ザヌブルチニブ
説明
ザヌブルチニブは、ブルキンサという商品名で販売されている、第2世代のブルトン型チロシンキナーゼ(BTK)阻害剤です。 主に、マントル細胞リンパ腫、ワルデンストロームマクログロブリン血症、辺縁帯リンパ腫、慢性リンパ性白血病などのさまざまなB細胞悪性腫瘍の治療に使用されます 。 この化合物は、第1世代のBTK阻害剤と比較して、著しい有効性と安全性の改善を示しており、これらの状態を持つ患者にとって有望な選択肢となっています .
科学的研究の応用
Clinical Applications
Zanubrutinib is primarily approved for the treatment of several hematological malignancies:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
- Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM)
- Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL)
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
In head-to-head trials against ibrutinib, zanubrutinib demonstrated superior efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL. The ALPINE trial showed that zanubrutinib achieved an overall response rate of 78.3% compared to 62.5% for ibrutinib. Additionally, progression-free survival was significantly higher at 94.9% for zanubrutinib versus 84.0% for ibrutinib at the 12-month mark .
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Zanubrutinib has shown promising results in MCL, with a reported overall response rate of 83.7% in clinical trials. The long-term follow-up indicated a high rate of complete responses and durable remissions among patients treated with zanubrutinib .
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
In WM, zanubrutinib has been evaluated in large-scale studies, demonstrating favorable safety and efficacy profiles similar to those observed in CLL and MCL .
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Recently, zanubrutinib received accelerated approval for use in relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma in combination with obinutuzumab. In clinical trials, this combination yielded an overall response rate of 69%, significantly higher than obinutuzumab monotherapy .
Safety Profile
Zanubrutinib's safety profile is notably improved compared to earlier BTK inhibitors:
- Reduced rates of atrial fibrillation (2.5% vs. 10.1% with ibrutinib).
- Lower incidence of major hemorrhages and treatment discontinuation due to adverse events .
Comparative Efficacy
The following table summarizes the comparative efficacy of zanubrutinib against other treatments:
| Condition | Zanubrutinib Efficacy | Comparison Treatment | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Higher overall response | Ibrutinib | 78.3% vs 62.5% |
| Mantle Cell Lymphoma | High overall response | N/A | 83.7% |
| Waldenström Macroglobulinemia | Favorable | N/A | N/A |
| Marginal Zone Lymphoma | Combined therapy | Obinutuzumab | 69% |
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Ongoing clinical trials are assessing the potential of zanubrutinib in various combinations with other therapies and exploring its efficacy in additional hematological malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The focus on enhancing patient outcomes while minimizing side effects continues to drive research initiatives.
作用機序
ザヌブルチニブは、B細胞受容体シグナル伝達経路における重要な酵素であるブルトン型チロシンキナーゼを選択的に阻害することで、その効果を発揮します。 ザヌブルチニブは、BTKの活性部位に結合することで、下流シグナル伝達分子のリン酸化と活性化を阻止し、最終的にB細胞の増殖と生存の阻害につながります 。 この標的化された作用は、腫瘍の増殖を抑制し、B細胞悪性腫瘍患者の転帰を改善します .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Zanubrutinib plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), an enzyme involved in B-cell receptor signaling . This inhibition disrupts the survival and proliferation of malignant B cells. Zanubrutinib interacts specifically with BTK by binding to its active site, leading to the inhibition of downstream signaling pathways that promote cell survival and proliferation . Compared to first-generation BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib, zanubrutinib exhibits higher selectivity for BTK with fewer off-target effects .
Cellular Effects
Zanubrutinib exerts significant effects on various types of cells, particularly B cells. By targeting BTK, zanubrutinib impairs cell proliferation, migration, and activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) . This inhibition leads to reduced cell survival and proliferation in malignant B cells. Additionally, zanubrutinib influences cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism, contributing to its therapeutic efficacy in B-cell malignancies .
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, zanubrutinib exerts its effects by binding covalently to the active site of BTK, thereby inhibiting its kinase activity . This binding prevents the phosphorylation of downstream signaling molecules, ultimately leading to the inhibition of B-cell receptor signaling pathways . The inhibition of BTK by zanubrutinib results in decreased activation of NF-κB and other transcription factors, reducing the expression of genes involved in cell survival and proliferation .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of zanubrutinib have been observed to change over time. Studies have shown that zanubrutinib maintains its stability and potency over extended periods . Long-term exposure to zanubrutinib can lead to the development of resistance in some cases . Additionally, the degradation of zanubrutinib and its metabolites has been studied to understand its long-term effects on cellular function .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of zanubrutinib vary with different dosages in animal models. Studies have demonstrated that zanubrutinib is well-tolerated at therapeutic doses, with minimal toxic or adverse effects . At higher doses, zanubrutinib can cause toxic effects, including hematological toxicity and liver damage . These findings highlight the importance of optimizing dosage to achieve therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Zanubrutinib is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A in the liver . The metabolic pathways of zanubrutinib involve oxidation and subsequent conjugation reactions, leading to the formation of various metabolites . These metabolites are then excreted through the urine and feces . The interaction of zanubrutinib with metabolic enzymes and cofactors plays a crucial role in determining its pharmacokinetic properties and overall efficacy .
Transport and Distribution
Zanubrutinib is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through passive diffusion and active transport mechanisms . It interacts with various transporters and binding proteins, which facilitate its uptake and distribution . The localization and accumulation of zanubrutinib within specific tissues and compartments are influenced by these interactions, contributing to its therapeutic effects .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of zanubrutinib is primarily within the cytoplasm, where it interacts with BTK and other signaling molecules . Zanubrutinib does not require specific targeting signals or post-translational modifications for its localization . Its activity and function are determined by its ability to bind to BTK and inhibit its kinase activity within the cytoplasm .
準備方法
ザヌブルチニブの合成には、いくつかの重要なステップが含まれています。主な合成経路の1つは、フェノキシフェニル誘導体とピペリジニルピラゾロピリミジン中間体のカップリングです。 最終生成物は、キラル高速液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)分離によって得られます 。 工業生産方法は、収率、化学純度、光学純度を最適化することに重点を置いており、化合物が大規模製造に適していることを保証しています .
化学反応の分析
ザヌブルチニブは、次のようなさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: ザヌブルチニブは、特定の条件下で酸化されて、分解生成物を生成する可能性があります。
還元: この化合物は、還元的なストレスを受けると、異なる分解生成物を生成する可能性があります。
これらの反応で使用される一般的な試薬には、酸、塩基、酸化剤が含まれます。 これらの反応から生成された主な生成物は、一般的には分解生成物であり、化合物の安定性と有効性を確保するために分析されます .
4. 科学研究への応用
ザヌブルチニブは、科学研究において幅広い用途があります。
化学: BTK阻害と、それがB細胞受容体シグナル伝達経路に及ぼす影響を研究するためのモデル化合物として使用されます。
生物学: ザヌブルチニブは、免疫応答や細胞増殖など、さまざまな細胞プロセスにおけるBTKの役割を理解するための研究に使用されます。
医学: 臨床的には、ザヌブルチニブはB細胞悪性腫瘍の治療に使用され、第1世代の阻害剤と比較して、標的療法の選択肢を提供し、オフターゲット効果が少なくなっています.
類似化合物との比較
ザヌブルチニブは、イブルチニブやアカラブルチニブなどの他のBTK阻害剤と比較されることがよくあります。 3つの化合物はすべてBTKを標的としていますが、ザヌブルチニブは、より高い選択性と効力を示しており、オフターゲット効果が少なく、安全性が向上しています 。 さらに、ザヌブルチニブは、阻害濃度を超える継続的な暴露を提供し、その有効性を高めます .
類似化合物
イブルチニブ: オフターゲット効果がより広範な第1世代のBTK阻害剤。
結論として、ザヌブルチニブは、B細胞悪性腫瘍の治療における大きな進歩であり、以前のBTK阻害剤よりも有効性と安全性が向上しています。その標的化された作用機序と幅広い科学的応用は、臨床および研究の両方の設定において貴重な化合物となっています。
生物活性
Zanubrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, has emerged as a significant therapeutic agent for various B-cell malignancies. This article delves into its biological activity, highlighting its pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, safety profile, and comparative studies with other BTK inhibitors, particularly ibrutinib.
Zanubrutinib is designed to irreversibly bind to BTK, inhibiting its activity and thereby blocking B-cell receptor signaling pathways essential for the survival and proliferation of malignant B-cells. The compound was developed to enhance specificity and reduce off-target effects compared to earlier BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib. Preclinical studies indicated that zanubrutinib exhibits greater selectivity for BTK, with over 50% inhibition in only seven kinases compared to 17 kinases for ibrutinib .
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetic Profile:
- Zanubrutinib demonstrates a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with a higher area-under-the-curve (AUC) compared to ibrutinib. It achieves 100% peripheral blood BTK blockade at a dose of 40 mg daily and maintains significant BTK occupancy in lymph nodes at approved doses .
- The steady-state exposures of zanubrutinib ensure sustained BTK inhibition, which is crucial for therapeutic efficacy .
Pharmacodynamic Effects:
- Clinical trials have shown that zanubrutinib maintains over 95% BTK occupancy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and lymph nodes, which correlates with its clinical efficacy .
- In a Phase 1 study involving patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), zanubrutinib achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 96.2%, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 100% at 12 months .
Clinical Efficacy
Zanubrutinib has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials across various B-cell malignancies:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL):
- Waldenström Macroglobulinemia:
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma:
Safety Profile
Zanubrutinib's safety profile is characterized by a lower incidence of major toxicities compared to traditional therapies:
- The most common adverse events are grade 1/2 toxicities, with neutropenia being the only grade 3/4 toxicity observed in more than two patients during clinical trials .
- The reduced off-target effects contribute to its improved tolerability and patient adherence compared to other BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib .
Comparative Studies
The following table summarizes key findings from comparative studies between zanubrutinib and ibrutinib:
特性
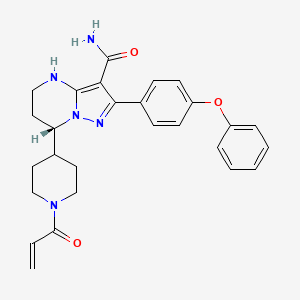
IUPAC Name |
(7S)-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-7-(1-prop-2-enoylpiperidin-4-yl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H29N5O3/c1-2-23(33)31-16-13-18(14-17-31)22-12-15-29-27-24(26(28)34)25(30-32(22)27)19-8-10-21(11-9-19)35-20-6-4-3-5-7-20/h2-11,18,22,29H,1,12-17H2,(H2,28,34)/t22-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
RNOAOAWBMHREKO-QFIPXVFZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)C2CCNC3=C(C(=NN23)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)[C@@H]2CCNC3=C(C(=NN23)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C27H29N5O3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID701026208 | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701026208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
471.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor kinase and a signalling molecule for the B cell receptors expressed on the peripheral B cell surface. The BCR signalling pathway plays a crucial role in normal B-cell development but also the proliferation and survival of malignant B cells in many B cell malignancies, including mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL). Once activated by upstream Src-family kinases, BTK phosphorylates phospholipase-Cγ (PLCγ), leading to Ca2+ mobilization and activation of NF-κB and MAP kinase pathways. These downstream cascades promote the expression of genes involved in B cell proliferation and survival. The BCR signalling pathway also induces the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL and regulates the integrin α4β1 (VLA-4)-mediated adhesion of B cells to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and fibronectin via BTK. Apart from the direct downstream signal transduction pathway of B cells, BTK is also involved in chemokine receptor, Toll-like receptor (TLR) and Fc receptor signalling pathways. Zanubrutinib inhibits BTK by forming a covalent bond with cysteine 481 residue in the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–binding pocket of BTK, which is the enzyme's active site. This binding specificity is commonly seen with other BTK inhibitors. Due to this binding profile, zanubrutinib may also bind with varying affinities to related and unrelated ATP-binding kinases that possess a cysteine residue at this position. By blocking the BCR signalling pathway, zanubrutinib inhibits the proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion of malignant B cells, ultimately leading to reduced tumour size. Zanubrutinib was also shown to downregulate programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-1) expression and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) on CD4+ T cells. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB15035 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1691249-45-2 | |
| Record name | (7S)-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-7-[1-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-4-piperidinyl]-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1691249-45-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1691249452 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB15035 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701026208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | ZANUBRUTINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/AG9MHG098Z | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















