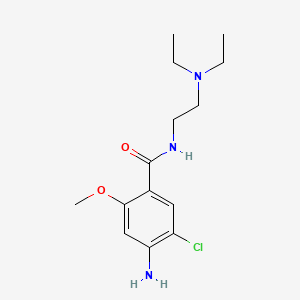
甲氧氯普胺
概述
描述
甲氧氯普胺是一种主要用于治疗恶心和呕吐的药物,以及帮助胃排空延迟的患者促进胃排空。 它还用于治疗胃食管反流病和偏头痛 .
作用机制
甲氧氯普胺主要通过拮抗中枢神经系统中的多巴胺 D2 受体来发挥作用。 这种作用会干扰引起恶心感觉的中枢机制,并刺激下食管括约肌收缩和胃动力 . 此外,甲氧氯普胺还作为 5-HT3 受体拮抗剂和 5-HT4 受体激动剂,进一步增强其促动力作用 .
科学研究应用
Pharmacological Overview
Metoclopramide acts primarily as an antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors and has additional effects on serotonin receptors (5HT3 and 5HT4). This dual action enhances gastrointestinal motility and reduces nausea and vomiting by blocking signals in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the brain.
Clinical Applications
Metoclopramide is utilized in several clinical scenarios:
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Diabetic Gastroparesis : Approved for the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis, metoclopramide improves gastric emptying and alleviates symptoms like nausea and vomiting .
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : It is indicated for patients who do not respond to conventional therapies, helping to reduce reflux symptoms .
-
Nausea and Vomiting
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV) : Metoclopramide is used to prevent nausea associated with chemotherapy, although it may be less effective than other agents like 5-HT3 antagonists .
- Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting : It is administered to prevent nausea following surgery when nasogastric suction is not feasible .
- Off-Label Uses
Case Study 1: Diabetic Gastroparesis
A multicenter placebo-controlled trial demonstrated that metoclopramide significantly reduced symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and postprandial fullness in patients with diabetic gastroparesis. The study involved 40 patients over three weeks, showing statistically significant improvements compared to placebo .
Case Study 2: Acute Dystonia
A recent report highlighted two adolescents who developed acute dystonia after metoclopramide administration. Both cases involved symptoms such as muscle spasms and abnormal eye movements, underscoring the need for careful monitoring of extrapyramidal side effects associated with this medication .
Case Study 3: Pregnancy Safety
A meta-analysis involving over 33,000 pregnant women found no significant association between first-trimester metoclopramide use and major congenital malformations, supporting its safety during early pregnancy .
Summary of Findings
The applications of metoclopramide are extensive, particularly in managing gastrointestinal disorders and preventing nausea in various clinical settings. However, awareness of potential side effects, including acute dystonia and tardive dyskinesia with prolonged use, is crucial for safe administration.
Data Table: Summary of Clinical Applications
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Metoclopramide interacts with various enzymes and proteins, primarily through its antagonistic effects on dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors . It also exhibits agonistic effects on serotonin 5-HT4 receptors and antagonizes muscarinic receptor inhibition . These interactions play a crucial role in its function in biochemical reactions .
Cellular Effects
Metoclopramide has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by inhibiting dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) located in the area postrema of the brain . This leads to prokinetic effects via inhibitory actions on presynaptic and postsynaptic D2 receptors, agonism of serotonin 5-HT4 receptors, and antagonism of muscarinic receptor inhibition .
Molecular Mechanism
Metoclopramide exerts its effects at the molecular level through several mechanisms. It inhibits dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) of the brain . This leads to prokinetic effects via inhibitory actions on presynaptic and postsynaptic D2 receptors, agonism of serotonin 5-HT4 receptors, and antagonism of muscarinic receptor inhibition .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of Metoclopramide can change over time in laboratory settings. The risk of acute neurological effects is higher in children than in adults . The review has confirmed a well‐established safety profile for metoclopramide, including the risks of neurological adverse effects (e.g. acute extrapyramidal symptoms and irreversible tardive dyskinesia) .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Metoclopramide can vary with different dosages in animal models. The dosage must be adapted in animals with renal or hepatic insufficiency due to an increase in the risk of side effects . The dosage should be carefully observed, especially in cats and small breed dogs .
Metabolic Pathways
Metoclopramide undergoes first-pass metabolism and its metabolism varies according to the individual . This drug is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver . CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 both contribute to its metabolism, with CYP2D6 being more heavily involved .
Transport and Distribution
The volume of distribution of Metoclopramide is approximately 3.5 L/kg . This implies a high level of tissue distribution. Metoclopramide crosses the placental barrier and can cause extrapyramidal symptoms in the fetus .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely to be found in areas where dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors are present, such as the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) located in the area postrema of the brain .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件
甲氧氯普胺可以通过多种方法合成。 一种常见的合成方法是,在碱的存在下,使 4-氨基-5-氯-2-甲氧基苯甲酸与 N,N-二乙基-2-氯乙胺反应生成中间体化合物,然后通过进一步的反应将其转化为甲氧氯普胺 .
工业生产方法
甲氧氯普胺的工业生产通常涉及甲氧氯普胺盐酸盐的制备。该工艺包括将甲氧氯普胺溶解在酒石酸溶液中,然后加入焦亚硫酸钠和醋酸钠溶液来调节 pH 值。 然后过滤溶液,并进行各种纯化步骤以获得最终产物 .
化学反应分析
反应类型
甲氧氯普胺会发生多种类型的化学反应,包括:
氧化: 甲氧氯普胺可以被氧化形成各种代谢产物。
还原: 还原反应可以改变甲氧氯普胺中存在的官能团。
取代: 取代反应可以在芳香环或其他官能团处发生。
常见的试剂和条件
用于涉及甲氧氯普胺的反应的常见试剂包括过氧化氢等氧化剂,硼氢化钠等还原剂,以及用于取代反应的各种酸和碱 .
形成的主要产物
相似化合物的比较
类似化合物
一些与甲氧氯普胺类似的化合物包括:
多潘立酮: 另一种用于治疗恶心和呕吐的多巴胺受体拮抗剂。
丙氯拉嗪: 用于治疗恶心、呕吐和偏头痛。
氯丙嗪: 一种具有抗呕吐作用的抗精神病药物.
甲氧氯普胺的独特性
甲氧氯普胺独特之处在于它结合了多巴胺 D2 受体拮抗作用和 5-HT3 受体拮抗作用/5-HT4 受体激动作用,这提供了广泛的促动力和抗呕吐作用。 这使其在治疗胃轻瘫和严重恶心等疾病时特别有效 .
生物活性
Metoclopramide is a widely used medication primarily known for its antiemetic properties. It functions as a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist and has significant effects on gastrointestinal motility. This article delves into its biological activity, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical applications, and associated case studies.
Metoclopramide exerts its effects through multiple pathways:
- Dopamine Receptor Antagonism : It primarily antagonizes dopamine D2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) of the brain, which reduces nausea and vomiting by inhibiting signals that trigger these sensations .
- Serotonin Receptor Interaction : Metoclopramide also acts as an antagonist at 5-HT3 receptors and an agonist at 5-HT4 receptors. This dual action enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing acetylcholine release, thereby improving lower esophageal sphincter tone and gastric emptying .
- Gastrointestinal Motility : The drug promotes gastric emptying without significantly increasing secretions from the biliary, gastric, or pancreatic systems. This property makes it effective in treating conditions like diabetic gastroparesis .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of metoclopramide includes:
Clinical Applications
Metoclopramide is indicated for various conditions, including:
- Nausea and Vomiting : Particularly effective in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) .
- Gastroparesis : Shown to improve symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and early satiety in diabetic patients .
- Chronic Intractable Hiccups (CIH) : Some studies suggest its effectiveness in managing CIH, although more data is needed for conclusive evidence .
Adverse Effects
Despite its benefits, metoclopramide can cause various side effects due to its antidopaminergic activity:
- Extrapyramidal Symptoms : These include tardive dyskinesia, acute dystonia, and akathisia, particularly with prolonged use or high doses .
- Other Side Effects : Commonly reported adverse effects include drowsiness, diarrhea, hypotension, and movement disorders .
Case Study 1: Effectiveness in CIH
A retrospective study involving 96 patients evaluated the long-term effectiveness of metoclopramide for CIH. Out of 14 eligible patients, six continued treatment for an average of 27 months with notable improvements on various clinical scales. However, eight patients discontinued treatment after a mean duration of eight months due to side effects .
Case Study 2: Acute Dystonic Reaction
A case report described a 17-year-old male who developed acute dystonia after receiving metoclopramide for gastroenteritis. Symptoms included facial grimacing and muscle spasms following administration of the drug. The reaction was resolved with diazepam, highlighting the potential for acute adverse effects even with standard dosing regimens .
属性
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-5-chloro-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H22ClN3O2/c1-4-18(5-2)7-6-17-14(19)10-8-11(15)12(16)9-13(10)20-3/h8-9H,4-7,16H2,1-3H3,(H,17,19) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
TTWJBBZEZQICBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=CC(=C(C=C1OC)N)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H22ClN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
2576-84-3 (di-hydrochloride), 54143-57-6 (mono-hydrochloride, mono-hydrate), 7232-21-5 (mono-hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide [INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000364625 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6045169 | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6045169 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
299.79 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015363 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Crystal; decomposes at 145 °C. Solubility at 25 °C (g/100 mL): water 48; ethanol (95%) 9; absolute ethanol 6; benzene 0.10; chloroform 0.10. Stable in acidic solutions. Unstable in strongly alkaline solutions. /Metoclopramide Dihydrochloride monohydrate/, Solubility at 25 °C (g/100 mL): 95% ethanol 2.30; absolute ethanol 1.90; benzene 0.10; chloroform 6.60, In water, 0.02 g/100 mL at 25 °C, 3.10e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7841 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015363 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Metoclopramide causes antiemetic effects by inhibiting dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) located in the area postrema of the brain. Administration of this drug leads to prokinetic effects via inhibitory actions on presynaptic and postsynaptic D2 receptors, agonism of serotonin 5-HT4 receptors, and antagonism of muscarinic receptor inhibition. This action enhances the release of acetylcholine, causing increased lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and gastric tone, accelerating gastric emptying and transit through the gut. Metoclopramide antagonizes the dopamine D2 receptors. Dopamine exerts relaxant effect on the gastrointestinal tract through binding to muscular D2 receptors., Metoclopramide accelerates gastric emptying and intestinal transit from the duodenum to the ileocecal valve by increasing the amplitude and duration of esophageal contractions, the resting tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, and the amplitude and tone of gastric (especially antral) contractions and by relaxing the pyloric sphincter and the duodenal bulb, while increasing peristalsis of the duodenum and jejunum. Unlike nonspecific cholinergic-like stimulation of upper GI smooth muscle, the stimulant effects of metoclopramide on GI smooth muscle coordinate gastric, pyloric, and duodenal motor activity., The pharmacologic actions of metoclopramide on the upper GI tract are similar to those of cholinergic drugs (e.g., bethanechol); however, unlike cholinergic drugs, metoclopramide does not stimulate gastric, biliary, or pancreatic secretions and does not affect serum gastrin concentration. Although the exact mechanism of action of metoclopramide is unclear, the effects of metoclopramide on GI motility may be mediated via enhancement of cholinergic excitatory processes at the postganglionic neuromuscular junction; antagonism of nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory motor nerves (i.e., dopaminergic); and/or a direct effect on smooth muscle., The effects of metoclopramide on GI motility do not depend on intact vagal innervations but are reduced or abolished by anticholinergic drugs (e.g., atropine) and potentiated by cholinergic drugs (e.g., carbachol, methacholine). These findings suggest that metoclopramide's effects on GI motility may depend in part on intramural cholinergic neurons of smooth muscle that are intact after vagal denervation. Unlike cholinergic drugs, metoclopramide requires intrinsic neuronal storage sites of acetylcholine to exert its pharmacologic effects. Postsynaptic activity results from metoclopramide's ability to enhance release of acetylcholine from postganglionic cholinergic neurons in the GI tract and to sensitize muscarinic receptors of GI smooth muscle to the actions of acetylcholine., Metoclopramide is a potent dopamine-receptor antagonist, and some of the actions of metoclopramide on GI smooth muscle may be mediated via antagonism of dopaminergic neurotransmission, Specific dopamine receptors in the esophagus and stomach have been identified; however, it is not known if there is a dopaminergic control system for smooth muscle function in the upper GI tract. In the GI tract, dopamine is principally an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Dopamine decreases the intensity of esophageal contractions, relaxes the proximal stomach, and reduces gastric secretion. Although metoclopramide blocks these inhibitory effects of dopamine, the actual role of dopamine in the peripheral control of GI motility has not been fully elucidated. Since cholinergic mechanisms are responsible for most excitatory motor activity in the GI tract, it appears that metoclopramide's therapeutic effects are principally caused by the drug's cholinergic-like activity; however, antagonism of GI dopaminergic activity may augment metoclopramide's cholinergic-like activity., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Metoclopramide (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01233 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7841 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
364-62-5 | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=364-62-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide [INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000364625 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01233 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6045169 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.006.058 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | METOCLOPRAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/L4YEB44I46 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7841 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015363 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
171-173, 146.5-148 °C, 147.25 °C | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01233 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7841 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Metoclopramide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015363 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。














