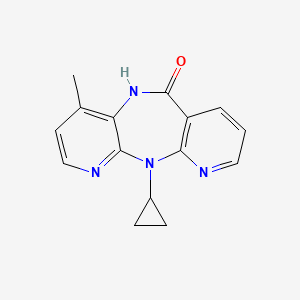
ネビラピン
概要
説明
ネビラピンは、ヒト免疫不全ウイルス1型(HIV-1)感染の治療と予防に主に使用される非ヌクレオシド系逆転写酵素阻害剤です。その有効性を高めるために、他の抗レトロウイルス薬と組み合わせて使用されることが多いです。 ネビラピンは、HIV-1の複製に不可欠な逆転写酵素を阻害することで作用します .
作用機序
ネビラピンは、HIV-1の逆転写酵素に直接結合することにより作用を発揮します。この結合により、酵素の触媒部位が破壊され、RNA依存性およびDNA依存性DNAポリメラーゼ活性が阻害されます。 この阻害により、HIV-1の複製が阻止され、患者の体内のウイルス量を減らすことができます .
類似の化合物:
エファビレンツ: HIV-1の治療に使用される別の非ヌクレオシド系逆転写酵素阻害剤。
エトラビリン: 他の非ヌクレオシド系逆転写酵素阻害剤に耐性のあるHIV-1株に対する有効性で知られています。
ネビラピンの独自性: ネビラピンは、他の非ヌクレオシド系逆転写酵素阻害剤では一般的に見られない特徴である、出産時の母子感染を防ぐことができる点が特徴です。 さらに、その長い半減期により、投与回数を減らすことができ、治療レジメンへの患者のアドヒアランスを向上させることができます .
科学的研究の応用
HIV Treatment
Nevirapine is mainly prescribed as part of combination antiretroviral therapy for HIV-1 infection. Its effectiveness is well-documented in numerous clinical studies.
Efficacy and Safety
- Nevirapine has shown durable virological and immunological responses in approximately 50% of antiretroviral-naive patients when used in combination with two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) such as zidovudine or lamivudine .
- A systematic review indicated that nevirapine-based regimens are comparable to efavirenz-based regimens in terms of achieving undetectable plasma HIV RNA levels .
Combination Therapy
- Nevirapine is often combined with other antiretroviral medications to reduce the risk of viral resistance. For instance, it is commonly used with NRTIs and sometimes with protease inhibitors .
- The drug is particularly important in preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV during childbirth, often administered as a single dose to mothers and infants .
Potential Applications Beyond HIV
Recent research has indicated that nevirapine may have therapeutic effects beyond its original application for HIV treatment.
Thyroid Cancer
- Experimental studies have shown that nevirapine can inhibit the migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells. This suggests that the drug may have potential applications in oncology, particularly for certain types of cancer .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness and safety profile of nevirapine in various populations.
Pharmacokinetics and Resistance
Nevirapine has a low genetic barrier to resistance, which can lead to rapid emergence of resistant viral strains if not used correctly. Studies indicate that monitoring drug levels can help mitigate this risk:
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Nevirapine is extensively biotransformed via cytochrome P450 3A4 metabolism to several hydroxylated metabolites . This interaction with the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme plays a crucial role in the biochemical reactions involving Nevirapine.
Cellular Effects
Nevirapine has been shown to be effective in reducing HIV-1 levels when used in combination with other antiretroviral agents . It influences cell function by inhibiting the action of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, an enzyme crucial for the replication of the virus .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Nevirapine involves its binding to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase . This binding inhibits the action of the enzyme, thereby preventing the replication of the virus at the molecular level .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that Nevirapine is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily via cytochrome P450 3A4 .
Metabolic Pathways
Nevirapine is involved in the metabolic pathway of cytochrome P450 3A4 . It is extensively metabolized in the liver to several hydroxylated metabolites .
Transport and Distribution
The transport and distribution of Nevirapine within cells and tissues are complex processes that involve its extensive metabolism in the liver
Subcellular Localization
Given its role as an inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, it is likely to be localized where this enzyme is present within the cell .
準備方法
合成経路と反応条件: ネビラピンは、2-クロロ-3-シアノピリジンとシクロプロピルアミンを縮合させ、その後環化およびメチル化を行うなど、さまざまな方法で合成することができます。 反応条件には、通常、ジメチルホルムアミドなどの溶媒と、炭酸カリウムなどの触媒の使用が含まれます .
工業的生産方法: ネビラピンの工業的生産には、通常、同様の化学経路を使用した大規模合成が伴いますが、収率と純度を高めるために最適化されています。 高圧均質化やナノ懸濁液調製などの技術が、化合物の溶解性とバイオアベイラビリティを向上させるために用いられます .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: ネビラピンは、以下を含むいくつかの種類の化学反応を起こします。
酸化: ネビラピンは、酸化されてさまざまな代謝産物を生成することができます。
還元: 還元反応はそれほど一般的ではありませんが、特定の条件下で起こることがあります。
一般的な試薬と条件:
酸化: 一般的な酸化剤には、過酸化水素と過マンガン酸カリウムが含まれます。
還元: 水素化ホウ素ナトリウムなどの還元剤を使用することができます。
主な生成物: これらの反応から生成される主な生成物には、さまざまな代謝産物やネビラピンの誘導体があり、それらは異なる薬理学的特性を持つ可能性があります .
4. 科学研究アプリケーション
ネビラピンは、以下を含む、幅広い科学研究アプリケーションを持っています。
類似化合物との比較
Efavirenz: Another non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV-1.
Etravirine: Known for its efficacy against HIV-1 strains resistant to other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Rilpivirine: A newer non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a favorable side effect profile
Uniqueness of Nevirapine: Nevirapine is unique due to its ability to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV during childbirth, a feature not commonly associated with other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Additionally, its long half-life allows for less frequent dosing, which can improve patient adherence to the treatment regimen .
生物活性
Nevirapine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) primarily used in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection. It is often part of combination therapy regimens and is especially noted for its role in managing HIV-1. Nevirapine's mechanism of action involves binding to the reverse transcriptase enzyme, thereby inhibiting its function and preventing viral replication.
Nevirapine exerts its antiviral effects by binding to the reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme, which is crucial for the replication of HIV. This binding inhibits both RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities, leading to a disruption of the enzyme's catalytic site. Notably, nevirapine does not compete with nucleoside triphosphates or the template, which allows it to effectively inhibit HIV replication without affecting human DNA polymerases .
Pharmacokinetics
Nevirapine is rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with over 90% bioavailability. It has a low level of protein binding (approximately 60%) and is extensively metabolized in the liver via cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP 3A4 and CYP 2B6). The drug undergoes autoinduction, which increases its clearance rate over time, resulting in a decrease in its terminal half-life from approximately 45 hours after a single dose to about 25-30 hours during chronic dosing .
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Nevirapine
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | >90% |
| Protein Binding | ~60% |
| Half-life (single dose) | ~45 hours |
| Half-life (multiple dosing) | 25-30 hours |
| Clearance Increase | 1.5-2 fold over time |
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
Nevirapine has been evaluated in numerous clinical trials, demonstrating significant efficacy in reducing viral load and increasing CD4 cell counts among HIV-infected patients.
Case Study: Combination Therapy
A randomized double-blind trial compared the effects of various combinations including nevirapine. The study found that patients receiving a triple drug therapy regimen containing nevirapine showed a significantly greater decrease in plasma viral load compared to those on dual therapies. Specifically, at week 52, 51% of patients on triple therapy had undetectable plasma HIV-1 RNA levels compared to only 12% and 0% in the other groups .
Table 2: Efficacy Outcomes from Clinical Trials
| Treatment Group | Plasma HIV-1 RNA <20 copies/mL (%) | Disease Progression/Death (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Triple Drug Therapy | 51% | 12% |
| Zidovudine + Didanosine | 12% | 25% |
| Zidovudine + Nevirapine | 0% | 23% |
Safety Profile and Adverse Effects
While nevirapine is effective, it is associated with several adverse effects, particularly skin rashes and liver toxicity. In clinical studies, rash occurred in approximately 22% of patients treated with nevirapine, with severe cases reported at a lower frequency . Liver function tests often showed elevated levels in patients on nevirapine, necessitating monitoring during treatment.
Table 3: Common Adverse Effects Associated with Nevirapine
| Adverse Effect | Incidence (%) |
|---|---|
| Rash | 22% |
| Elevated Liver Enzymes | 30% |
| Gastrointestinal Complaints | Varies |
Long-term Efficacy and Resistance
Long-term studies have shown that nevirapine-containing regimens can remain effective for over ten years. However, resistance can develop if nevirapine is used as monotherapy or if adherence is poor. Resistance mutations have been identified in patients who experienced treatment failure while on nevirapine .
Case Study: Resistance Development
In a study involving patients who were treated with zidovudine plus nevirapine, resistance was observed in all patients who had viral amplification after six months of therapy. This highlights the importance of adherence to combination therapy to prevent resistance development .
特性
IUPAC Name |
2-cyclopropyl-7-methyl-2,4,9,15-tetrazatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3,5,7,12,14-hexaen-10-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H14N4O/c1-9-6-8-17-14-12(9)18-15(20)11-3-2-7-16-13(11)19(14)10-4-5-10/h2-3,6-8,10H,4-5H2,1H3,(H,18,20) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
NQDJXKOVJZTUJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C2C(=NC=C1)N(C3=C(C=CC=N3)C(=O)N2)C4CC4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C15H14N4O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7031797 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7031797 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
266.30 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>39.9 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), In water, 100 mg/l @ neutral pH, 1.05e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID865943 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Vapor Pressure |
3.4X10-9 mm Hg @ 25 °C /Estimated/ | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Nevirapine binds directly to reverse transcriptase (RT) and blocks the RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by causing a disruption of the enzyme's catalytic site. The activity of nevirapine does not compete with template or nucleoside triphosphates., The binding site for nevirapine on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is near, but not at the proposed site of active polymerization, in a deep pocket lying between the beta sheets of the palm and at the base of the thumb subdomains of the enzyme's p66 subunit. In the absence of nevirapine, the binding of deoxynucleoside triphosphate to the reverse transcriptase-template complex results in a change in the conformation of reverse transcriptase. This conformational change is followed by a magnesium-dependent chemical reaction in which deoxynucleoside triphosphate is incorporated into the newly forming viral DNA; the conformational change appears to be the rate-limiting step of the reverse transcriptase catalysis of viral DNA formation. Nevirapine appears to have no appreciable effect on the rate of or equilibrium constant for the conformational change but may slow the chemical reaction, which then becomes the rate-limiting step in the catalytic sequence. When nevirapine binds to the reverse transcriptase-template complex, changes may occur in the position of aspartic acid carboxyl groups in reverse transcriptase so that magnesium ions are not in proper alignment for the chemical reaction to occur efficiently, and the reaction is slowed. Therefore, although the nevirapine-reverse transcriptase-template complex may continue to bind deoxynucleoside triphosphate and to catalyze its incorporation into the newly forming viral DNA, it appears to do so at a slower rate., The mechanism of action of nevirapine differs from that of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., abacavir, didanosine, lamivudine, stavudine, zalcitabine, zidovudine). Nucleoside antiretroviral agents require intracellular conversion to triphosphate metabolites, which then compete with naturally occurring deoxynucleoside triphosphates for incorporation into viral DNA by reverse transcriptase and cause premature viral DNA chain termination by preventing further 5 to 3 phosphodiester linkages. Nevirapine, however, is noncompetitive with respect to primer-template or nucleoside triphosphate binding and is specific for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. The drug binds directly to heterodimeric HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and appears to inhibit viral RNA- and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activities by disrupting the catalytic site of the enzyme., Nevirapine diffuses into the cell and binds to reverse transcriptase adjacent to the catalytic site. This induces conformational changes that inactivate the enzyme. Resistance develops rapidly in cells exposed to nevirapine. High-level resistance is associated with mutations at reverse transcriptase codons 101, 103, 106,108, 135, 181, 188, and 190. A single mutation at either codon 103 or 181 decreases susceptibility more than 100 fold. Cross-resistance may extend to all FDA-approved nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, especially with the codon 103 mutation., Nevirapine is a highly specific inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, and results of in vitro studies indicate that nevirapine does not appear to inhibit cellular DNA polymerases, including human alpha-, beta-, Gamma-, or Delta-polymerases. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from pyridine and water | |
CAS No. |
129618-40-2 | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=129618-40-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0129618402 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | nevirapine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759902 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | nevirapine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=641530 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7031797 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/99DK7FVK1H | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
247-249 °C, 196.06 °C | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00238 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | NEVIRAPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7164 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Nevirapine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014383 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details




Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。













