Troglitazone
Vue d'ensemble
Description
La troglitazone est un médicament antidiabétique et anti-inflammatoire appartenant à la classe des thiazolidinediones. Il a été initialement développé pour traiter le diabète de type 2 en améliorant la sensibilité à l’insuline. La this compound a été brevetée en 1983 et approuvée pour un usage médical en 1997. Elle a été retirée du marché en 2000 en raison de son association avec une hépatotoxicité grave .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Troglitazone is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used to manage type II diabetes, also known as noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult-onset diabetes . It is not chemically or functionally related to sulfonylureas, biguanides, or g-glucosidase inhibitors . It was withdrawn from the US, European, and Japanese markets in 2000 due to idiosyncratic hepatic reactions leading to hepatic failure and death .
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
This compound improves metabolic control in individuals with NIDDM and enhances insulin action . It can be used concomitantly with a sulfonylurea or insulin to improve glycemic control .
Effects on Metabolic Parameters
- Fasting Plasma Insulin this compound has been shown to lower fasting plasma insulin concentrations by 12-26% compared to a placebo .
- Insulin Sensitivity It increases insulin sensitivity, which can be assessed by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) .
- Serum Lipids this compound can significantly lower serum triglyceride and non-esterified fatty acid concentrations and increase HDL cholesterol at specific doses . LDL cholesterol increases at 400 and 600 mg doses but not at 800 mg once daily or 400 mg twice daily, while the LDL/HDL ratio does not change during treatment .
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes
This compound can reduce the incidence of diabetes, but this action may not persist after its use is discontinued . In one study, this compound reduced the development of diabetes by 75% compared to placebo .
Diabetic Neuropathy
This compound has shown benefits in diabetic neuropathy by decreasing inflammatory markers .
Adverse Events
In clinical trials, the incidence of adverse events in this compound-treated patients was no higher than in those treated with a placebo . However, a tendency to reduce neutrophil counts has been observed in patients taking the highest doses of this compound .
Liver Failure
This compound was withdrawn from the market due to reports of idiosyncratic hepatic reactions, leading to hepatic failure and death . Ninety-four cases of liver failure (89 acute, 5 chronic) were reported .
Comparison with Other Anti-diabetic Drugs
Mécanisme D'action
La troglitazone exerce ses effets en activant les récepteurs activés par les proliférateurs de peroxysomes (PPAR), en particulier le PPARγ et, dans une moindre mesure, le PPARα. Ces récepteurs nucléaires régulent la transcription des gènes impliqués dans le métabolisme du glucose et des lipides. La this compound diminue la production hépatique de glucose et augmente l’élimination du glucose dépendante de l’insuline dans le muscle squelettique. De plus, elle possède des propriétés anti-inflammatoires en réduisant l’activité du facteur nucléaire kappa-B (NF-κB) et en augmentant son inhibiteur (IκB) .
Composés Similaires :
Pioglitazone : Une autre thiazolidinedione ayant un mécanisme d’action similaire, mais un meilleur profil de sécurité.
Rosiglitazone : Semblable à la pioglitazone, elle active le PPARγ, mais elle a été associée à des risques cardiovasculaires .
Unicité : La this compound a été la première thiazolidinedione introduite pour un usage clinique, ce qui en fait un pionnier dans cette classe de médicaments. Sa structure unique comprend un cycle chromane, qui n’est pas présent dans les autres thiazolidinediones. Malgré son retrait, la this compound a fourni des informations précieuses pour le développement de médicaments antidiabétiques plus sûrs et plus efficaces .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Troglitazone works by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). It is a ligand to both PPARα and – more strongly – PPARγ . This compound also contains an α-Tocopherol moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity in addition to its PPAR activation . It has been shown to reduce inflammation . This compound decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle .
Cellular Effects
This compound improves insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes by facilitating glucose transport activity, which thereby leads to increased rates of muscle glycogen synthesis and glucose oxidation . This compound has been shown to induce apoptosis in various hepatic and nonhepatic cells .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound’s mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin-responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism . This compound is a ligand to both PPARα and PPARγ, with a higher affinity for PPARγ .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, this compound was found to significantly improve HbA1c and fasting serum glucose, while lowering insulin and C-peptide in patients with type 2 diabetes . No signs of hepatotoxicity were apparent at 2 weeks of treatment .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
Prolonged administration of this compound can superimpose oxidant stress, potentiate mitochondrial damage, and induce delayed hepatic necrosis in mice with genetically compromised mitochondrial function .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle . Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin-responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism .
Transport and Distribution
This compound contains the structure of a unique chroman ring of vitamin E, and this structure has the potential to undergo metabolic biotransformation to form quinone metabolites, phenoxy radical intermediate, and epoxide species .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action involving nuclear receptors (PPAR), it can be inferred that this compound likely interacts with these receptors in the cell nucleus .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de Synthèse et Conditions de Réaction : La synthèse de la troglitazone implique plusieurs étapes clés :
Formation du Cycle Thiazolidinedione : Ceci est généralement réalisé en faisant réagir la thiazolidine-2,4-dione avec un halogénure de benzyle approprié en conditions basiques.
Fixation du Cycle Chromane : Le cycle chromane, qui est un analogue structurel de la vitamine E, est introduit par une réaction de substitution nucléophile impliquant un dérivé chromane approprié et l’intermédiaire de thiazolidinedione benzylé.
Assemblage Final : Le produit final est obtenu en purifiant les composés intermédiaires et en effectuant les modifications chimiques nécessaires pour obtenir la structure souhaitée .
Méthodes de Production Industrielle : La production industrielle de la this compound suit des voies de synthèse similaires, mais à plus grande échelle. Le processus implique l’optimisation des conditions de réaction pour maximiser le rendement et la pureté tout en minimisant les sous-produits. Des techniques de pointe telles que la chromatographie liquide haute performance (HPLC) sont utilisées pour la purification .
Types de Réactions :
Oxydation : La this compound subit des réactions d’oxydation, en particulier dans le foie, conduisant à la formation de métabolites réactifs.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction sont moins fréquentes mais peuvent se produire dans des conditions spécifiques.
Substitution : Les réactions de substitution nucléophile sont impliquées dans la synthèse de la this compound .
Réactifs et Conditions Communs :
Agents Oxydants : Enzymes du cytochrome P450 dans le foie.
Agents Réducteurs : Agents réducteurs spécifiques dans des conditions contrôlées.
Nucléophiles : Divers nucléophiles utilisés dans le processus de synthèse .
Principaux Produits :
Métabolites Réactifs : Formés lors de l’oxydation, contribuant à l’hépatotoxicité.
Métabolites Stables : Formés lors de processus métaboliques .
4. Applications de la Recherche Scientifique
La this compound a fait l’objet de nombreuses études pour ses applications dans divers domaines :
Chimie : Utilisée comme composé modèle pour étudier la chimie des thiazolidinediones et ses interactions avec d’autres molécules.
Biologie : Investigée pour ses effets sur les processus cellulaires, notamment l’apoptose et la régulation du cycle cellulaire.
Médecine : Initialement utilisée pour traiter le diabète de type 2 en améliorant la sensibilité à l’insuline.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Pioglitazone: Another thiazolidinedione with a similar mechanism of action but a better safety profile.
Rosiglitazone: Similar to pioglitazone, it activates PPARγ but has been associated with cardiovascular risks.
Uniqueness: Troglitazone was the first thiazolidinedione introduced for clinical use, making it a pioneer in this drug class. Its unique structure includes a chroman ring, which is not present in other thiazolidinediones. Despite its withdrawal, this compound provided valuable insights into the development of safer and more effective antidiabetic drugs .
Activité Biologique
Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione (TZD) and was the first drug approved in this class for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Its primary mechanism of action involves the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), which plays a crucial role in glucose and lipid metabolism. Despite its initial promise, this compound was withdrawn from the market due to severe liver toxicity. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, including its pharmacokinetics, effects on insulin sensitivity, and adverse events.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits unique pharmacokinetic properties that influence its clinical use:
- Absorption : this compound is rapidly absorbed with an absolute bioavailability of 40-50%. Food intake can increase absorption by 30-80% .
- Metabolism : The drug undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism, primarily through sulfation and glucuronidation, resulting in several metabolites, including M1 (sulfate conjugate) and M3 (quinone metabolite) .
- Half-life : The mean elimination half-life ranges from 7.6 to 24 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing .
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of this compound
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | 40-50% |
| Food effect | Increases by 30-80% |
| Half-life | 7.6 - 24 hours |
| Major metabolites | M1 (sulfate), M3 (quinone) |
Insulin Sensitization
This compound enhances insulin sensitivity, which is critical for managing type 2 diabetes. Clinical studies indicate that it significantly improves glycemic control by increasing glucose uptake in adipose tissues without affecting insulin-stimulated uptake . Specifically, it enhances basal glucose transport by increasing the expression of the Glut1 glucose transporter .
Case Studies
A pivotal study demonstrated that this compound reduced the incidence of type 2 diabetes by 75% compared to placebo during its administration period. However, this protective effect did not persist after withdrawal of the drug . In a cohort study involving 387 participants treated with this compound, only 10 developed diabetes over a follow-up period, highlighting its efficacy during treatment .
Adverse Effects
Despite its benefits, this compound is associated with severe hepatotoxicity. A systematic review identified 94 cases of liver failure linked to this compound use, with a significant number requiring liver transplantation . The risk of liver injury increased with prolonged use, leading to the drug's market withdrawal due to safety concerns .
Table 2: Summary of Clinical Findings on this compound
This compound primarily exerts its effects through PPAR-γ activation, which regulates gene expression involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. This mechanism promotes differentiation of preadipocytes into adipocytes and enhances insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
Off-target Effects
Recent studies have indicated that this compound has a broader range of biological activities compared to other TZDs like rosiglitazone. It activated more assays across various biological processes in vitro, suggesting potential off-target effects that could contribute to its adverse events .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
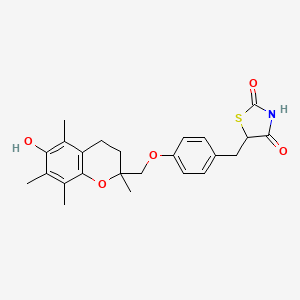
5-[[4-[(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H27NO5S/c1-13-14(2)21-18(15(3)20(13)26)9-10-24(4,30-21)12-29-17-7-5-16(6-8-17)11-19-22(27)25-23(28)31-19/h5-8,19,26H,9-12H2,1-4H3,(H,25,27,28) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
GXPHKUHSUJUWKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C2=C(CCC(O2)(C)COC3=CC=C(C=C3)CC4C(=O)NC(=O)S4)C(=C1O)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H27NO5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID8023719 | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8023719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
441.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent that lowers blood glucose by improving target cell response to insulin. It has a unique mechanism of action that is dependent on the presence of insulin for activity. Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle. Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism. Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPARα and PPARγ, with a highter affinity for PPARγ. The drug also contains an α-tocopheroyl moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity. Troglitazone has been shown to reduce inflammation, and is associated with a decrase in nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (IκB). Unlike sulfonylureas, troglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
97322-87-7 | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=97322-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0097322877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8023719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Melting Point |
184-186 °C | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.













