利巴韦林
概述
描述
Ledipasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent used primarily for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It was developed by Gilead Sciences and is commonly used in combination with sofosbuvir under the brand name Harvoni. Ledipasvir targets the non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) of the hepatitis C virus, which is essential for viral replication and assembly .
科学研究应用
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Ledipasvir is approved for use in combination with sofosbuvir in various treatment regimens:
- 8-week regimen : For treatment-naive patients without cirrhosis and low baseline HCV RNA levels (<6 million IU/mL).
- 12-week regimen : For a broader range of patients, including those with cirrhosis or prior treatment experience.
Efficacy Data:
- In clinical trials, sustained virologic response (SVR) rates have been reported as high as 95%-100% across different populations and treatment durations. For instance, a study involving 2,099 participants showed SVR12 rates of 96% for the 8-week regimen and 97% for the 12-week regimen .
Real-World Effectiveness
Real-world studies have corroborated clinical trial findings, demonstrating high SVR rates in diverse patient populations:
- A multicenter observational study reported SVR12 rates of 96% among patients treated with ledipasvir-sofosbuvir for 8 weeks .
- Factors influencing treatment outcomes included liver function indicators such as albumin levels and bilirubin levels .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of ledipasvir has been assessed in numerous studies. Common adverse effects include:
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Nausea
Serious adverse events are rare but can occur, particularly when ribavirin is included in the treatment regimen .
Comparative Efficacy
The combination therapy of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir has been compared to other antiviral treatments. The following table summarizes key findings from various studies:
Case Studies
Several case studies highlight the effectiveness of ledipasvir in diverse settings:
- Egyptian Cohort Study : This study enrolled 255 patients with HCV genotype 4 and demonstrated high SVR rates (95% for the 8-week regimen and 98% for the 12-week regimen), emphasizing its efficacy even among previously treated patients .
- HCV-TARGET Study : An extensive analysis involving over 2,000 participants showed that higher baseline albumin and lower bilirubin levels were associated with better treatment outcomes .
作用机制
利巴韦林抑制丙型肝炎病毒非结构蛋白 5A (NS5A),这对病毒 RNA 复制和 HCV 病毒粒子的组装至关重要。 通过阻止 NS5A 的过度磷酸化,利巴韦林破坏了病毒蛋白的产生,从而抑制了病毒复制和组装 .
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Ledipasvir interacts with the NS5A protein, a phosphoprotein that plays an essential role in the replication of the hepatitis C virus . By binding to this protein, Ledipasvir disrupts the replication process of the virus .
Cellular Effects
Ledipasvir has a profound effect on cells infected with the hepatitis C virus. It inhibits the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the viral load within the cells . This can lead to a decrease in the severity of the disease and potentially to a complete cure .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Ledipasvir involves its interaction with the NS5A protein. Ledipasvir binds to this protein, preventing it from assisting in the replication of the viral RNA . This stops the virus from multiplying and spreading to other cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Ledipasvir have been observed to be both rapid and long-lasting . The drug quickly reduces the viral load in cells, and this effect can be sustained over a long period, leading to a sustained virological response .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
While specific studies on dosage effects in animal models were not found in the search results, clinical studies have shown that Ledipasvir, in combination with other antiviral drugs, is effective in treating hepatitis C in humans .
Metabolic Pathways
It is known that the drug works by interfering with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus, specifically by inhibiting the NS5A protein .
Transport and Distribution
Given its effectiveness in reducing viral load, it can be inferred that the drug is able to reach the sites of viral replication within the cells .
Subcellular Localization
Given that it targets the NS5A protein, which is involved in the replication of the hepatitis C virus, it is likely that the drug localizes to the sites within the cell where this process takes place .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件
利巴韦林的合成涉及多个步骤,包括关键中间体的制备。 一种方法涉及通过酶促水解制备高纯度中间体 (1R, 3S, 4S)-N-叔丁氧羰基-2-氮杂双环[2.2.1]庚烷-3-羧酸 . 另一种方法涉及后期环丙烷化和氟化过程,这为利巴韦林的制备提供了一条新颖且高效的路线,总收率为 20%,跨越八个线性步骤 .
工业生产方法
利巴韦林的工业生产侧重于优化收率、纯度和成本效益。该过程通常涉及使用高纯度中间体和环境友好的反应条件。 这些方法旨在能够进行大规模生产,确保高选择性和降低生产成本 .
化学反应分析
反应类型
利巴韦林经历各种化学反应,包括:
还原: 利巴韦林的还原反应不太常见。
常用试剂和条件
利巴韦林合成和反应中常用的试剂包括乙腈、乙酸和异丙醚。 反应条件通常涉及升高的温度和受控的环境,以确保高收率和纯度 .
形成的主要产物
利巴韦林反应形成的主要产物是用于治疗丙型肝炎的最终活性药物成分。 其他中间体和副产物通常通过纯化过程去除 .
相似化合物的比较
类似化合物
索非布韦: 另一种直接作用抗病毒剂,与利巴韦林联合使用。它抑制 HCV 的 NS5B 聚合酶。
达拉他韦: 一种类似于利巴韦林的 NS5A 抑制剂,但具有不同的药代动力学特性。
利巴韦林的独特性
利巴韦林的独特性在于它对多种 HCV 基因型具有高效力,并且当与索非布韦联合使用时,能够达到超过 95% 的持续病毒学应答 (SVR) 率。 它的长半衰期和最小的副作用使其成为 HCV 治疗的首选 .
生物活性
Ledipasvir is a potent antiviral agent used primarily in the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It functions as an NS5A inhibitor, targeting the NS5A protein crucial for HCV replication. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the biological activity of ledipasvir, including its pharmacological properties, efficacy in clinical studies, and safety profile.
Ledipasvir inhibits HCV replication by binding to the NS5A protein, which is essential for viral RNA replication and assembly. Although the exact biochemical mechanism remains unconfirmed due to the lack of known enzymatic functions of NS5A, studies indicate that ledipasvir effectively disrupts HCV lifecycle processes.
- In vitro Activity : Ledipasvir exhibits varying inhibitory concentrations (EC50) against different HCV genotypes:
Pharmacokinetics
Ledipasvir is characterized by high plasma protein binding (>99.8%) and demonstrates a wide volume of distribution. Following administration, it shows minimal metabolism with over 98% of systemic exposure attributed to the parent compound. The pharmacokinetic profile indicates a long mean residence time, supporting its efficacy in sustained viral response (SVR) outcomes .
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy of ledipasvir, often in combination with sofosbuvir (LDV/SOF). The following table summarizes key findings from prominent studies:
| Study | Treatment Duration | Population | SVR12 Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| LONESTAR Study | 8 weeks | Treatment-naïve GT1 | 95% |
| LONESTAR Study | 12 weeks | Treatment-naïve GT1 | 100% |
| Phase II Trial | 12 weeks | Treatment-experienced | 95% |
| Phase II Trial | 8 weeks | Acute HCV in HIV-infected men | 100% |
| Egyptian Study | 12 weeks | Non-cirrhotic patients | ≥94% |
These results indicate that ledipasvir combined with sofosbuvir is highly effective across various patient populations, including those with prior treatment failures and different HCV genotypes .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of ledipasvir has been assessed in various studies, revealing that it is generally well tolerated. Common adverse events include headache and fatigue, particularly in patients receiving ribavirin alongside ledipasvir . Serious adverse events are rare, making it a favorable option for many patients.
Case Studies
-
Case Study: Treatment-Naïve Patients
In a multicenter trial involving treatment-naïve patients with HCV genotype 4, SVR12 rates reached up to 98% after a 12-week regimen of LDV/SOF, demonstrating high effectiveness even in populations previously underrepresented in clinical trials . -
Case Study: Patients with HIV Co-Infection
A study focusing on men with HIV co-infection who received an eight-week course of LDV/SOF achieved a remarkable SVR rate of 100%, highlighting the compound's efficacy even in complex patient populations .
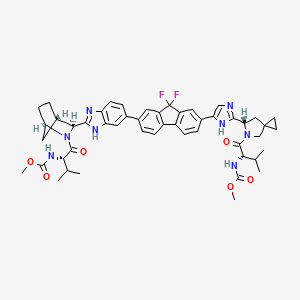
属性
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(6S)-6-[5-[9,9-difluoro-7-[2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-yl]-3H-benzimidazol-5-yl]fluoren-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]heptan-5-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C49H54F2N8O6/c1-24(2)39(56-46(62)64-5)44(60)58-23-48(15-16-48)21-38(58)42-52-22-37(55-42)28-9-13-32-31-12-8-26(18-33(31)49(50,51)34(32)19-28)27-10-14-35-36(20-27)54-43(53-35)41-29-7-11-30(17-29)59(41)45(61)40(25(3)4)57-47(63)65-6/h8-10,12-14,18-20,22,24-25,29-30,38-41H,7,11,15-17,21,23H2,1-6H3,(H,52,55)(H,53,54)(H,56,62)(H,57,63)/t29-,30+,38-,39-,40-,41-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VRTWBAAJJOHBQU-KMWAZVGDSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)CC1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)C9C1CCC(C1)N9C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)C[C@H]1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)[C@@H]9[C@H]1CC[C@H](C1)N9C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C49H54F2N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID90154829 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
889.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ledipasvir is an inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS5A protein required for viral RNA replication and assembly of HCV virions. Although its exact mechanism of action is unknown, it is postulated to prevent hyperphosphorylation of NS5A which is required for viral production. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1256388-51-8 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1256388-51-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1256388518 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Methyl[(2S)-1-{(6S)-6-[5-(9,9-difluoro-7-{2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-{(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-3-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-6-yl}-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl}-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LEDIPASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/013TE6E4WV | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details












Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details












体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。













