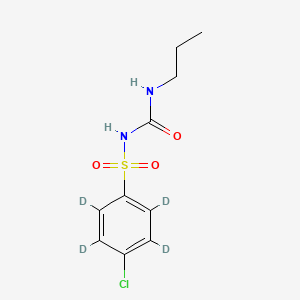
Chlorpropamide-d4
描述
Chlorpropamide-d4 is a deuterated form of chlorpropamide, an antidiabetic drug belonging to the sulfonylurea class of organic compounds. It is used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The deuterated form, this compound, is often used in scientific research as an internal standard in mass spectrometry due to its stable isotopic labeling .
准备方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of Chlorpropamide-d4 involves the incorporation of deuterium atoms into the chlorpropamide molecule. This can be achieved through various methods, including catalytic hydrogen-deuterium exchange reactions. The reaction typically involves the use of deuterium gas (D2) in the presence of a catalyst such as palladium on carbon (Pd/C) under controlled conditions .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process involves stringent quality control measures to ensure the purity and isotopic labeling of the final product. The use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry is common in the quality assessment of this compound .
化学反应分析
Types of Reactions
Chlorpropamide-d4, like its non-deuterated counterpart, undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized to form sulfoxides and sulfones.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can convert the sulfonyl group to a sulfide.
Substitution: Nucleophilic substitution reactions can occur at the chloro group, leading to the formation of various derivatives.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
Reduction: Reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) are used.
Substitution: Nucleophiles like sodium methoxide (NaOCH3) can be used for substitution reactions.
Major Products Formed
Oxidation: Sulfoxides and sulfones.
Reduction: Sulfides.
Substitution: Various substituted derivatives depending on the nucleophile used.
科学研究应用
Chlorpropamide-d4 is extensively used in scientific research, particularly in the fields of:
Chemistry: As an internal standard in mass spectrometry for the quantification of chlorpropamide and related compounds.
Biology: In studies involving the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of chlorpropamide.
Medicine: In research focused on the treatment of diabetes and the development of new antidiabetic drugs.
Industry: In the quality control and validation of pharmaceutical formulations containing chlorpropamide
作用机制
Chlorpropamide-d4, like chlorpropamide, acts by stimulating the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells. It binds to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the pancreatic cell surface, reducing potassium conductance and causing depolarization of the membrane. This depolarization opens voltage-gated calcium channels, leading to an influx of calcium ions and subsequent insulin release .
相似化合物的比较
Similar Compounds
Tolbutamide: Another first-generation sulfonylurea with a shorter duration of action.
Glipizide: A second-generation sulfonylurea with a more potent effect and shorter half-life.
Glyburide: A second-generation sulfonylurea with a longer duration of action compared to glipizide.
Uniqueness
Chlorpropamide-d4 is unique due to its deuterated nature, which makes it particularly useful as an internal standard in analytical chemistry. Its long half-life and potent insulin-releasing effect make it distinct among first-generation sulfonylureas .
生物活性
Chlorpropamide-d4 is a deuterated form of chlorpropamide, a sulfonylurea class medication primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Understanding its biological activity is crucial for optimizing therapeutic use and minimizing adverse effects. This article delves into the mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, potential side effects, and relevant case studies associated with this compound.
This compound, like its non-deuterated counterpart, functions as an insulin secretagogue. The primary mechanism involves the inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells. This inhibition results in membrane depolarization, leading to increased intracellular calcium levels through voltage-gated calcium channels. The elevated calcium concentration stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas, thereby lowering blood glucose levels .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits similar pharmacokinetic properties to chlorpropamide:
- Absorption : Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 2-4 hours post-administration.
- Half-life : Approximately 36 hours, with variability between individuals ranging from 25 to 60 hours.
- Metabolism : About 80% of the dose is metabolized in the liver to various metabolites, including 2-hydroxylchlorpropamide and p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea.
- Excretion : 80-90% of the administered dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug and metabolites within 96 hours .
Biological Activity and Side Effects
While this compound shares many characteristics with chlorpropamide, its deuteration may influence its metabolic stability and biological effects. The following table summarizes key findings related to its biological activity and potential side effects:
| Parameter | Chlorpropamide | This compound |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Management of type 2 diabetes | Investigational use; potential therapeutic benefits |
| Mechanism of Action | Insulin secretion stimulation | Similar mechanism; potential for altered pharmacodynamics |
| Common Side Effects | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, hyponatremia | Expected similar side effects; ongoing research needed |
| Metabolism | Liver metabolism; multiple metabolites | Potentially altered metabolism due to deuteration |
| Elimination Route | Urinary excretion | Expected similar elimination pathway |
Case Studies
- Hyponatremia Incidence : A study involving 176 patients treated with chlorpropamide reported a 6.3% incidence of hyponatremia. Factors such as age and concurrent use of thiazide diuretics significantly increased risk . While specific data on this compound is limited, it is essential to monitor sodium levels in patients receiving treatment.
- Hepatotoxicity Reports : Chlorpropamide has been linked to hepatotoxic reactions presenting as cholestatic liver injury. A case study highlighted an unusual presentation of hepatotoxicity in a patient treated with chlorpropamide, suggesting that monitoring liver function is critical during therapy . The implications for this compound regarding hepatotoxicity remain to be thoroughly investigated.
- Cardiovascular Risks : Research indicates that sulfonylureas may carry an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality compared to dietary management alone. This finding raises concerns about the long-term safety profile of chlorpropamide and potentially this compound .
属性
IUPAC Name |
1-(4-chloro-2,3,5,6-tetradeuteriophenyl)sulfonyl-3-propylurea | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H13ClN2O3S/c1-2-7-12-10(14)13-17(15,16)9-5-3-8(11)4-6-9/h3-6H,2,7H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14)/i3D,4D,5D,6D | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
RKWGIWYCVPQPMF-LNFUJOGGSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
[2H]C1=C(C(=C(C(=C1S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)NCCC)[2H])[2H])Cl)[2H] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H13ClN2O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
280.77 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details







体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。













