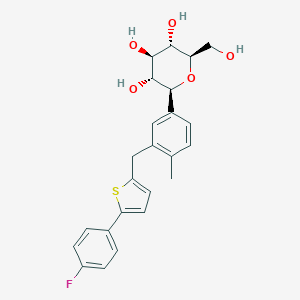
Canagliflozin
概要
説明
カナグリフロジンは、主に2型糖尿病の治療に使用される薬剤です。 これは、ナトリウム-グルコース共輸送体2(SGLT2)阻害剤のクラスに属し、腎臓でのグルコースの再吸収を阻害することで、尿中へのグルコース排泄を増加させることで作用します 。このメカニズムは、2型糖尿病患者の血糖値を下げるのに役立ちます。 カナグリフロジンは、2013年に米国、欧州連合、オーストラリアで医療用として承認されました .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: カナグリフロジンの合成には、鍵となる中間体の調製から始まる複数のステップが含まれます。 その方法の1つは、水または混合溶媒中のカナグリフロジンの懸濁系を形成し、その後結晶化することです 。 もう1つの方法は、テトラヒドロフランやメタノールなどの溶媒に中間体を溶解させ、塩酸を用いて加水分解することです .
工業生産方法: カナグリフロジンの工業生産には、一般的に化合物の溶解度とバイオアベイラビリティの最適化が含まれます。 マイクロエマルジョンプレコンセントレートなどの技術が、カナグリフロジンの溶解度と経口バイオアベイラビリティを向上させるために使用されています 。最適化された製剤は、その溶解速度、透過速度、および経口バイオアベイラビリティについて評価されます。
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of canagliflozin involves multiple steps, starting from the preparation of key intermediates. One of the methods includes the formation of a suspension system of this compound in water or a mixed solvent, followed by crystallization . Another method involves dissolving intermediates in solvents like tetrahydrofuran and methanol, followed by hydrolysis using hydrochloric acid .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound typically involves optimizing the solubility and bioavailability of the compound. Techniques such as microemulsion preconcentrates are employed to improve the solubility and oral bioavailability of this compound . The optimized formulation is evaluated for its dissolution rate, permeation rate, and oral bioavailability.
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: カナグリフロジンは、酸化やグルクロン酸抱合など、さまざまな化学反応を受けます。 主要な代謝経路には、O-グルクロン酸抱合代謝物の形成と酸化生成物の形成が含まれます .
一般的な試薬と条件:
酸化: カナグリフロジンは、M8やM9などの代謝物を生成するために酸化される可能性があります.
グルクロン酸抱合: この反応には、カナグリフロジンへのグルクロン酸の付加が含まれ、M5、M7、M17などの代謝物を生成します.
主要な生成物: これらの反応から生成される主要な生成物には、O-グルクロン酸抱合代謝物と酸化生成物が含まれ、これらは体から排泄されます .
4. 科学研究への応用
カナグリフロジンは、幅広い科学研究への応用があります。
科学的研究の応用
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Canagliflozin is primarily indicated for managing blood glucose levels in patients with T2DM. A long-term post-marketing surveillance study conducted in Japan assessed the safety and effectiveness of this compound in real-world clinical practice. The study included 12,227 patients and demonstrated that this compound maintained significant reductions in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels over three years, with an average decrease of -0.68% . Adverse drug reactions were reported in 10.73% of patients, primarily related to volume depletion and urinary tract infections.
| Parameter | Results |
|---|---|
| Patients Included | 12,227 |
| Mean Age | 58.4 years |
| Baseline HbA1c | 8.01% |
| Mean Change in HbA1c | -0.68% after 3 years |
| Adverse Drug Reactions | 10.73% (most common: volume depletion) |
Cardiovascular Benefits
This compound has been associated with a reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with T2DM at high risk for cardiovascular disease. The this compound Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS) program revealed that this compound significantly lowered the rates of myocardial infarction and stroke compared to placebo . Specifically, the composite outcome of sustained doubling of serum creatinine or end-stage kidney disease occurred less frequently in the this compound group (1.5 vs. 2.8 per 1000 patient-years) .
Renal Protection
Research indicates that this compound may provide protective effects against renal decline in patients with T2DM. In a prespecified exploratory analysis from the CANVAS program, participants treated with this compound experienced slower annual declines in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) compared to those on placebo (slope difference of 1.2 mL/min per year) . Furthermore, this compound reduced urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratios by 18%, suggesting a potential benefit for diabetic kidney disease management .
CHIEF-HF Study
The CHIEF-HF study investigated the effects of this compound on heart failure symptoms among patients with varying ejection fractions and diabetes status. Results indicated that patients receiving this compound experienced significant improvements in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire total symptom scores at 12 weeks compared to those on placebo . This study underscores the potential role of SGLT2 inhibitors in managing heart failure symptoms.
Real-World Evidence
In a real-world setting, a study involving over 10,000 patients demonstrated that this compound effectively lowered blood glucose levels while maintaining a favorable safety profile across different age groups and stages of chronic kidney disease . The findings support its use as a long-term treatment option for T2DM patients.
作用機序
カナグリフロジンは、腎臓の近位尿細管におけるナトリウム-グルコース共輸送体2(SGLT2)を阻害することでその効果を発揮します 。 この阻害は、腎臓尿細管腔からのグルコースの再吸収を阻止し、尿中へのグルコース排泄の増加につながります 。 このメカニズムに関与する分子標的には、腎臓でのグルコース再吸収に関与するSGLT2タンパク質が含まれます .
類似化合物:
- ダパグリフロジン
- エンパグリフロジン
- メトホルミン
- オゼンピック(セマグルチド)
比較:
類似化合物との比較
- Dapagliflozin
- Empagliflozin
- Metformin
- Ozempic (semaglutide)
Comparison:
- Efficacy: Canagliflozin has been shown to have similar efficacy in lowering HbA1c levels compared to empagliflozin and dapagliflozin . this compound may have a slightly higher efficacy at lowering HbA1c compared to dapagliflozin .
- Safety: The safety profiles of this compound, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin are comparable, with common side effects including urinary tract infections and genital infections .
- Uniqueness: this compound is unique in its ability to reduce brain swelling in cerebral ischemia, a property not commonly associated with other SGLT2 inhibitors .
生物活性
Canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, is primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, its biological activity extends beyond glycemic control, impacting various physiological processes including inflammation, cancer cell proliferation, and metabolic pathways. This article explores the diverse biological activities of this compound, supported by recent research findings and case studies.
1. Inhibition of SGLT2:
this compound works by inhibiting SGLT2 in the proximal renal tubules, leading to decreased glucose reabsorption and increased glucose excretion in urine. This mechanism is crucial for its role in lowering blood sugar levels in diabetic patients.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Recent studies indicate that this compound induces heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in human endothelial cells (ECs), contributing to its anti-inflammatory properties. It has been shown to reduce monocyte adhesion to ECs in diabetic environments, suggesting a protective cardiovascular effect .
3. Antitumor Activity:
this compound has demonstrated potential as an anticancer agent. Research indicates that it suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells and enhances their sensitivity to radiotherapy. The drug appears to inhibit mitochondrial respiration and activate AMPK, which are critical pathways for cell survival and proliferation .
Table 1: Summary of Biological Activities of this compound
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Cardiovascular Benefits
A clinical trial evaluated the effects of this compound on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with T2DM and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Results showed significant reductions in heart failure hospitalization rates and improved renal outcomes compared to standard care .
Case Study 2: Cancer Treatment Synergy
In a preclinical study involving prostate cancer models, this compound was found to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy. Tumor growth was significantly inhibited when this compound was administered alongside radiation therapy, suggesting a potential new therapeutic strategy for managing resistant cancer types .
Inflammation and Endothelial Function
A study focused on the effects of this compound on human endothelial cells revealed that it promotes HO-1 expression, which is associated with reduced inflammation. The blockade of EC proliferation and migration by this compound was shown to be independent of HO-1 activity, indicating multiple pathways are involved in its action .
Mechanistic Insights into Antitumor Effects
This compound's ability to modulate metabolic pathways was further elucidated through RNA sequencing analysis. It was found to downregulate genes associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer while upregulating protective genes. This transcriptional reprogramming may contribute to its anticancer effects .
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What are the key considerations in designing randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess canagliflozin’s renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes?
Methodological Answer: RCTs such as CREDENCE and CANVAS used double-blind, placebo-controlled designs with strict inclusion criteria (e.g., eGFR 30–90 mL/min/1.73 m² and albuminuria >300 mg/g creatinine) to target high-risk populations . Composite endpoints (e.g., end-stage kidney disease, doubling of serum creatinine, or renal/cardiovascular death) were prioritized to capture multifactorial benefits. Hierarchical statistical testing ensured robustness in secondary outcome analyses, reducing type I error risks .
Q. How are composite endpoints structured in this compound trials to capture renal and cardiovascular outcomes simultaneously?
Methodological Answer: Composite endpoints integrate clinically significant events (e.g., dialysis, cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction) to enhance statistical power and reflect real-world disease progression. For example, the CREDENCE trial’s primary outcome combined end-stage kidney disease, sustained eGFR decline, and renal/cardiovascular mortality, with pre-specified hierarchical testing to validate secondary outcomes like hospitalization for heart failure .
Q. What safety monitoring protocols are implemented in trials to detect adverse events like genital infections or volume depletion?
Methodological Answer: Adverse events (AEs) are systematically recorded using standardized case report forms. For genital mycotic infections, supplemental electronic forms captured symptom onset, severity, and treatment response. AE incidence rates are compared between treatment arms with adjusted hazard ratios, and sensitivity analyses assess dose-dependence or temporal patterns .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How do researchers reconcile contradictory findings regarding this compound-associated amputation risks across clinical trials?
Methodological Answer: Discrepancies between CANVAS (increased amputation risk: HR 1.97) and CREDENCE (no significant risk) are analyzed via subgroup and meta-analyses. Differences in baseline populations (e.g., peripheral artery disease prevalence) and trial designs (e.g., CANVAS included participants with prior amputations) may explain variance. Sensitivity analyses in pooled datasets and observational studies (e.g., claims databases) further contextualize risks .
Q. What advanced statistical methods are used to analyze this compound’s blood pressure-lowering effects in chronic kidney disease (CKD) subgroups?
Methodological Answer: Post hoc analyses of CREDENCE employed mixed-effects models to assess systolic blood pressure (BP) changes across baseline BP strata. Interaction tests evaluated consistency in treatment effects, while time-to-event analyses quantified reduced need for additional BP-lowering therapies. These methods confirmed this compound’s BP benefits were independent of baseline antihypertensive regimens .
Q. How do network-based molecular models elucidate this compound’s mechanism of action in diabetic kidney disease (DKD)?
Methodological Answer: Omics data (transcriptomics, metabolomics) and literature-derived pathways are integrated into molecular networks. For example, this compound’s impact on fibrosis biomarkers (e.g., TGF-β1, collagen IV) and amino acid metabolism (e.g., hepatic arginine synthesis) is modeled to identify upstream regulators and downstream effectors. Experimental validation via cell culture and animal models confirms mechanistic hypotheses .
Q. What analytical quality-by-design (AQbD) strategies optimize HPLC quantification of this compound in pharmacokinetic studies?
Methodological Answer: Central composite design (CCD) optimizes critical parameters (e.g., mobile phase pH, flow rate) to resolve this compound/metformin peaks. Contour plots define method operable design regions (MODR), ensuring robustness across variable conditions. Forced degradation studies (acid/alkaline hydrolysis, oxidation) validate stability-indicating properties, supporting regulatory compliance .
Q. Contradictory Data Analysis
Q. How do researchers address conflicting evidence on this compound’s fracture risk in type 2 diabetes?
Methodological Answer: Pooled analyses of Phase 3 trials and dedicated bone safety studies (e.g., CANVAS vs. CREDENCE) stratify participants by baseline fracture risk factors. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and MRI assess bone density/microarchitecture in animal models. Meta-regressions adjust for confounding variables (e.g., age, osteoporosis prevalence), clarifying that fracture risk is not significant in low-risk populations .
Q. Methodological Innovations
Q. What novel biomarker panels are validated to predict this compound’s efficacy in metabolic syndrome components?
Methodological Answer: Targeted metabolomics identifies biomarkers like adiponectin, leptin, and free fatty acids, which correlate with this compound’s effects on insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Machine learning algorithms integrate these biomarkers with clinical variables (e.g., HbA1c, BMI) to develop predictive efficacy scores, validated in post hoc analyses of RCTs .
特性
IUPAC Name |
(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[3-[[5-(4-fluorophenyl)thiophen-2-yl]methyl]-4-methylphenyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H25FO5S/c1-13-2-3-15(24-23(29)22(28)21(27)19(12-26)30-24)10-16(13)11-18-8-9-20(31-18)14-4-6-17(25)7-5-14/h2-10,19,21-24,26-29H,11-12H2,1H3/t19-,21-,22+,23-,24+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XTNGUQKDFGDXSJ-ZXGKGEBGSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2C(C(C(C(O2)CO)O)O)O)CC3=CC=C(S3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)O)CC3=CC=C(S3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H25FO5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID601004469 | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID601004469 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
444.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Boiling Point |
642.9±55.0 | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08907 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Solubility |
almost insoluble, Practically insoluble in aqueous media from pH 1.1 to pH 12.9 /Canagliflozin hemihydrate/ | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08907 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8284 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The sodium-glucose co-transporter2 (SGLT2), is found in the proximal tubules of the kidney, and reabsorbs filtered glucose from the renal tubular lumen. Canagliflozin inhibits the SGLT2 co-transporter. This inhibition leads to lower reabsorption of filtered glucose into the body and decreases the renal threshold for glucose (RTG), leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine., Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2), expressed in the proximal renal tubules, is responsible for the majority of the reabsorption of filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Canagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, canagliflozin reduces reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose (RTG), and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion (UGE). | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08907 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8284 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
842133-18-0 | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=842133-18-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0842133180 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08907 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID601004469 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-C-(3-{[5-(4-fluorophenyl)thiophen-2-yl]methyl]}-4-methylphenyl)-D-glucitol | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CANAGLIFLOZIN ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6S49DGR869 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8284 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
68-72 | |
| Record name | Canagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08907 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















