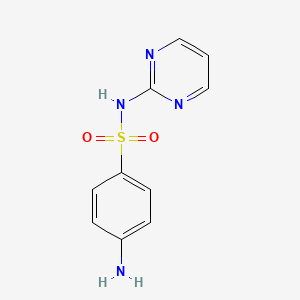
Sulfadiazine
Overview
Description
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic widely used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. It is particularly effective against urinary tract infections, trachoma, and chancroid . This compound is also used in combination with pyrimethamine to treat toxoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and in newborns with congenital infections . This compound is known for its ability to inhibit the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, thereby preventing their growth and proliferation .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of sulfadiazine typically begins with the acetylation of aniline derivatives using acetic anhydride to form acetanilide derivatives . These derivatives are then reacted with chlorosulfonic acid to produce 4-acetylaminobenzenesulfonyl chloride . In parallel, 2-aminopyrimidine is prepared by reacting tetramethoxypropane with a guanidine salt . The final step involves reacting 4-acetylaminobenzenesulfonyl chloride with 2-aminopyrimidine, followed by hydrolysis with sodium hydroxide to yield this compound .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process involves stringent control of reaction conditions to ensure high yield and purity. The use of automated reactors and continuous flow systems helps in maintaining consistent quality and efficiency in production .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions
Sulfadiazine undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution . The compound contains two reactive groups: an aromatic amine and a sulfonamide group, which participate in these reactions .
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidation: This compound can be oxidized using reagents like hydrogen peroxide and persulfate under acidic conditions.
Reduction: Reduction of this compound can be achieved using reducing agents such as sodium borohydride.
Substitution: The aromatic amine group in this compound can undergo substitution reactions with electrophiles in the presence of catalysts.
Major Products
The major products formed from these reactions include various derivatives of this compound, which can be further utilized in pharmaceutical applications .
Scientific Research Applications
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic with various applications in medicine, pharmacology, and other scientific fields . It functions by inhibiting bacteria's ability to produce folic acid, which is essential for DNA synthesis, thereby preventing the spread of infection .
Scientific Research Applications
Antibacterial Agent: this compound is effective against various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections . It can also be used topically to treat burn and wound infections . The drug inhibits the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase, which is crucial for folic acid synthesis .
Treatment of Infections: this compound is used in the treatment of several infections, such as trachoma and chancroid . Laboratory studies on animals have indicated that this compound has less toxicity compared to other drugs like sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole and is highly effective against common pathogens .
Silver this compound in Wound Care: Silver this compound (SSDZ) is a common choice for treating skin burns . It can be integrated into hydrogels for topical wound treatment because hydrogels have minimal toxicity and can sustain the release of pharmaceuticals .
Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), including those incorporating silver this compound, have demonstrated antimicrobial properties and have contributed to the development of nanotechnology . AgNPs can potentially replace traditional antibiotics due to increasing bacterial resistance .
Combination Therapies: this compound can be combined with other substances like hyaluronic acid (HA) to treat conditions such as parastomal skin ulceration . The combination of HA and silver this compound has shown success in promoting healing and reducing pain in such cases .
Data Table: Properties and Applications of this compound
Case Studies
Parastomal Ulcer Healing: A case study demonstrated the successful treatment of chronic parastomal skin ulceration using a combination cream of 0.2% Hyaluronic acid and 1% Silver this compound . Patients treated with this combination experienced complete healing, reduced pain, and decreased purulent fluid, leading to a reduced cost of treatment compared to standard protocols .
Silver this compound Hydrogels for Wound Treatment: Silver this compound has been integrated into hydrogels for wound treatment due to the hydrogels' low toxicity and capacity for extended pharmaceutical release .
Research Findings and Insights
Efficacy of Silver this compound: A systematic review comparing Silver this compound with other dressings for burns showed a statistically significant difference in healing time for silver dressings . While some animal studies support the use of Silver this compound for partial-thickness burns, others question its effectiveness .
Toxicity and Safety: Laboratory studies on animals suggest that this compound has lower toxicity compared to sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole .
Mechanism of Action
Sulfadiazine acts by inhibiting the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase . This enzyme is crucial for the synthesis of folic acid, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication . By competitively inhibiting this enzyme, this compound prevents the bacteria from synthesizing folic acid, leading to their eventual death .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Similar Compounds
Sulfamethoxazole: Another sulfonamide antibiotic used in combination with trimethoprim to treat various bacterial infections.
Sulfisoxazole: Used to treat urinary tract infections and other bacterial infections.
Silver sulfadiazine: A topical agent used in the treatment of burns and wound infections.
Uniqueness
This compound is unique due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and its ability to be used in combination with other drugs like pyrimethamine for the treatment of specific infections like toxoplasmosis . Its effectiveness in both human and veterinary medicine further highlights its versatility .
Biological Activity
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic that has been widely studied for its biological activity, particularly in the treatment of bacterial infections and its potential applications in various medical fields. This article discusses the compound's mechanisms of action, antimicrobial properties, clinical applications, and recent research findings.
This compound functions primarily by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. It acts as a competitive antagonist of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate required for the synthesis of folate in bacteria. By blocking this pathway, this compound effectively prevents bacterial growth and reproduction, leading to cell death. This mechanism is common among sulfonamides, which have been utilized since their introduction in the 1930s.
Antimicrobial Properties
This compound exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity against various pathogens. It has been shown to be effective against:
- Gram-positive bacteria : Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative bacteria : Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Fungi : Candida albicans
- Protozoa : Toxoplasma gondii
Comparative Antimicrobial Efficacy
Recent studies have highlighted the enhanced efficacy of this compound when used in combination with metal complexes. For instance, metal complexes of this compound have demonstrated superior antibacterial activity compared to the free ligand itself, particularly against resistant strains of bacteria .
| Pathogen | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 32 µg/mL |
| Escherichia coli | 16 µg/mL |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 64 µg/mL |
| Candida albicans | 8 µg/mL |
Clinical Applications
This compound is commonly used in clinical settings for treating various infections, including:
- Toxoplasmosis : Often administered in combination with pyrimethamine for effective treatment.
- Burn wounds : Silver this compound is a topical formulation used extensively for burn management due to its antimicrobial properties .
Case Studies
-
Silver this compound in Burn Treatment :
A clinical trial involving children with severe burns demonstrated that silver this compound significantly reduced infection rates and facilitated wound healing compared to traditional treatments. The study reported no progression to critical infection stages among treated patients . -
Aerosol Formulation for Pressure Ulcers :
A novel aerosol formulation combining silver this compound with lidocaine and vitamin A showed promising results in treating scalp pressure ulcers in ICU patients. The treatment was associated with improved healing rates and reduced costs compared to conventional dressings .
Recent Research Findings
Recent studies have explored the multifaceted biological activities of this compound beyond its antibacterial properties:
- Anticancer Activity : Research indicates that this compound exhibits antiproliferative effects on human liver cancer (HepG2) and breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines by inhibiting the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway. The IC50 values were determined to be approximately 245.69 µM for HepG2 cells and 215.68 µM for MCF7 cells .
- Cytotoxic Effects : this compound derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines, revealing potential as therapeutic agents in oncology .
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What experimental methodologies are recommended for determining Sulfadiazine’s mechanism of action against bacterial pathogens?
- Methodological Answer : Use minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays to establish efficacy across bacterial strains, complemented by molecular docking studies to identify binding interactions with dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) . For validation, employ gene knockout models (e.g., E. coli DHPS mutants) to confirm target specificity. Include spectrophotometric analysis to monitor folate synthesis inhibition .
Q. How can researchers standardize in vitro susceptibility testing for this compound to ensure reproducibility?
- Methodological Answer : Follow Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines for broth microdilution or agar dilution methods. Document variables such as pH, inoculum size, and cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth composition. Report results with 95% confidence intervals and include positive/negative controls (e.g., trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) .
Q. What are the primary pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters to assess in preclinical this compound studies?
- Methodological Answer : Measure plasma concentration-time profiles to calculate AUC, Cmax, Tmax, and elimination half-life (t1/2) in animal models. Use high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for quantification. Compare results against established PK/PD targets (e.g., time above MIC) to predict clinical efficacy .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can contradictory data on this compound’s efficacy in biofilm-associated infections be resolved?
- Methodological Answer : Conduct systematic reviews with meta-analysis to quantify heterogeneity (I² statistic). Stratify studies by biofilm model (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus vs. Pseudomonas aeruginosa), this compound concentration, and exposure time. Use sensitivity analysis to identify confounding variables (e.g., pH, extracellular DNA content) .
Q. What strategies are effective for modeling this compound resistance evolution in polymicrobial environments?
- Methodological Answer : Develop chemostat-based continuous culture systems to simulate competitive microbial communities. Monitor resistance gene transfer (e.g., sul1, sul2) via qPCR and whole-genome sequencing. Incorporate pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling to predict resistance thresholds under varying dosing regimens .
Q. How can ecological risks of this compound be assessed given limited environmental toxicity data?
- Methodological Answer : Use read-across methodologies with structurally similar sulfonamides (e.g., sulfamethoxazole) to estimate ecotoxicity. Perform algal growth inhibition tests (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata) and Daphnia magna acute toxicity assays. Apply quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models to predict biodegradation pathways .
Q. What ethical and methodological considerations are critical in designing this compound toxicity studies using animal models?
- Methodological Answer : Adhere to ARRIVE guidelines for experimental design. Use the 3Rs principle (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) and justify sample size via power analysis. Include histopathological evaluation of target organs (e.g., kidneys, liver) and measure biomarkers like serum creatinine for nephrotoxicity .
Q. Data Analysis & Presentation
Q. How should researchers address uncertainties in this compound’s dose-response relationships?
- Methodological Answer : Apply Bayesian statistical models to incorporate prior data (e.g., historical toxicity thresholds). Report uncertainty intervals and use Monte Carlo simulations for probabilistic risk assessment. Visualize dose-response curves with 95% credible intervals using tools like R or Python .
Q. What are best practices for presenting this compound interaction data in combination therapies?
- Methodological Answer : Use isobolograms to classify interactions (synergistic, additive, antagonistic). Calculate fractional inhibitory concentration indices (FICI) and validate with checkerboard assays. Tabulate results with confidence intervals and highlight clinical relevance (e.g., reduced resistance emergence) .
Q. Research Design Frameworks
Q. How can the FINER criteria improve the formulation of this compound-related research questions?
- Methodological Answer : Evaluate feasibility by aligning with available analytical tools (e.g., LC-MS/MS for metabolite detection). Ensure novelty by conducting a scoping review of PubMed/MEDLINE (2015–2025). Address relevance through alignment with WHO priority pathogens (e.g., ESKAPE organisms) .
Q. What systematic review protocols are recommended for synthesizing this compound’s off-label uses?
- Methodological Answer : Follow PRISMA guidelines, define PICO criteria (Population: Immunocompromised patients; Intervention: this compound; Comparison: Standard care; Outcome: Infection resolution). Extract data into standardized templates and assess bias via ROBINS-I tool. Register the protocol on PROSPERO .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-pyrimidin-2-ylbenzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H10N4O2S/c11-8-2-4-9(5-3-8)17(15,16)14-10-12-6-1-7-13-10/h1-7H,11H2,(H,12,13,14) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SEEPANYCNGTZFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CN=C(N=C1)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H10N4O2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7044130 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
250.28 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
6.01e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is needed for the proper processing of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) which is essential for folic acid synthesis. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
68-35-9 | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=68-35-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000068359 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00359 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757324 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfadiazine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=35600 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7044130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.623 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFADIAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0N7609K889 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Sulfadiazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014503 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.














