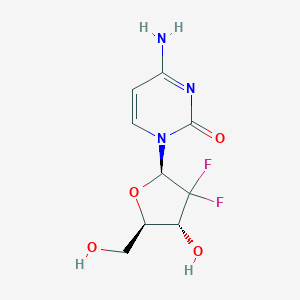
Gemcitabine
概要
説明
Gemcitabine, known chemically as 2’,2’-difluoro 2’-deoxycytidine, is a nucleoside analog used as a chemotherapy medication. It is primarily employed in the treatment of various carcinomas, including pancreatic, breast, ovarian, and non-small cell lung cancers . This compound works by inhibiting DNA synthesis, thereby preventing cancer cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis .
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of gemcitabine involves multiple steps, starting from cytosine. One common method includes the preparation of 2-deoxy-D-erythro-2,2-difluoro-ribofuranose-3,5-dibenzoate, followed by its coupling with a silyl-ether protecting group . The reaction conditions typically involve the use of hexamethyldisilazane and hydrochloric acid for the final product formation .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound hydrochloride often involves the reduction of 2-deoxy-D-erythro-2,2-difluoro-ribofuranose protected at the hydroxyls at the 3- and 5-positions with diisobutyl-aluminium hydride in toluene (DIBAL) . The final purification is achieved through chromatography and crystallization techniques to meet pharmacopoeia standards .
化学反応の分析
Phosphorylation and Activation Pathway
Gemcitabine undergoes sequential phosphorylation to form active metabolites:
This cascade enables "self-potentiation," where dFdCDP-mediated dNTP depletion enhances dFdCTP incorporation into DNA .
Deamination and Metabolic Inactivation
Up to 90% of administered this compound is deaminated by cytidine deaminase (CDA) , producing the inactive metabolite 2',2'-difluorodeoxyuridine (dFdU) . Key factors influencing this reaction:
- Tissue specificity : High CDA activity in the liver and blood .
- Pharmacogenetic variability : Polymorphisms in CDA genes affect inactivation rates .
DNA/RNA Interaction Mechanisms
dFdCTP incorporation into nucleic acids drives cytotoxicity through:
- Masked chain termination : dFdCTP integrates into DNA, allowing one additional nucleotide addition before stalling replication .
- RNA synthesis inhibition : Misincorporation into RNA disrupts processing and function .
- Enzyme inhibition : dFdCDP suppresses RNR, while dFdCTP blocks CTP synthetase, depleting nucleotide reserves .
Prodrug Strategies to Enhance Stability
The This compound-threonine amide (Gem-Thr) prodrug demonstrates improved pharmacokinetics:
| Parameter | Gem-Thr (4 mg/kg) | Free this compound (4 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| AUC (μg·min/mL) | 1739.88 ± 282.00 | 948.38 ± 52.04 |
| Total Clearance (mL/min/kg) | 0.60 ± 0.10 | 4.23 ± 0.23 |
| Metabolic Stability | 1.83-fold increase | Baseline |
Synthesis involves amide bond formation between this compound and N-Boc-L-threonine using HOBt/EDC coupling, followed by Boc deprotection . This modification leverages amino acid transporters (e.g., LAT-1) for targeted uptake in pancreatic cancer cells .
Critical Enzymatic Interactions
科学的研究の応用
Approved Indications
Gemcitabine is approved for use in several cancer types, often in combination with other agents. The following table summarizes its approved indications:
Drug Delivery Systems
Recent studies have focused on enhancing the delivery mechanisms of this compound to improve its therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects. Various innovative drug delivery systems include:
- Polymeric Nanoparticles : These systems enhance the bioavailability of this compound and target tumor cells more effectively.
- Liposomes : Encapsulation of this compound in liposomes has shown improved pharmacokinetics and reduced systemic toxicity .
- Aerosol Delivery : Research has demonstrated the potential of aerosolized this compound to treat pulmonary metastases, particularly in osteosarcoma models, showing significant necrosis in treated tumors .
Case Studies
- Pancreatic Cancer : In clinical trials, this compound monotherapy yielded objective response rates ranging from 5% to 12%, with median survival times between 3.9 to 6.3 months. Combination therapies have shown improved outcomes compared to monotherapy .
- Ovarian Cancer : A Phase II trial reported a response rate of 57.1% in patients treated with this compound, with a median progression-free survival of 13.4 months .
- Colorectal Cancer : Recent analyses indicate that this compound serves as a second-line treatment option, with ongoing research identifying novel molecular targets to enhance its efficacy against colorectal tumors .
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its effectiveness, the clinical use of this compound faces challenges such as:
- Short Biological Half-Life : Rapid metabolism limits its therapeutic window.
- Drug Resistance : Increased expression of ribonucleotide reductase can lead to diminished drug efficacy.
Future research aims to overcome these barriers through advanced drug delivery systems and combination therapies that can enhance the selectivity and effectiveness of this compound.
作用機序
Gemcitabine acts as an antimetabolite, mimicking the building blocks of RNA and DNA. It disrupts DNA synthesis by incorporating itself into the DNA strand during replication, leading to chain termination and apoptosis . The molecular targets include ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerase . This mechanism is similar to that of cytarabine but with a broader spectrum of antitumor activity .
類似化合物との比較
Cytarabine: Another nucleoside analog with a similar mechanism of action but a narrower spectrum of activity.
Fluorouracil: A pyrimidine analog used in chemotherapy, differing in its metabolic pathway and target specificity.
Capecitabine: An oral prodrug of fluorouracil with similar applications but different pharmacokinetics.
Uniqueness of Gemcitabine: this compound’s unique feature lies in its dual fluorine substitution, which enhances its stability and efficacy compared to other nucleoside analogs . This structural modification allows for a broader range of applications and improved therapeutic outcomes .
生物活性
Gemcitabine, a nucleoside analog, is a chemotherapeutic agent primarily used in the treatment of various cancers, including pancreatic, breast, and non-small cell lung cancer. Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy in clinical settings. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its mechanisms, case studies, and research findings.
This compound exerts its anticancer effects by inhibiting DNA synthesis. It is phosphorylated intracellularly to form this compound triphosphate (dFdCTP), which competes with deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP) for incorporation into DNA. This incorporation leads to chain termination during DNA replication. Additionally, this compound inhibits ribonucleotide reductase, reducing the levels of dNTPs necessary for DNA synthesis .
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of DNA Synthesis : this compound is incorporated into DNA, causing chain termination.
- Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibition : Reduces dNTP levels, further inhibiting DNA synthesis.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is administered intravenously and has a short half-life (approximately 30 minutes). Its pharmacokinetics are influenced by factors such as dose, administration route, and patient characteristics. The drug is rapidly distributed and metabolized primarily in the liver and kidneys .
Pharmacokinetic Properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Half-life | ~30 minutes |
| Bioavailability | Low (due to rapid metabolism) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (mainly) |
| Excretion | Renal |
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
This compound has been evaluated in numerous clinical trials for various cancers. Below are summaries from significant studies:
Case Study Summaries:
- Pancreatic Cancer :
- Breast Cancer :
- Combination Therapies :
Research Findings
Recent studies have explored novel formulations and conjugates of this compound to enhance its therapeutic efficacy:
- This compound Conjugates : Research on this compound conjugated with cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) demonstrated improved cellular uptake and cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines compared to free this compound . For instance, the Gem-Cys-pVEC conjugate showed IC50 values significantly lower than those for unmodified this compound.
- PEGylation : Modifications such as PEGylation have been shown to increase the bioavailability and therapeutic index of this compound. Studies indicated that PEG-gemcitabine had a 21-fold higher bioavailability compared to native this compound after intravenous administration in animal models .
特性
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-1-[(2R,4R,5R)-3,3-difluoro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H11F2N3O4.ClH/c10-9(11)6(16)4(3-15)18-7(9)14-2-1-5(12)13-8(14)17;/h1-2,4,6-7,15-16H,3H2,(H2,12,13,17);1H/t4-,6-,7-;/m1./s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
OKKDEIYWILRZIA-OSZBKLCCSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CN(C(=O)N=C1N)C2C(C(C(O2)CO)O)(F)F.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1=CN(C(=O)N=C1N)[C@H]2C([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)(F)F.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C9H12ClF2N3O4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
95058-81-4, 103882-84-4 | |
| Record name | Gemcitabine hydrochloride [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0122111039 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID3047849 | |
| Record name | 2'-Deoxy-2',2'-difluorocytidine monohydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3047849 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
299.66 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
122111-03-9 | |
| Record name | Gemcitabine hydrochloride | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=122111-03-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Gemcitabine hydrochloride [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0122111039 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | 2'-Deoxy-2',2'-difluorocytidine monohydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3047849 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Cytidine, 2'-deoxy-2',2'-difluoro-, hydrochloride (1:1) | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.108.693 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | GEMCITABINE HYDROCHLORIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/U347PV74IL | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















