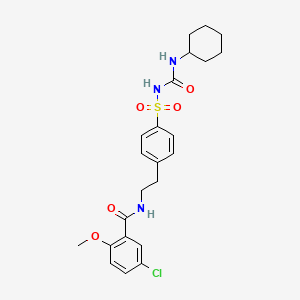
Glyburide
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件: 格列本脲通过多步合成过程合成,涉及5-氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸与2-氨基乙基磺酰胺反应生成5-氯-2-甲氧基-N-(2-(4-磺酰胺苯基)乙基)苯甲酰胺。 然后,该中间体与环己基异氰酸酯反应生成格列本脲 .
工业生产方法: 格列本脲的工业生产涉及优化反应条件,以确保高收率和纯度。 该过程通常包括结晶、过滤和干燥等步骤,以获得纯净的最终产品 .
化学反应分析
反应类型: 格列本脲会发生各种化学反应,包括氧化、还原和取代反应。
常见试剂和条件:
氧化: 格列本脲可在酸性条件下使用过氧化氢或高锰酸钾等试剂氧化。
还原: 格列本脲的还原可以使用硼氢化钠或氢化铝锂等还原剂实现。
主要生成物: 这些反应产生的主要产物取决于所使用的特定试剂和条件。 例如,氧化可能产生羟基化的衍生物,而还原可以生成脱氯或脱甲基化的产物 .
科学研究应用
Diabetes Management
Glyburide is commonly prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes who are unable to achieve adequate glycemic control with lifestyle changes or metformin alone. A systematic review indicated that this compound is associated with a higher risk of hypoglycemia compared to other sulfonylureas but does not significantly increase cardiovascular risks or mortality rates .
Table 1: this compound vs. Other Antidiabetic Medications
| Medication | Risk of Hypoglycemia | Cardiovascular Risk | Weight Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| This compound | Higher | No significant increase | +1.69 kg |
| Gliclazide | Lower | No significant increase | -0.41 kg |
| Metformin | Lowest | No significant increase | -1.5 kg |
Neuroprotection
Recent studies have identified this compound's neuroprotective properties, particularly in retinal diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Research demonstrated that this compound administration protects human cone cell lines against oxidative stress and apoptosis, showing promise as a repurposable drug for neurodegenerative conditions . A case-control study further indicated that this compound use correlates with reduced odds of developing new-onset dry AMD, suggesting a dose-response relationship .
Table 2: Neuroprotective Effects of this compound
| Study Focus | Findings |
|---|---|
| Oxidative Stress Protection | Reduced apoptosis in human cone cells |
| AMD Risk Reduction | Lower odds of new-onset dry AMD with increased doses |
Anti-inflammatory Effects
This compound has been observed to exert anti-inflammatory effects in various clinical contexts. A study involving patients with melioidosis (a severe bacterial infection) found that those taking this compound had improved survival rates compared to non-users, likely due to its modulation of the immune response . The drug was linked to differential expression of immune-related genes, suggesting it may help contain excessive inflammatory responses in infections.
Table 3: this compound's Impact on Inflammatory Conditions
| Condition | Observational Findings |
|---|---|
| Melioidosis | Higher survival rates in diabetics using this compound |
| General Inflammation | Modulation of immune response genes |
Wound Healing
This compound has also shown potential in promoting wound healing. A study indicated that topical application of this compound significantly improved wound healing in obese mice by regulating protein levels associated with inflammation . The drug was found to enhance the degradation of nuclear receptor coregulator RIP140, which plays a role in inflammatory processes.
Table 4: Wound Healing Efficacy of this compound
| Study Type | Results |
|---|---|
| Animal Model | Improved wound healing in high-fat diet mice |
| Mechanism | Reduced RIP140 levels; enhanced M2 macrophage markers |
作用机制
格列本脲通过结合并抑制胰腺β细胞上的ATP敏感性钾通道发挥其降糖作用。这种抑制导致这些通道关闭,导致细胞膜去极化,随后电压门控钙通道打开。 钙离子流入触发β细胞释放胰岛素,从而降低血糖水平 .
类似化合物:
格列吡嗪: 另一种第二代磺酰脲类药物,与格列本脲相比,其起效更快,半衰期更短.
格列美脲: 以其更长的作用时间和更低的低血糖风险而闻名.
格列本脲的独特性: 格列本脲在磺酰脲类药物中独一无二,因为它具有平衡的药代动力学特征,这使其在保持相对较低的低血糖风险的同时,提供了延长作用时间。 其双重排泄途径(尿液和粪便)也使其区别于其他磺酰脲类药物 .
相似化合物的比较
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique among sulfonylureas due to its balanced pharmacokinetic profile, which provides a prolonged duration of action while maintaining a relatively low risk of hypoglycemia. Its dual excretion pathway (urine and feces) also distinguishes it from other sulfonylureas .
生物活性
Glyburide, a second-generation sulfonylurea, is primarily known for its role in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. This article delves into the various biological activities of this compound, incorporating research findings, case studies, and data tables to highlight its multifaceted effects.
This compound exerts its biological effects primarily through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K_ATP) on pancreatic beta cells. Under normal conditions, these channels remain open at low glucose levels, allowing potassium efflux and maintaining a hyperpolarized membrane potential. When glucose levels rise, K_ATP channels close, leading to cell depolarization, opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, and subsequent insulin release. This compound mimics this effect by directly closing K_ATP channels, thereby promoting insulin secretion independent of glucose levels .
Efficacy in Diabetes Management
This compound has been compared with other antidiabetic agents such as metformin. A study involving patients with gestational diabetes showed that this compound was comparable to metformin in terms of glucose control but had a higher failure rate due to adverse effects and lack of glycemic control. In this study, 38% of patients on this compound experienced treatment failure compared to 24% on metformin .
| Drug | Treatment Failure (%) | Adverse Effects (%) | Insulin Requirement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| This compound | 38 | 11 | 17 |
| Metformin | 24 | 2 | 4 |
Case Studies
A notable case study involved transitioning a young man with insulin-dependent diabetes to this compound. After stabilizing his regimen at a dose of 1.02 mg/kg/day, his metabolic control improved significantly, evidenced by an average blood glucose level of 147.5 mg/dl and an A1C of 6.6% .
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Recent research has uncovered this compound's anti-inflammatory effects beyond its role in diabetes management. It has been shown to prevent neutrophil extravasation in animal models, suggesting a potential role in modulating immune responses during infections . Additionally, a study indicated that patients taking this compound had a reduced risk of severe outcomes from melioidosis, a serious infection often seen in diabetic patients .
Neuroprotective Effects
This compound also exhibits neuroprotective properties. A study found that intravenous administration of this compound improved clinical outcomes in patients with malignant edema following large hemispheric infarcts. The treatment was associated with fewer deaths attributed to cerebral edema and improved midline shift measurements .
Wound Healing Enhancement
Interestingly, this compound has been implicated in promoting wound healing through its effects on macrophages. Research demonstrated that this compound reduces RIP140 protein levels in macrophages via a proteasome-mediated degradation pathway, which is crucial for inflammation resolution and tissue repair .
Summary of Findings
The biological activity of this compound extends beyond its primary function as an antidiabetic agent. Its mechanisms include:
- Insulin Secretion Stimulation : Direct closure of K_ATP channels leading to increased insulin release.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects : Modulation of immune responses and reduction in neutrophil activity.
- Neuroprotection : Improved outcomes in cerebral edema cases.
- Wound Healing : Enhanced macrophage function through protein degradation pathways.
属性
IUPAC Name |
5-chloro-N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H28ClN3O5S/c1-32-21-12-9-17(24)15-20(21)22(28)25-14-13-16-7-10-19(11-8-16)33(30,31)27-23(29)26-18-5-3-2-4-6-18/h7-12,15,18H,2-6,13-14H2,1H3,(H,25,28)(H2,26,27,29) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ZNNLBTZKUZBEKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)Cl)C(=O)NCCC2=CC=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)NC3CCCCC3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C23H28ClN3O5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0037237 | |
| Record name | Glybenclamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0037237 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
494.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015151 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
2.06e-03 g/L | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015151 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Glyburide belongs to a class of drugs known as sulfonylureas. These drugs act by closing ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells. The ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells are known as sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1). Under low glucose concentrations, SUR1 remains open, allowing for potassium ion efflux to create a -70mV membrane potential. Normally SUR1 closes in response to high glucose concentrations, the membrane potential of the cells becomes less negative, the cell depolarizes, voltage gated calcium channels open, calcium ions enter the cell, and the increased intracellular calcium concentration stimulates the release of insulin containing granules. Glyburide bypasses this process by forcing SUR1 closed and stimulating increased insulin secretion. | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01016 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
10238-21-8 | |
| Record name | Glibenclamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=10238-21-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Glyburide [USAN:USP] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0010238218 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01016 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | glyburide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759618 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Glybenclamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0037237 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Glibenclamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.030.505 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | GLYBURIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/SX6K58TVWC | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015151 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
169 - 170 °C | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01016 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Glyburide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015151 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。
















