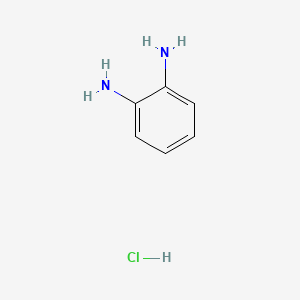
Benzene-o-diamine monohydrochloride
Descripción general
Descripción
Benzene-o-diamine monohydrochloride is a useful research compound. Its molecular formula is C6H9ClN2 and its molecular weight is 144.60 g/mol. The purity is usually 95%.
BenchChem offers high-quality this compound suitable for many research applications. Different packaging options are available to accommodate customers' requirements. Please inquire for more information about this compound including the price, delivery time, and more detailed information at [email protected].
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Common Synthetic Routes
- Hydrochlorination of o-Phenylenediamine : This method involves treating o-phenylenediamine with hydrochloric acid to yield the monohydrochloride salt.
- Condensation Reactions : Benzene-o-diamine can react with various aldehydes and ketones to form valuable organic compounds such as benzimidazoles, which are important in medicinal chemistry.
Organic Synthesis
Benzene-o-diamine monohydrochloride serves as a versatile building block in organic synthesis. It participates in various condensation reactions leading to the formation of complex molecules.
- Benzimidazole Derivatives : It condenses with carboxylic acids to produce benzimidazole derivatives, which have applications in drug development and agrochemicals .
| Reaction Type | Product | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Condensation with carboxylic acids | Benzimidazoles | Pharmaceuticals |
| Reaction with aldehydes | 2-substituted benzimidazoles | Anticancer agents |
Pharmaceutical Applications
This compound is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for synthesizing various drugs. Its derivatives exhibit a range of biological activities including:
- Anticancer Properties : Compounds derived from benzene-o-diamine have shown potential in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation .
- Antimicrobial Activity : Certain derivatives demonstrate significant antimicrobial effects against bacteria and fungi, making them candidates for developing new antibiotics.
Dye Manufacturing
The compound is also utilized in the dye industry due to its ability to form colored complexes with metals. It is particularly effective in producing azo dyes, which are widely used in textiles.
Case Study 1: Anticancer Activity
A study evaluated the anticancer properties of benzene-o-diamine derivatives against various cancer cell lines. The results indicated that specific derivatives inhibited cell growth significantly:
- Cell Lines Tested : A549 (lung adenocarcinoma), C6 (rat glioma).
- Inhibition Rates : Some derivatives achieved over 70% inhibition at specific concentrations.
Case Study 2: Antimicrobial Efficacy
Research focused on the incorporation of benzene-o-diamine derivatives into polymer matrices for dental applications showed promising results:
- Microbial Strains Tested : Candida albicans.
- Concentration Levels : Formulations containing 3% and 5% of the compound led to a reduction of fungal colonies by up to 3 log units compared to control groups.
Propiedades
Número CAS |
39145-59-0 |
|---|---|
Fórmula molecular |
C6H9ClN2 |
Peso molecular |
144.60 g/mol |
Nombre IUPAC |
benzene-1,2-diamine;hydrochloride |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H8N2.ClH/c7-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8;/h1-4H,7-8H2;1H |
Clave InChI |
GNNALEGJVYVIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES canónico |
C1=CC=C(C(=C1)N)N.Cl |
Origen del producto |
United States |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details












Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.














