Nifurtimox
Overview
Description
Nifurtimox is a nitrofuran derivative used primarily as an antiparasitic medication. It is marketed under the brand name Lampit and is used to treat Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) and African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) . This compound was developed by Bayer and has been in use since 1965 . It is included in the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
Nifurtimox is synthesized through a multi-step process involving the reaction of 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde with 3-methyl-4-thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide . The reaction conditions typically involve the use of solvents such as ethanol and catalysts to facilitate the formation of the final product .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound involves large-scale synthesis using similar reaction conditions as in the laboratory synthesis. The process is optimized for yield and purity, with stringent quality control measures to ensure the consistency of the final product .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions
Nifurtimox undergoes several types of chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: The nitro group in this compound can be reduced to form nitro anion radicals.
Reduction: The nitro group can also undergo reduction to form amines.
Substitution: This compound can participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in the reactions of this compound include reducing agents such as sodium borohydride and oxidizing agents like hydrogen peroxide . The reactions are typically carried out under controlled temperature and pH conditions to ensure the desired product formation .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from the reactions of this compound include reduced amines and substituted derivatives, depending on the specific reaction conditions and reagents used .
Scientific Research Applications
Nifurtimox has a wide range of scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study nitrofuran derivatives and their reactivity.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cellular processes and its potential as an antiparasitic agent.
Medicine: Used in the treatment of Chagas disease and sleeping sickness.
Industry: Employed in the development of new antiparasitic drugs and formulations.
Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of action of nifurtimox is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the bioreduction of the nitro group to form nitro anion radicals . These radicals undergo redox cycling with molecular oxygen, leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) . The ROS cause damage to cellular components, including DNA, proteins, and lipids, ultimately leading to the death of the parasite .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Similar Compounds
Benznidazole: Another nitrofuran derivative used to treat Chagas disease.
Pentamidine: Used to treat African trypanosomiasis and other parasitic infections.
Uniqueness of Nifurtimox
This compound is unique in its ability to generate reactive oxygen species through redox cycling, which contributes to its antiparasitic activity . It is also notable for its inclusion in combination therapies, such as the this compound-eflornithine combination treatment for sleeping sickness .
Biological Activity
Nifurtimox is a nitrofuran derivative primarily used in the treatment of Chagas disease, caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. Its biological activity involves complex mechanisms that target the parasite while sparing mammalian cells, although some cytotoxic effects on human cells have also been observed. This article reviews the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profiles based on diverse research findings.
This compound is activated by nitroreductase enzymes, particularly type I nitroreductases (NTRs) found in trypanosomes. These enzymes reduce this compound to reactive metabolites that exert cytotoxic effects on T. cruzi by:
- Inhibiting Dehydrogenase Activity : this compound reduces the activity of key dehydrogenases in the parasite, disrupting its metabolic processes .
- Generating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) : The activation of this compound leads to the production of ROS, which can damage cellular components and lead to cell death .
- Oxygen-Insensitive Reduction : NTRs catalyze the four-electron reduction of this compound under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, producing an unsaturated open-chain nitrile that is cytotoxic to both parasites and mammalian cells at similar concentrations .
Chagas Disease Treatment
This compound has been shown to be effective in treating both acute and chronic Chagas disease. A significant study involving pediatric patients demonstrated:
- Serological Response : In a cohort treated for 60 days, 32.9% achieved negative seroconversion, indicating successful treatment outcomes compared to historical controls .
- Long-Term Efficacy : A long-term follow-up study involving 1,497 adults indicated that those treated with this compound were more than twice as likely to achieve negative seroconversion compared to untreated individuals (hazard ratio of 2.22) over a median follow-up period of 2.1 years .
Combination Therapy
Recent studies have explored the efficacy of this compound in combination with other treatments:
- This compound and Eflornithine : A study involving late-stage sleeping sickness patients showed high efficacy rates (90.3% to 100%) with this combination therapy .
Safety Profile
While this compound is effective, it is associated with various side effects:
- Adverse Events : In pediatric studies, treatment-emergent adverse events were reported in about 28% of patients, mostly mild or moderate .
- Tolerability Issues : In adults with chronic Chagas disease, this compound was poorly tolerated, leading to low treatment completion rates due to side effects such as nausea and neuropathy .
Data Summary Table
| Study | Population | Treatment Duration | Negative Seroconversion Rate | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric Chagas Disease Study | 72 children | 60 days | 32.9% | 28.3% mild/moderate |
| Adult Chronic Chagas Disease Study | 1,497 adults | Variable | Hazard ratio 2.22 | Poor tolerability reported |
| Combination Therapy Study | 48 late-stage patients | 10 days | 90.3% - 100% | Major adverse events noted |
Q & A
Q. Basic: What experimental approaches are used to study nifurtimox's mechanism of action against Trypanosoma cruzi?
This compound is activated via a bacterial-like nitroreductase (NTR) in trypanosomes, generating toxic metabolites. Key methodologies include:
- Enzyme activity assays : Measure NTR-mediated reduction of this compound using spectrophotometry or LC-MS to track nitro group conversion to hydroxylamine derivatives .
- Gene knockout studies : Downregulate NTR expression (e.g., CRISPR/Cas9) to validate its role in drug activation and cross-resistance patterns .
- Metabolite profiling : Use untargeted metabolomics to identify intermediates like the open-chain nitrile metabolite (C10H15N3O3S) formed during activation .
Q. Basic: How can researchers quantify this compound in biological samples with high sensitivity?
Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (IL-DLLME) coupled with HPLC-UV is recommended:
- Achieves detection limits of 15.7 ng/mL for this compound in plasma.
- Advantages: Low sample volume (200 µL), inter-day reproducibility (<4%), and cost-effectiveness .
Q. Basic: What pharmacokinetic methods assess this compound distribution across the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
- In situ murine brain perfusion : Perfuse radiolabeled [³H]this compound and correct for vascular space using [¹⁴C]sucrose. Analyze homogenate, supernatant, and pellet fractions via capillary depletion to distinguish parenchymal vs. vascular uptake .
- Kinetic parameters : Calculate unidirectional transfer constants (e.g., Kin = 251.8 µL/min/g in pons) and half-life (114 min) using HPLC .
Q. Advanced: Why do studies report contradictory results on this compound-eflornithine synergy?
Evidence suggests antagonism in vitro but clinical efficacy in African trypanosomiasis:
- Metabolomic profiling : Eflornithine reduces polyamines, lowering trypanothione (antioxidant), while this compound increases oxidative stress. However, no synergistic metabolite changes were observed in joint treatments .
- Experimental design : Use standardized alamar blue assays (IC50 = 4 µM for this compound vs. 35 µM for eflornithine) and validate with in vivo models .
Q. Advanced: How does this compound resistance develop in trypanosomes?
Resistance arises via NTR gene downregulation :
- Single-copy deletion : Reduces nitroreductase activity by ~50%, conferring cross-resistance to benznidazole and other nitroheterocyclics .
- Phenotypic screening : Monitor IC50 shifts in drug-selected strains and validate via qPCR or Western blot for NTR expression .
Q. Advanced: What molecular pathways explain this compound's antitumor activity in medulloblastoma?
Combination with tetrathiomolybdate (TM) enhances oxidative stress:
- Transcriptomics : this compound upregulates Nrf2 targets (HMOX1, GCLM) and stress-response genes (DUSP1, NR4A2) by ≥2-fold. Use microarray/RNA-seq with FDR correction (p<3×10⁻⁸) .
- ROS quantification : Measure superoxide levels via DHE fluorescence or glutathione depletion assays to confirm synergy with TM .
Q. Advanced: How can untargeted metabolomics resolve this compound's off-target effects?
- Workflow :
- LC-MS peak detection : Use XCMS/mzMatch for raw data processing (intensity threshold >3000, gap filling).
- Annotation : Match exact masses to KEGG/MetaCyc databases; confirm with authentic standards (e.g., polyamine pathway metabolites) .
- Statistical validation : Apply ANOVA (p<0.05) and fold-change thresholds to identify altered nucleotides/lipids .
Q. Advanced: What challenges arise in pediatric clinical trials for this compound?
- Endpoint selection : Seroconversion (antibody decline) at 12 months/4 years post-treatment requires longitudinal observational controls .
- Safety monitoring : 56.2% of adults discontinued treatment due to adverse events (AEs); pediatric protocols must include AE tracking (e.g., DRESS, myocarditis) .
Q. Basic: How does this compound induce oxidative stress in parasites?
- Redox cycling : Nitro group reduction generates ROS (e.g., superoxide) via flavin-dependent enzymes.
- Validation : Measure trypanothione depletion or use H2O2 probes in T. cruzi cultures .
Q. Advanced: What methods identify cross-resistance between nitroheterocyclic drugs?
Properties
Key on ui mechanism of action |
The mechanism of action of nifurtimox has not been fully elucidated, however, is believed to occur by the activation of nitroreductase enzymes that produce reactive metabolites with a series of deleterious effects on Trypanosoma cruzi, the parasite causing Chagas disease. The antiprotozoal actions of nifurtimox occur both intracellularly and extracellularly. Inhibition of parasite dehydrogenase activity is another purported mode of action of nifurtimox that warrants further research. |
|---|---|
CAS No. |
23256-30-6 |
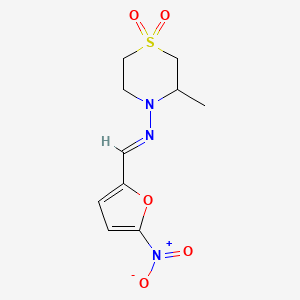
Molecular Formula |
C10H13N3O5S |
Molecular Weight |
287.29 g/mol |
IUPAC Name |
(Z)-N-(3-methyl-1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)-1-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methanimine |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H13N3O5S/c1-8-7-19(16,17)5-4-12(8)11-6-9-2-3-10(18-9)13(14)15/h2-3,6,8H,4-5,7H2,1H3/b11-6- |
InChI Key |
ARFHIAQFJWUCFH-WDZFZDKYSA-N |
SMILES |
CC1CS(=O)(=O)CCN1N=CC2=CC=C(O2)[N+](=O)[O-] |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC1CS(=O)(=O)CCN1/N=C\C2=CC=C(O2)[N+](=O)[O-] |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1CS(=O)(=O)CCN1N=CC2=CC=C(O2)[N+](=O)[O-] |
Appearance |
Solid powder |
boiling_point |
550.3±50.0 |
melting_point |
177-183 |
Key on ui other cas no. |
23256-30-6 |
Pictograms |
Health Hazard |
Purity |
>98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
shelf_life |
>5 years if stored properly |
solubility |
Soluble in DMSO, not in water |
storage |
Dry, dark and at 0 - 4 C for short term (days to weeks) or -20 C for long term (months to years). |
Synonyms |
Bayer 2502 Lampit Nifurtimox |
Origin of Product |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















