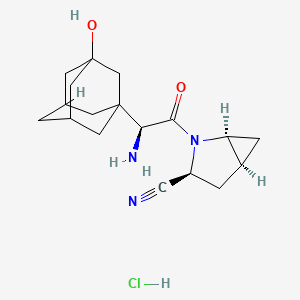
Saxagliptin hydrochloride
説明
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩は、2型糖尿病の管理に使用される経口活性降血糖薬です。これは、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)阻害剤のクラスに属し、体内のインクレチンホルモンのレベルを上昇させることで作用します。 これらのホルモンは、インスリン産生を増加させ、肝臓によるグルコース産生を減少させることで、血糖値を調節するのに役立ちます .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: サクサグリプチン塩酸塩の合成には、いくつかの重要なステップが含まれます。一般的な方法の1つは、カップリング試薬の存在下で2つのアミノ酸誘導体をカップリングすることです。 (S)-(+)-p-トルエンスルホンアミド、チタン(IV)エトキシド、アダマンタン-1-カルボキシアルデヒドをカップリングしてヒドロキシベンゾトリアゾールおよびEDC(1-エチル-3-(3-ジメチルアミノプロピル)カルボジイミド)を得るアミドカップリングは、重要なステップです .
工業的製造方法: サクサグリプチン塩酸塩の工業的製造は、しばしば、化合物の定量および確認のために、高性能液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)の使用が含まれます。 この方法は、最終製品の純度と品質を保証します .
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of Saxagliptin Hydrochloride involves several key steps. One common method includes the coupling of two amino acid derivatives in the presence of a coupling reagent. The amide coupling of (S)-(+)-p-toluenesulfonamide, titanium(IV) ethoxide, and adamantane-1-carboxaldehyde to obtain hydroxybenzotriazole and EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide) is a crucial step .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound often involves the use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the quantification and validation of the compound. This method ensures the purity and quality of the final product .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: サクサグリプチン塩酸塩は、次のようなさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: この反応は、酸素の付加または水素の除去を含みます。
還元: この反応は、水素の付加または酸素の除去を含みます。
置換: この反応は、1つの原子または原子団を別の原子または原子団で置き換えることを含みます。
一般的な試薬と条件: これらの反応で使用される一般的な試薬には、過マンガン酸カリウムなどの酸化剤、水素化ホウ素ナトリウムなどの還元剤、ハロゲンなどの置換試薬があります。 これらの反応の条件は、通常、目的の結果を確保するために、制御された温度とpHレベルを伴います .
生成される主な生成物: これらの反応から生成される主な生成物には、サクサグリプチン塩酸塩の合成に不可欠なさまざまな中間体があります。 これらの中間体は、その後、最終化合物を得るためにさらに処理されます .
4. 科学研究への応用
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩は、幅広い科学研究への応用があります。
化学: 酵素阻害剤とその代謝経路への影響に関する研究に使用されます。
生物学: グルコース調節におけるインクレチンホルモンの役割を理解するために使用されます。
医学: 主に、血糖コントロールを改善するために、2型糖尿病の治療に使用されます。
科学的研究の応用
Primary Use in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Saxagliptin is primarily indicated for use as an adjunct to diet and exercise in adults with type 2 diabetes. It has shown effectiveness in lowering blood sugar levels, improving glycemic control as measured by reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. Clinical studies have demonstrated that saxagliptin can lead to significant improvements in fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose levels across diverse patient populations, including those with varying cardiovascular risk factors .
Combination Therapy
Recent studies have explored the efficacy of saxagliptin when used in combination with other treatments:
- With Insulin : Saxagliptin has been shown to be effective in patients already on insulin therapy, providing additional glycemic control .
- With Vitamin D : A study indicated that saxagliptin combined with vitamin D could help preserve beta-cell function in adult-onset type 1 diabetes, demonstrating a potential role beyond type 2 diabetes management .
Cardiovascular Implications
Research has suggested that saxagliptin may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular health. In various clinical trials, it was found to be well-tolerated and associated with improved glycemic control without significant adverse cardiovascular events, making it a suitable option for diabetic patients with cardiovascular concerns .
Renal Impairment Considerations
Saxagliptin's pharmacokinetics are affected by renal function. Studies indicate that dosage adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment to avoid increased exposure and potential side effects. This highlights the importance of individualized treatment plans based on renal function .
Clinical Trials Overview
A comprehensive review of clinical trials involving saxagliptin reveals consistent findings regarding its efficacy and safety:
Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, saxagliptin can cause side effects such as:
- Headache
- Nasopharyngitis
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Rarely, pancreatitis or severe allergic reactions .
Case Study: Saxagliptin and Beta-Cell Function Preservation
A multicenter randomized trial evaluated the impact of saxagliptin combined with vitamin D on beta-cell function in patients with adult-onset type 1 diabetes. The study demonstrated that this combination therapy led to a statistically significant preservation of C-peptide levels over a 24-month period compared to conventional therapy alone, suggesting potential benefits for patients beyond standard diabetes management .
Observational Study: Hospitalized Heart Failure Risk
An observational study assessed the risk of hospitalized heart failure among new users of saxagliptin compared to other DPP-4 inhibitors. The findings indicated no significant increase in heart failure risk among saxagliptin users, reinforcing its safety profile in diabetic patients with pre-existing heart conditions .
作用機序
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩は、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)酵素を阻害することで作用します。この阻害は、グルカゴン様ペプチド-1(GLP-1)およびグルコース依存性インスリン分泌促進ポリペプチド(GIP)などのインクレチンホルモンのレベルを上昇させます。 これらのホルモンは、インスリン分泌を増加させ、肝臓からのグルカゴン分泌を減少させることで、血糖値を下げるのに役立ちます .
類似化合物:
メトホルミン: インスリン感受性を改善する別の抗糖尿病薬。
セマグルチド: インクレチンホルモンの効果を模倣するGLP-1受容体アゴニスト。
比較:
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩対メトホルミン: サクサグリプチン塩酸塩はDPP-4を阻害することで作用しますが、メトホルミンはインスリン感受性を改善します。
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩対セマグルチド: 両方の薬物はインクレチンホルモンのレベルを上昇させますが、セマグルチドはGLP-1受容体アゴニストであり、サクサグリプチン塩酸塩はDPP-4阻害剤です。
サクサグリプチン塩酸塩は、その独特の作用機序と2型糖尿病の併用療法における有効性により際立っています。
類似化合物との比較
Metformin: Another antidiabetic drug that improves insulin sensitivity.
Semaglutide: A GLP-1 receptor agonist that mimics the effects of incretin hormones.
Comparison:
Saxagliptin Hydrochloride vs. Metformin: this compound works by inhibiting DPP-4, while Metformin improves insulin sensitivity.
This compound vs. Semaglutide: Both drugs increase the levels of incretin hormones, but Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, while this compound is a DPP-4 inhibitor.
This compound stands out due to its specific mechanism of action and its effectiveness in combination therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
生物活性
Saxagliptin hydrochloride is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Its biological activity is characterized by its ability to enhance glycemic control through various mechanisms, including the modulation of incretin hormones. This article explores the biological activity of saxagliptin, supported by data tables, case studies, and detailed research findings.
Saxagliptin acts by inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme, which is responsible for the degradation of incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). By preventing the breakdown of these hormones, saxagliptin increases their levels in circulation, leading to:
- Increased Insulin Secretion : Saxagliptin enhances insulin release from pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Decreased Glucagon Secretion : It reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, which helps lower hepatic glucose production.
- Improved Glycemic Control : The overall effect is a reduction in fasting plasma glucose and postprandial glucose levels.
The selectivity of saxagliptin for DPP-4 over other DPP enzymes (DPP-8 and DPP-9) is notable, with a 400-fold and 950-fold selectivity, respectively . This selectivity contributes to its favorable safety profile, minimizing adverse effects associated with non-selective DPP inhibition.
Pharmacokinetics
Saxagliptin exhibits first-order kinetics with a median time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) of approximately 2 hours after oral administration. The elimination half-life is about 2.5 hours for saxagliptin and 3.1 hours for its active metabolite M2 . Key pharmacokinetic parameters are summarized in Table 1.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | 67% |
| Volume of Distribution | 151 L |
| Protein Binding | <10% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4/5 |
| Elimination | Renal and hepatic |
| Half-life | Saxagliptin: 2.5 hours; M2: 3.1 hours |
Clinical Efficacy
Saxagliptin has demonstrated significant efficacy in improving glycemic control in various clinical settings:
- Monotherapy : In clinical trials, saxagliptin reduced HbA1c levels by approximately 0.7% to 0.9% compared to placebo .
- Combination Therapy : When used in combination with metformin or sulfonylureas, saxagliptin showed enhanced efficacy without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia .
Case Study Findings
A recent multi-center randomized controlled trial investigated the effects of saxagliptin combined with vitamin D on β-cell preservation in T2DM patients. Results indicated that participants receiving saxagliptin plus vitamin D had a significant preservation of β-cell function compared to those on conventional therapy alone:
- C-peptide AUC Change at 24 Months :
- Saxagliptin + Vitamin D: -276 pmol/L
- Saxagliptin Alone: -314 pmol/L
- Conventional Therapy: -419 pmol/L
The proportion of participants showing a ΔC-peptide response was significantly higher in the saxagliptin plus vitamin D group (57.6%) compared to conventional therapy (37.2%) .
Safety Profile
Saxagliptin is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of hypoglycemia and weight neutrality observed across clinical trials. Adverse effects are comparable to placebo, making it a favorable option for T2DM management .
Q & A
Q. How can researchers optimize analytical methods for simultaneous quantification of Saxagliptin hydrochloride in combination therapies (e.g., with Metformin or Dapagliflozin)?
Answer:
Researchers should prioritize chromatographic techniques such as HPTLC or RP-HPLC due to their specificity and reproducibility. For HPTLC, a validated method using silica gel plates with a mobile phase of acetonitrile:1% ammonium acetate (9:1 v/v) and detection at 210 nm enables simultaneous analysis of Saxagliptin (SAX), Metformin (MET), and Dapagliflozin (DAP) with linear ranges of 0.25–10 μg/band (SAX/DAP) and 0.25–25 μg/band (MET) . For HPLC, a C18 column with phosphate buffer (pH 4.5) and acetonitrile gradient elution achieves baseline separation of SAX and MET, with validation per ICH guidelines for precision (RSD <2%) and accuracy (98–102%) .
Q. What safety protocols are critical for handling this compound in laboratory settings?
Answer:
this compound poses risks of skin sensitization and respiratory irritation. Key protocols include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Nitrile gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles to avoid direct contact .
- Ventilation: Use fume hoods for powder handling to prevent inhalation of dust/particulates .
- Storage: Keep in airtight containers at 2–8°C, away from moisture and incompatible substances (e.g., strong oxidizers) .
- Spill Management: Neutralize spills with inert absorbents (e.g., vermiculite) and dispose of as hazardous waste .
Q. What experimental design considerations are essential for developing controlled-release formulations of this compound?
Answer:
Preformulation studies should focus on:
- Solubility and Stability: Assess pH-dependent solubility (optimal at 4.5–6.5) and photostability under ICH Q1B guidelines .
- Excipient Compatibility: Screen with osmotic agents (e.g., cellulose acetate) and plasticizers (e.g., PEG 400) for bilayer tablets combining immediate-release SAX and controlled-release MET .
- In Vitro Release Testing: Use USP Apparatus II (paddle) at 50 rpm in 0.1N HCl for 2 hours followed by pH 6.8 buffer to simulate gastrointestinal conditions .
Q. How can researchers resolve contradictions between preclinical and clinical pharmacokinetic data for this compound?
Answer:
Discrepancies often arise from species-specific DPP-4 enzyme affinity or metabolite activity. Strategies include:
- Metabolite Profiling: SAX’s active metabolite (M2) contributes 50% of DPP-4 inhibition in humans but exhibits lower potency in rodents .
- Dose Adjustments: Use allometric scaling based on body surface area and enzyme expression levels in target tissues .
- Population Pharmacokinetics: Apply nonlinear mixed-effects modeling (NONMEM) to account for inter-individual variability in clinical trials .
Q. What methodological approaches validate this compound’s selectivity for DPP-4 inhibition over related proteases?
Answer:
- Enzyme Assays: Compare IC₅₀ values against DPP-8 and DPP-9 using fluorogenic substrates (e.g., H-Gly-Pro-AMC). SAX shows >400-fold selectivity for DPP-4 (Ki = 0.6–1.3 nM) .
- Structural Analysis: Molecular docking studies reveal SAX’s cyanopyrrolidine group forms hydrogen bonds with DPP-4’s Glu205 and Tyr547 residues, unlike DPP-8/9 .
Q. What stability challenges arise in this compound formulations, and how are they mitigated?
Answer:
- Hydrolysis: SAX degrades in acidic conditions (e.g., gastric pH). Use enteric coatings (e.g., Eudragit L100) for delayed release .
- Oxidation: Include antioxidants (e.g., ascorbic acid) in lyophilized parenteral formulations to prevent degradation during storage .
- Photodegradation: Protect tablets with opaque packaging (e.g., aluminum blisters) .
Q. How should clinical trials be designed to assess Saxagliptin’s long-term cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes?
Answer:
- Endpoint Selection: Composite endpoints (e.g., MACE: cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI/stroke) aligned with FDA guidance .
- Comparator Arms: Use active controls (e.g., Sitagliptin) and adjust for baseline HbA1c variability .
- Follow-Up Duration: Minimum 2 years to detect treatment-emergent effects (e.g., heart failure risk) .
特性
IUPAC Name |
(1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-amino-2-(3-hydroxy-1-adamantyl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H25N3O2.ClH/c19-8-13-2-12-3-14(12)21(13)16(22)15(20)17-4-10-1-11(5-17)7-18(23,6-10)9-17;/h10-15,23H,1-7,9,20H2;1H/t10?,11?,12-,13+,14+,15-,17?,18?;/m1./s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
TUAZNHHHYVBVBR-NHKADLRUSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1C2CC2N(C1C#N)C(=O)C(C34CC5CC(C3)CC(C5)(C4)O)N.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1[C@@H]2C[C@@H]2N([C@@H]1C#N)C(=O)[C@H](C34CC5CC(C3)CC(C5)(C4)O)N.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C18H26ClN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID50991191 | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID50991191 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
351.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
709031-78-7 | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0709031787 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Saxagliptin hydrochloride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID50991191 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SAXAGLIPTIN HYDROCHLORIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/Z8J84YIX6L | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















