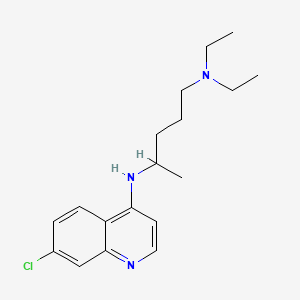
クロロキン
概要
説明
作用機序
クロロキンは、いくつかのメカニズムを通じてその効果を発揮します。
抗マラリア作用: クロロキンは、マラリアトロフォゾイトにおけるヘムポリメラーゼの作用を阻害し、ヘムからヘマゾインへの変換を防ぎます。
抗炎症作用: クロロキンは、プロ炎症性サイトカインの産生を阻害し、抗原提示を妨げることで、免疫応答を調節します.
抗ウイルス作用: クロロキンは、エンドソーム、リソソーム、ゴルジ小胞のpHを上昇させ、ウイルス粒子が融合および細胞への侵入に使用できないようにします.
類似化合物の比較
クロロキンは、他の類似化合物と比較して、その独自性を強調しています。
ヘムポリメラーゼを阻害し、免疫応答を調節する能力など、クロロキンの独自の特性は、医療および科学研究の両方において、貴重な化合物となっています。
科学的研究の応用
Antimalarial Applications
Chloroquine is primarily known for its role in treating malaria caused by Plasmodium species. It is effective against chloroquine-sensitive strains of P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. The drug functions by preventing the polymerization of heme into hemozoin, leading to toxic accumulation of free heme within the parasite .
Autoimmune Disorders
Chloroquine has established roles in managing several autoimmune diseases, including:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Chloroquine is effective in treating different forms of SLE, including discoid lupus and systemic lupus erythematosus, and is particularly beneficial for pregnant patients .
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) : It acts as a first-line disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), preventing the activation of CD4+ T cells by inhibiting autoantigen presentation .
- Other Conditions : Chloroquine has shown efficacy in treating skin diseases like lichen planus and Sjögren's syndrome .
Cancer Treatment
Recent studies indicate that chloroquine may enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in cancer treatment:
- Mechanism : Chloroquine disrupts autophagy in cancer cells, potentially making them more susceptible to anticancer agents .
- Clinical Trials : Investigational studies have explored its use in various cancers, including local metastatic melanoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia .
Infectious Diseases Beyond Malaria
Chloroquine's antiviral properties have been investigated in the context of several viral infections:
- COVID-19 : Initially proposed as a treatment due to its immunomodulatory effects and ability to alter endosomal pH, chloroquine was used during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, clinical trials yielded mixed results regarding its efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 .
- SARS and AIDS : Research has also explored chloroquine's potential against severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) due to its ability to inhibit viral entry .
Pharmacokinetics and Safety Profile
Chloroquine is generally well-tolerated but can cause side effects such as retinopathy with long-term use. Monitoring is essential for patients on prolonged therapy . The safety profile varies across populations, necessitating further research to establish comprehensive guidelines for its use.
Table 1: Approved Indications for Chloroquine
| Condition | FDA Approval Status |
|---|---|
| Malaria | Approved |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Approved |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Approved |
| Extraintestinal Amebiasis | Approved |
| Cancer (adjunct therapy) | Investigational |
Table 2: Summary of Clinical Trials on Chloroquine for COVID-19
| Study Reference | Sample Size | Outcome Measure | Results Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gao et al. | 100 | Symptom alleviation | Reported improvement but lacked peer review |
| Million et al. | Various | Meta-analysis | Criticized for flawed methodologies |
| Karolyi et al. | Various | Time to negative test conversion | Moderate reduction observed |
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Chloroquine interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to UV detectors is the most employed method to quantify Chloroquine in pharmaceutical products and biological samples .
Cellular Effects
Chloroquine has exhibited a broad spectrum of action against various fungus, bacteria, and viruses . It has been identified to have severe gastrointestinal, neurological, cardiac, and ocular side effects, which are commonly related to Chloroquine dose and treatment time .
Molecular Mechanism
Chloroquine and its analog, hydroxychloroquine, have similar chemical structure and pharmacokinetics properties . Both drugs cross cell membranes well . Hydroxychloroquine is more polar, less lipophilic, and has more difficulty diffusing across cell membranes .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The main chromatographic conditions used to identify and quantify Chloroquine from tablets and injections, degradation products, and metabolites are presented and discussed .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The occurrence and intensity of side effects of Chloroquine are commonly related to its dose and treatment time .
Metabolic Pathways
Chloroquine is involved in various metabolic pathways. The main chromatographic conditions used to identify and quantify Chloroquine from tablets and injections, degradation products, and metabolites are presented and discussed .
Transport and Distribution
Both Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine cross cell membranes well . Hydroxychloroquine is more polar, less lipophilic, and has more difficulty diffusing across cell membranes .
準備方法
合成経路と反応条件
クロロキンの合成には、4,7-ジクロロキノリンと2-アミノ-5-ジエチルアミノペンタンの縮合反応が関与します . 反応は以下の手順で進行します。
縮合反応: 4,7-ジクロロキノリンは、2-アミノ-5-ジエチルアミノペンタンと反応してクロロキンを生成します。
アルカリ化抽出: 反応混合物は、アルカリ化抽出によってクロロキンを分離されます。
濃縮と結晶化: 分離されたクロロキンは、濃縮および結晶化によって純度が向上します。
工業生産方法
クロロキンの工業生産は、同様の合成経路に従いますが、より大規模に行われます。 このプロセスには以下が含まれます。
バルク合成: 4,7-ジクロロキノリンと2-アミノ-5-ジエチルアミノペンタンを大量に使用します。
連続抽出と結晶化: 反応混合物は、連続抽出および結晶化によって、高収率と高純度が確保されます。
化学反応の分析
反応の種類
クロロキンは、以下を含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: クロロキンは、酸化されてキノリン誘導体を生成することができます。
還元: 還元反応は、キノリン環構造を変更することができます。
一般的な試薬と条件
酸化: 一般的な酸化剤には、過マンガン酸カリウムと過酸化水素が含まれます。
還元: 水素化リチウムアルミニウムや水素化ホウ素ナトリウムなどの還元剤が使用されます。
主な生成物
酸化生成物: 環構造が変更されたキノリン誘導体。
還元生成物: 還元されたキノリン化合物。
置換生成物: さまざまな官能基を持つ置換クロロキン誘導体.
科学研究への応用
クロロキンは、幅広い科学研究用途を持っています。
化学: 有機合成における試薬として、およびキノリン化学の研究におけるモデル化合物として使用されます.
生物学: オートファジーとリソソーム機能の研究に用いられる細胞生物学研究に用いられます.
類似化合物との比較
Chloroquine is compared with other similar compounds, highlighting its uniqueness:
Hydroxychloroquine: Similar in structure and function to chloroquine but generally considered less toxic.
Quinine: A natural compound used to treat malaria.
Mefloquine: Another synthetic antimalarial agent with a different mechanism of action.
Artemisinin: A natural compound with potent antimalarial activity.
Chloroquine’s unique properties, such as its ability to inhibit heme polymerase and modulate immune responses, make it a valuable compound in both medical and scientific research.
生物活性
Chloroquine (CQ) is a 4-aminoquinoline compound primarily known for its antimalarial properties. Its biological activity extends beyond malaria treatment, encompassing antiviral and anticancer effects. This article delves into the mechanisms, clinical applications, and research findings related to chloroquine's biological activity.
Chloroquine exerts its biological effects through several mechanisms:
- Antimalarial Activity : CQ inhibits heme polymerase in Plasmodium species, leading to the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. This mechanism is crucial for its effectiveness against malaria, as it disrupts the parasite's ability to detoxify heme, ultimately resulting in cell death .
- Antiviral Effects : CQ has been shown to interfere with viral entry and replication. It raises the pH in endosomes, which prevents virus particles from fusing with host cell membranes. Additionally, it inhibits glycosylation of the ACE2 receptor, which is essential for SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells .
- Anticancer Properties : The compound has demonstrated immunomodulatory effects and the ability to inhibit autophagy, which can contribute to tumor growth suppression. These properties suggest potential applications in cancer therapy .
Pharmacokinetics
Chloroquine is well-absorbed when taken orally, with bioavailability ranging from 52% to 114% depending on the formulation. The drug has a long half-life of approximately 20-60 days, allowing for sustained therapeutic effects .
Antimalarial Use
Chloroquine remains a first-line treatment for malaria in many regions. Its efficacy against both chloroquine-sensitive and resistant strains of Plasmodium has been documented extensively. A notable study indicated that CQ effectively reduced parasitemia in patients with malaria, demonstrating a significant clinical response .
COVID-19 Research
Chloroquine gained attention during the COVID-19 pandemic as a potential treatment. Several studies have investigated its efficacy:
- A multicenter observational study involving 197 patients showed that CQ treatment resulted in a median reduction of 6 days to achieve undetectable viral RNA compared to controls. Additionally, the duration of fever was significantly shorter in the CQ group .
- Another study reported that patients treated with CQ experienced lung clearance improvements on CT scans compared to those receiving standard care (lopinavir/ritonavir) .
Summary of Findings
The following table summarizes key findings from various studies on chloroquine:
特性
IUPAC Name |
4-N-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-1-N,1-N-diethylpentane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H26ClN3/c1-4-22(5-2)12-6-7-14(3)21-17-10-11-20-18-13-15(19)8-9-16(17)18/h8-11,13-14H,4-7,12H2,1-3H3,(H,20,21) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WHTVZRBIWZFKQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=C2C=CC(=CC2=NC=C1)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C18H26ClN3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2040446 | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2040446 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
319.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014746 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Bitter colorless crystals, dimorphic. Freely soluble in water, less sol in neutral or alkaline pH. Stable to heat in soln pH4 to 6.5. Practically in soluble in alcohol, benzene and chloroform /Diphosphate/, WHITE CRYSTALLINE POWDER; ODORLESS; BITTER TASTE; FREELY SOL IN WATER;PRACTICALLY INSOL IN ALCOHOL, CHLOROFORM, ETHER; AQ SOLN HAS PH OF ABOUT 4.5; PKA1= 7; PKA2= 9.2 /PHOSPHATE/, VERY SLIGHTLY SOL IN WATER; SOL IN DIL ACIDS, CHLOROFORM, ETHER, Insoluble in alcohol, benzene, chloroform, ether., 1.75e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | CHLOROQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3029 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014746 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Chloroquine inhibits the action of heme polymerase in malarial trophozoites, preventing the conversion of heme to hemazoin. _Plasmodium_ species continue to accumulate toxic heme, killing the parasite. Chloroquine passively diffuses through cell membranes and into endosomes, lysosomes, and Golgi vesicles; where it becomes protonated, trapping the chloroquine in the organelle and raising the surrounding pH. The raised pH in endosomes, prevent virus particles from utilizing their activity for fusion and entry into the cell. Chloroquine does not affect the level of ACE2 expression on cell surfaces, but inhibits terminal glycosylation of ACE2, the receptor that SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 target for cell entry. ACE2 that is not in the glycosylated state may less efficiently interact with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, further inhibiting viral entry., The exact mechanism of antimalarial activity of chloroquine has not been determined. The 4-aminoquinoline derivatives appear to bind to nucleoproteins and interfere with protein synthesis in susceptible organisms; the drugs intercalate readily into double-stranded DNA and inhibit both DNA and RNA polymerase. In addition, studies using chloroquine indicate that the drug apparently concentrates in parasite digestive vacuoles, increases the pH of the vacuoles, and interferes with the parasite's ability to metabolize and utilize erythrocyte hemoglobin. Plasmodial forms that do not have digestive vacuoles and do not utilize hemoglobin, such as exoerythrocytic forms, are not affected by chloroquine., The 4-aminoquinoline derivatives, including chloroquine, also have anti-inflammatory activity; however, the mechanism(s) of action of the drugs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus has not been determined. Chloroquine reportedly antagonizes histamine in vitro, has antiserotonin effects, and inhibits prostaglandin effects in mammalian cells presumably by inhibiting conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin F2. In vitro studies indicate that chloroquine also inhibits chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils., Antiprotozoal-Malaria: /Mechanism of action/ may be based on ability of chloroquine to bind and alter the properties of DNA. Chloroquine also is taken up into the acidic food vacuoles of the parasite in the erythrocyte. It increases the pH of the acid vesicles, interfering with vesicle functions and possibly inhibiting phospholipid metabolism. In suppressive treatment, chloroquine inhibits the erythrocytic stage of development of plasmodia. In acute attacks of malaria, chloroquine interrupts erythrocytic schizogony of the parasite. its ability to concentrate in parasitized erythrocytes may account for its selective toxicity against the erythrocytic stages of plasmodial infection., Antirheumatic-Chloroquine is though to act as a mild immunosuppressant, inhibiting the production of rheumatoid factor and acute phase reactants. It also accumulates in white blood cells, stabilizing lysosomal membranes and inhibiting the activity of many enzymes, including collagenase and the proteases that cause cartilage breakdown. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CHLOROQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3029 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
WHITE TO SLIGHTLY YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER, Colorless crystals | |
CAS No. |
54-05-7 | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=54-05-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine [USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000054057 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | chloroquine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=187208 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2040446 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.175 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CHLOROQUINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/886U3H6UFF | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | CHLOROQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3029 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014746 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
87-89.5, 87 °C, 289 °C | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CHLOROQUINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3029 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chloroquine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014746 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details




Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details




Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。














