binding : About 98% .
- Half-Life (t_1/2) : Ranges from 30 to 50 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing .
The metabolism of amlodipine occurs primarily in the liver, where it is converted to inactive metabolites. Approximately 90% of the drug undergoes hepatic metabolism, with only 10% excreted unchanged in urine .
Efficacy in Hypertension Management
Amlodipine has been shown to effectively reduce systolic blood pressure (BP) across various patient populations. A retrospective study involving 1,175 hypertensive adults demonstrated significant reductions in systolic BP after initiating amlodipine therapy:
| Previous Antihypertensive Drugs | Adjusted Systolic BP Change (mm Hg) | BP Goal Attainment (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -16.1 (95% CI: -17.9, -14.3) | 39 |
| 1 | -17.6 (95% CI: -19.6, -15.5) | 45 |
| 2 | -16.7 (95% CI: -19.0, -14.5) | 41 |
| ≥3 | -15.7 (95% CI: -18.7, -12.8) | 45 |
This study concluded that amlodipine could be effective as monotherapy or as an add-on treatment with other antihypertensive agents .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
-
Bioequivalence Studies :
A study assessing the bioequivalence of a new dispersible amlodipine formulation compared to a standard tablet showed that both formulations were well tolerated and met regulatory criteria for bioequivalence based on pharmacokinetic parameters such as C_max and AUC . -
SARS-CoV-2 Inhibition :
Recent research indicates that amlodipine besylate may inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro, suggesting potential applications beyond cardiovascular therapy. In studies involving Vero E6 cells, amlodipine demonstrated significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 with a calculated half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) lower than other calcium channel blockers tested .
Safety Profile
Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated; however, some adverse effects have been reported:
- Common Adverse Reactions :
- Edema: 8.9%
- Headache: 8.3%
- Dizziness: 3.0%
In clinical trials involving over 800 hypertensive patients, approximately 29.9% reported adverse effects, with only a small percentage requiring discontinuation due to side effects .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
benzenesulfonic acid;3-O-ethyl 5-O-methyl 2-(2-aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H25ClN2O5.C6H6O3S/c1-4-28-20(25)18-15(11-27-10-9-22)23-12(2)16(19(24)26-3)17(18)13-7-5-6-8-14(13)21;7-10(8,9)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h5-8,17,23H,4,9-11,22H2,1-3H3;1-5H,(H,7,8,9) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ZPBWCRDSRKPIDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C2=CC=CC=C2Cl)C(=O)OC)C)COCCN.C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C26H31ClN2O8S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2043909 | |
| Record name | Amlodipine besylate | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2043909 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
567.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
111470-99-6 | |
| Record name | Amlodipine besylate | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=111470-99-6 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Amlodipine besylate [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0111470996 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | AMLODIPINE BESYLATE | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=758922 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Amlodipine besylate | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2043909 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Amlodipine besylate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | AMLODIPINE BESYLATE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/864V2Q084H | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
A: Amlodipine besylate acts as a potent calcium channel blocker, specifically targeting L-type calcium channels. [, , ] This inhibition reduces the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells. [, ] By limiting calcium availability, amlodipine besylate promotes vasodilation, reducing peripheral vascular resistance and ultimately lowering blood pressure. [, , , , , ] It also demonstrates efficacy in managing angina pectoris by preventing coronary artery spasm. [, , ]
A: The primary downstream effect of amlodipine besylate's inhibition of calcium channels is vasodilation, leading to reduced peripheral vascular resistance and decreased blood pressure. [, , , , , ] This effect is particularly beneficial in treating hypertension. Additionally, by inhibiting calcium influx into cardiac muscle cells, amlodipine besylate can help manage angina pectoris by preventing coronary artery spasm. [, , ]
A: Amlodipine besylate has the molecular formula C20H25ClN2O5·C6H6O3S, representing the besylate salt form of amlodipine. Its molecular weight is 567.1 g/mol. [, , , ]
A: Research indicates that amlodipine besylate exhibits a maximum absorbance wavelength (λmax) around 237 nm in methanol, making UV spectrophotometry a suitable analytical technique. [, , , , ] Furthermore, FTIR and 1H-NMR spectroscopy provide valuable insights into the structural features of amlodipine besylate and its inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins. []
A: Amlodipine besylate exhibits limited water solubility, which presents challenges for its bioavailability. [, ] To address this, researchers have explored various approaches, such as solid dispersion techniques utilizing polymers like polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000 and PEG 6000. [] These techniques aim to enhance the drug's dissolution rate and improve its bioavailability, ultimately enhancing its therapeutic efficacy.
A: While generally stable in solid formulations, studies indicate potential incompatibility of amlodipine besylate with certain excipients. For example, the presence of lactose, magnesium stearate, and water in formulations can trigger instability, leading to the formation of a glycosyl degradation product through the Maillard reaction. [] This highlights the importance of careful excipient selection during formulation development to ensure drug stability and product quality.
A: Research has investigated the stability of compounded amlodipine besylate suspensions in specific pharmaceutical bases. One study demonstrated that amlodipine besylate remains physically and chemically stable in PCCA Base, SuspendIt, for 90 days under refrigeration (5°C) and 7 days at room temperature (25°C). [] This finding suggests that compounded suspensions can be a viable option for patients requiring alternative dosage forms, provided they adhere to the established beyond-use dates.
A: Researchers utilize a range of analytical methods for the quantification of amlodipine besylate in various matrices. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with various detectors like UV-Vis, diode array detectors (DAD), and mass spectrometry (MS) is widely employed for simultaneous estimation of amlodipine besylate in combination with other drugs. [, , , , , , , , , ] Additionally, UV spectrophotometry, particularly when coupled with techniques like absorption factor method and first-order derivative spectrophotometry, offers a simple and cost-effective approach for analyzing amlodipine besylate in pharmaceutical formulations. [, , ] Furthermore, High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) with densitometric detection proves valuable for simultaneous estimation in combined dosage forms. [, , ]
A: Analytical methods for amlodipine besylate undergo rigorous validation procedures following ICH guidelines to ensure accuracy, precision, specificity, and sensitivity. [, , , , , , , , , , , ] Researchers meticulously evaluate method performance parameters such as linearity, accuracy, precision, robustness, limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantification (LOQ) to demonstrate the suitability of the chosen technique for its intended application.
A: Researchers have investigated the combined use of amlodipine besylate with other drugs to address specific clinical challenges. For example, studies have explored the efficacy of combining amlodipine besylate with valsartan in elderly patients with hypertension, demonstrating promising results in blood pressure control. [] Similarly, combining amlodipine besylate with Ambovir has shown potential in managing renal hypertension, effectively reducing urinary protein, serum creatinine, and blood uric acid levels. []
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













