Misoprostol
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue used for various medical purposes, including the prevention and treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers, induction of labor, abortion, and treatment of postpartum bleeding due to poor contraction of the uterus . It is a versatile compound with significant applications in medicine.
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Misoprostol is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1). It primarily targets prostaglandin E1 receptors on parietal cells in the stomach and myometrial cells in the uterus . In the stomach, these receptors play a crucial role in the secretion of gastric acid, while in the uterus and cervix, they influence the strength and frequency of contractions and cervical tone .
Mode of Action
This compound’s interaction with its targets leads to a series of changes. In the stomach, it reduces gastric acid secretion by inhibiting adenylate cyclase via G-protein coupled receptor-mediated action, leading to decreased intracellular cyclic AMP levels and decreased proton pump activity at the apical surface of the parietal cell . In the uterus, this compound causes strong myometrial contractions leading to the expulsion of tissue .
Biochemical Pathways
This compound affects several biochemical pathways. It increases mucus and bicarbonate secretion and thickens the mucosal bilayer, enabling the mucosa to generate new cells . It also stimulates nitric oxide (NO) release, which in turn increases prostaglandin production during inflammation .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is extensively absorbed and rapidly converted by de-esterification to its active metabolite, this compound acid . Further metabolic conversion occurs via beta-oxidation of the alpha side chain, omega-oxidation of the beta side chain, and reduction to the prostaglandin F analogs . The elimination half-life is 20-40 minutes, and it is primarily excreted in urine . The route of administration significantly impacts the bioavailability of this compound .
Result of Action
The action of this compound results in several molecular and cellular effects. In the stomach, it protects the gastric mucosa from NSAID-induced ulcers by reducing gastric acid secretion . In the uterus, it induces labor, causes abortion, and treats postpartum bleeding due to poor contraction of the uterus . It also causes cervical ripening with softening and dilation of the cervix .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of this compound can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the route of administration can significantly impact its bioavailability and effectiveness . Moreover, the physiological state of the patient, such as pregnancy, can also affect the drug’s action .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Gastroenterology
Ulcer Prevention
Misoprostol is primarily indicated for the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced gastric ulcers. It acts by inhibiting gastric acid secretion through direct stimulation of prostaglandin E1 receptors on parietal cells, promoting mucosal protection .
Efficacy and Limitations
While effective, this compound is often less tolerated than alternative treatments like omeprazole, leading to its limited use as a first-line therapy due to side effects such as diarrhea and the need for multiple daily doses .
| Indication | Effectiveness | Alternative Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| NSAID-induced gastric ulcers | Effective | Omeprazole |
| Postoperative ulcer prevention | Moderate | Proton pump inhibitors |
Obstetrics
Labor Induction
this compound is widely used for cervical ripening and labor induction due to its ability to stimulate uterine contractions. It is often favored for its cost-effectiveness compared to dinoprostone .
Case Study: Labor Induction Efficacy
A study involving 500 women showed that this compound resulted in successful labor induction in 85% of cases, with fewer side effects compared to traditional methods .
| Study Parameter | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Total Participants | 500 |
| Successful Induction Rate | 85% |
| Adverse Effects Reported | Minimal |
Reproductive Health
Medical Abortion
this compound is commonly used in combination with mifepristone for medical abortion, achieving effectiveness rates between 95% and 98% . The regimen allows for non-invasive management of early pregnancy loss.
Factors Influencing Success Rates
Research indicates that factors such as the timing of administration and the presence of symptoms like abdominal pain can significantly affect the success rates of this compound in abortion procedures .
| Factor | Success Rate Impact |
|---|---|
| Timing of Administration | Higher success when within 24 hours of symptoms |
| Presence of Abdominal Pain | Increases likelihood of successful expulsion |
Postpartum Hemorrhage
This compound is also utilized in managing postpartum hemorrhage due to its uterotonic properties. It effectively reduces blood loss by promoting uterine contractions .
Safety and Adverse Effects
Despite its benefits, this compound is associated with several adverse effects, including uterine tachysystole and potential lacerations during labor induction . A comprehensive analysis from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System highlighted various adverse events linked to this compound use, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring during its administration .
| Adverse Event | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Uterine Tachysystole | 95 occurrences |
| Uterine Rupture | 95 occurrences |
| Fetal Heart Rate Decrease | 93 occurrences |
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Misoprostol acts upon gastric parietal cells, inhibiting the secretion of gastric acid by G-protein coupled receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase, which leads to decreased intracellular cyclic AMP levels and decreased proton pump activity at the apical surface of the parietal cell . This compound is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The drug undergoes extensive and rapid first-pass metabolism (de-esterification) to form this compound acid .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a significant impact on various types of cells and cellular processes. It reduces gastric acid secretion, increases bicarbonate and mucus secretion, and thickens the mucosal bilayer so the mucosa can generate new cells . This compound also stimulates prostaglandin receptors in the uterus and cervix, increasing the strength and frequency of contractions and decreasing cervical tone .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog that stimulates prostaglandin E1 receptors on parietal cells in the stomach to reduce gastric acid secretion . It also increases mucus and bicarbonate secretion along with thickening of the mucosal bilayer so the mucosa can generate new cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that this compound is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, this compound has been used to treat or prevent stomach ulcers due to NSAID use . It can also be used in combination with other medications to treat uterine infections, protect the kidneys, treat skin allergies, or to terminate pregnancy . The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound undergoes extensive and rapid first-pass metabolism (de-esterification) to form this compound acid . Further metabolic conversion occurs over time via beta-oxidation of the alpha side chain, omega-oxidation of the beta side chain, and reduction to the prostaglandin F analogs .
Subcellular Localization
It is known that this compound acts upon gastric parietal cells, suggesting that it localizes at least in part to these cells .
Méthodes De Préparation
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
Misoprostol is synthesized through a multi-step process starting from commercially available precursors. The synthesis involves the following key steps:
Formation of the cyclopentane ring: This step involves the cyclization of a suitable precursor to form the cyclopentane ring structure.
Introduction of the hydroxyl groups: Hydroxyl groups are introduced at specific positions on the cyclopentane ring through selective hydroxylation reactions.
Esterification: The hydroxylated cyclopentane intermediate is esterified to form the final this compound structure.
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound involves large-scale synthesis using optimized reaction conditions to ensure high yield and purity. The process typically includes:
Batch or continuous flow reactors: These reactors are used to carry out the cyclization and hydroxylation reactions under controlled conditions.
Purification steps: The crude product is purified using techniques such as crystallization, distillation, and chromatography to obtain high-purity this compound.
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types of Reactions
Misoprostol undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized to form corresponding ketones and aldehydes.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can convert this compound to its corresponding alcohols.
Substitution: this compound can undergo substitution reactions where functional groups are replaced with other groups.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidizing agents: Common oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate and chromium trioxide.
Reducing agents: Sodium borohydride and lithium aluminum hydride are commonly used reducing agents.
Substitution reagents: Halogenating agents such as thionyl chloride and phosphorus tribromide are used for substitution reactions.
Major Products
Oxidation products: Ketones and aldehydes.
Reduction products: Alcohols.
Substitution products: Halogenated derivatives.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Misoprostol is compared with other prostaglandin analogues such as gemeprost and isosorbide mononitrate:
Gemeprost: Similar to this compound, gemeprost is used for labor induction and abortion.
Isosorbide mononitrate: Used in combination with this compound for enhanced efficacy in medical abortion.
Similar Compounds
- Gemeprost
- Isosorbide mononitrate
- Dinoprostone
- Carboprost
This compound’s unique properties and wide range of applications make it a valuable compound in both research and clinical settings.
Activité Biologique
Misoprostol, a synthetic analog of prostaglandin E1, is widely recognized for its diverse biological activities, particularly in gastroprotection and reproductive health. This article delves into the compound's mechanisms of action, clinical applications, and research findings, supported by data tables and case studies.
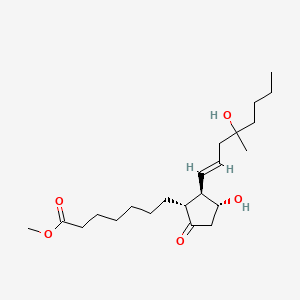
Chemical Structure : this compound is chemically defined as (±)-(11a,13 E)-11,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxo-prost-13-en-1-oic acid methyl ester. Its molecular formula is C22H38O5.
Mechanism : this compound exerts its biological effects primarily through agonistic activity at the EP receptors (EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4). It inhibits gastric acid secretion by stimulating prostaglandin E1 receptors on parietal cells in the stomach. This action reduces acid secretion triggered by various stimuli such as food intake and NSAIDs. Moreover, it promotes the secretion of mucus and bicarbonate, enhancing mucosal defense mechanisms .
Biological Activities
- Gastroprotective Effects : this compound is effective in preventing NSAID-induced gastric ulcers. It facilitates the thickening of the mucosal layer and enhances blood flow to the gastric mucosa, which aids in mucosal regeneration .
- Reproductive Health : this compound is utilized for medical abortion and management of early pregnancy loss. It has been shown to be highly effective when used alone or in combination with mifepristone. Studies indicate that the efficacy of this compound for pregnancy termination ranges from 84% to 96% depending on dosage and administration route .
Table 1: Efficacy of this compound in Medical Abortion
| Study Reference | Gestational Age | Efficacy Rate (%) | Complications (%) | Need for Surgical Intervention (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤63 days | 84 - 96 | 0.7 | 22 | |
| ≤63 days | 92 | 1.0 | 18 | |
| Early Pregnancy Loss | 90 | 3.5 | 10.5 |
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Medical Abortion with this compound Alone
A systematic review involving over 12,000 women demonstrated that this compound alone resulted in a complete abortion rate of approximately 90%. The study highlighted that complications were minimal, with only a small percentage requiring surgical intervention due to incomplete abortion .
Case Study 2: Mifepristone Plus this compound
In a cohort study assessing the combination therapy of mifepristone followed by this compound, it was found that this regimen significantly reduced the need for subsequent surgical procedures compared to this compound alone (10.5% vs. 14%) . This suggests that the combination may enhance efficacy while minimizing complications.
Research Findings
Recent studies have expanded our understanding of this compound's receptor interactions:
- Receptor Binding Studies : Research has shown that this compound binds effectively to EP receptors with Ki values indicating high affinity (EP1: 120 nM; EP3: 67 nM) . This binding is critical for its agonistic effects.
- Structural Analysis : A crystal structure analysis revealed detailed interactions between this compound and the EP3 receptor, providing insights into how structural modifications could lead to more effective analogs for therapeutic use .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
methyl 7-[(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(E)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-enyl]-5-oxocyclopentyl]heptanoate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H38O5/c1-4-5-14-22(2,26)15-10-12-18-17(19(23)16-20(18)24)11-8-6-7-9-13-21(25)27-3/h10,12,17-18,20,24,26H,4-9,11,13-16H2,1-3H3/b12-10+/t17-,18-,20-,22?/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
OJLOPKGSLYJEMD-URPKTTJQSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCCC(C)(CC=CC1C(CC(=O)C1CCCCCCC(=O)OC)O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCCCC(C)(C/C=C/[C@H]1[C@@H](CC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCCCCC(=O)OC)O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H38O5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7020897 | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7020897 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
382.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Liquid | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015064 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
1.6mg/mL, Water-soluble, 1.64e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00929 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MISOPROSTOL | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3573 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015064 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog that stimulates prostaglandin E1 receptors on parietal cells in the stomach to reduce gastric acid secretion. Mucus and bicarbonate secretion are also increased along with thickening of the mucosal bilayer so the mucosa can generate new cells. Misoprostol binds to smooth muscle cells in the uterine lining to increase the strength and frequency of contractions as well as degrade collagen and reduce cervical tone., Misoprostol enhances natural gastromucosal defense mechanisms and healing in acid-related disorders, probably by increasing production of gastric mucus and mucosal secretion of bicarbonate., Misoprostol inhibits basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion by direct action on the parietal cells; also inhibits gastric acid secretion stimulated by food, histamine, and pentagastrin. It decreases pepsin secretion under basal, but not histamine stimulation. Misoprostol has no significant effect on fasting or postprandial gastrin or intrinsic factor output. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00929 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MISOPROSTOL | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3573 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Light yellow oil, Viscous liquid | |
CAS No. |
59122-46-2 | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59122-46-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0059122462 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00929 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7020897 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | MISOPROSTOL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0E43V0BB57 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | MISOPROSTOL | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3573 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015064 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
261-263 | |
| Record name | Misoprostol | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00929 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
















