Vicriviroc
Overview
Description
Vicriviroc is a pyrimidine-based compound that functions as a CCR5 entry inhibitor of HIV-1. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Schering-Plough and has been investigated for its potential in managing HIV-1 infections . This compound inhibits the interaction of HIV-1 with the CCR5 receptor, preventing the virus from entering host cells .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of Vicriviroc involves multiple steps, starting with the preparation of key intermediatesSpecific reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvents, and catalysts, are optimized to ensure high yield and purity .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but is scaled up to meet commercial demands. The process involves stringent quality control measures to ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. Advanced techniques, such as continuous flow chemistry and automated synthesis, may be employed to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions
Vicriviroc undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: This compound can be oxidized to form this compound N-oxide, a major metabolite.
Reduction: Reduction reactions may be employed to modify specific functional groups within the molecule.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can be used to introduce or replace substituents on the pyrimidine core.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents like cytochrome P450 enzymes for oxidation, reducing agents for reduction, and nucleophiles for substitution reactions. Reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, and solvent choice are carefully controlled to achieve the desired outcomes .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from these reactions include this compound N-oxide and other metabolites that result from the modification of the parent compound .
Scientific Research Applications
Phase 2 Study (ACTG A5211)
- Objective : To assess the safety and virologic activity of vicriviroc in treatment-experienced subjects.
- Design : Double-blind, randomized trial involving 118 subjects who received either this compound (5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or placebo over 24 weeks.
- Results :
- Significant reductions in HIV-1 RNA levels were observed in all this compound groups compared to placebo.
- The mean change in HIV-1 RNA at week 24 was greater for this compound groups (−1.51 to −1.86 log copies/mL) compared to placebo (+0.06 log copies/mL) with statistical significance () .
- Virologic failure rates were lower in the this compound groups, with time to failure significantly longer for those receiving this compound compared to placebo .
VICTOR-E1 Study
- Objective : To evaluate the molecular basis for resistance mutations in subjects treated with this compound.
- Findings : Among 79 this compound-treated subjects, a subset developed resistance mutations leading to virologic failure. Genetic analysis revealed specific amino acid changes in the viral envelope that were associated with reduced susceptibility to this compound .
Efficacy and Safety Profile
This compound has demonstrated a favorable safety profile across multiple studies. Adverse events were comparable between this compound and placebo groups, with no significant increase in severe adverse events reported . Long-term follow-up indicated sustained virologic suppression in approximately 49% of subjects who achieved viral load suppression below 50 copies/mL after three years .
Resistance Patterns
Resistance to this compound has been documented, primarily among treatment-experienced patients. Studies indicate that while some patients develop resistance mutations, only a small proportion of treatment failures were directly associated with these mutations . The mapping of resistance mutations has revealed diverse genetic alterations that contribute to reduced drug efficacy .
Data Summary Table
| Study Name | Population | Dosage | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTG A5211 | Treatment-experienced | 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg | Significant reduction in HIV-1 RNA levels; longer time to virologic failure |
| VICTOR-E1 | Treatment-experienced | 20 mg, 30 mg | Resistance mutations identified; specific amino acid changes linked to reduced susceptibility |
Conclusions
This compound represents a promising therapeutic option for HIV-1-infected individuals who are treatment-experienced. Its ability to suppress viral load effectively while maintaining a manageable safety profile underscores its potential role in antiretroviral therapy. However, ongoing research is necessary to further elucidate its resistance patterns and optimize its use within combination therapy regimens.
Mechanism of Action
Vicriviroc functions as a noncompetitive allosteric antagonist of the CCR5 receptor. It binds to a hydrophobic pocket between the transmembrane helices near the extracellular surface of the CCR5 receptor. This binding causes a conformational change in the receptor, preventing the binding of the HIV-1 gp120 protein to CCR5. As a result, the entry of HIV-1 into host cells is inhibited, blocking the initial stages of the viral life cycle .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Vicriviroc is part of a class of compounds known as CCR5 inhibitors. Similar compounds include:
Maraviroc: Another CCR5 inhibitor approved for clinical use in treating HIV-1 infections.
Aplaviroc: A CCR5 inhibitor that was discontinued due to hepatotoxicity concerns.
INCB009471: A CCR5 inhibitor in clinical development.
This compound is unique due to its potent in vitro activity against a wide range of HIV subtypes and its favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties . It has shown promise in clinical trials, particularly in treatment-experienced patients .
Biological Activity
Vicriviroc (VCV), a CCR5 antagonist, is an investigational compound primarily studied for its efficacy in treating HIV-1 infection. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, summarizing key research findings, clinical trial outcomes, and resistance patterns.
This compound functions by selectively inhibiting the CCR5 coreceptor on CD4+ T cells, which is crucial for the entry of R5-tropic HIV-1 strains. By blocking this receptor, this compound prevents the virus from infecting host cells. This mechanism positions it as a valuable option in antiretroviral therapy, particularly for patients with CCR5-tropic HIV-1.
Phase 2 Studies
Several phase 2 studies have demonstrated this compound's potential in achieving virologic suppression among treatment-experienced patients:
- Study Design : In a randomized, double-blind study involving 118 subjects, participants received either this compound (at doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or placebo. The primary endpoint was the change in plasma HIV-1 RNA levels after 14 days of treatment.
- Results :
Long-Term Outcomes
In extended follow-up studies:
- Patients receiving 30 mg of this compound achieved viral loads below 50 copies/mL at rates significantly higher than those on placebo (59% vs. 25%) .
- Over a period of up to 192 weeks, average CD4 counts increased steadily among this compound recipients, indicating sustained immunologic benefit .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound has been generally favorable:
- Adverse events were comparable across treatment groups, with a similar incidence of grade 3/4 adverse events reported .
- However, concerns arose regarding malignancies; six cases were reported among this compound recipients compared to two in the placebo group .
Resistance Patterns
Resistance to this compound has been documented in some patients:
- In the VICTOR-E1 study, five subjects developed VCV-resistant HIV variants after virologic failure .
- Resistance mutations were linked to changes in the V3 loop of the gp160 envelope protein, although no consistent mutation pattern was observed across subjects .
Summary of Key Findings
| Study | Sample Size | Doses | Viral Load Reduction (log copies/mL) | Response Rate (<50 copies/mL) | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 2 Study | 118 | 5 mg | -1.51 | Not specified | Similar across groups |
| 10 mg | -1.86 | Not specified | Similar across groups | ||
| 15 mg | -1.68 | Not specified | Similar across groups | ||
| VICTOR-E1 | Varied | 20/30 mg | >2 | 59% (30 mg) | Malignancies noted |
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What experimental models are most appropriate for evaluating Vicriviroc’s mechanism of action as a CCR5 antagonist?
this compound’s mechanism involves blocking HIV-1 entry via CCR5 co-receptor antagonism. In vitro models using CCR5-tropic HIV-1 isolates in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or cell lines like HEK293/CCR5 are standard for assessing antiviral activity . In vivo models include humanized mice or non-human primates infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1. Dose-response curves and IC50 values should be calculated using validated assays (e.g., p24 antigen reduction assays) .
Q. How do researchers reconcile discrepancies between tropism assay results (original vs. enhanced-sensitivity) in this compound clinical trials?
Original tropism assays may misclassify dual/mixed (DM) tropic viruses as CCR5-tropic (R5), leading to suboptimal virologic responses. Enhanced-sensitivity assays (e.g., population-based sequencing with deep sequencing) improve detection of minority X4/DM variants. Researchers should retest baseline samples with enhanced assays and stratify outcomes based on updated tropism classifications .
Q. What pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters are critical for optimizing this compound dosing in clinical studies?
Key PK parameters include:
- Ctrough : Maintain concentrations above the protein-binding-adjusted IC90 (e.g., 30 mg daily achieves ~50 ng/mL trough levels) .
- Half-life : this compound’s half-life (~24–30 hours) supports once-daily dosing .
- Drug-drug interactions : Co-administration with ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors (PI/r) increases this compound exposure by ~2-fold, necessitating dose adjustments .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How should clinical trials be designed to address this compound’s variable efficacy across doses (e.g., 5 mg vs. 15 mg) in treatment-experienced patients?
Phase II trials (e.g., ACTG A5211) used a double-blind, randomized design with dose escalation (5–30 mg) and optimized background regimens (OBR). Key considerations:
- Primary endpoint : Change in HIV-1 RNA at day 14 (short-term activity) .
- Secondary endpoints : CD4 count changes, safety/tolerability at 24–48 weeks .
- Dose selection : Higher doses (15–30 mg) showed sustained virologic suppression, while lower doses (5 mg) had higher failure rates due to emergent X4 tropism .
| Dose (mg) | Mean HIV-1 RNA Reduction (log10 copies/mL) at 24 Weeks | Virologic Failure Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | -1.51 | 40 |
| 10 | -1.86 | 27 |
| 15 | -1.68 | 33 |
| Data from ACTG A5211 trial |
Q. What methodologies identify this compound resistance in patients with virologic failure despite CCR5-tropic virus?
Resistance mechanisms include:
- Phenotypic assays : Reduced maximal percentage inhibition (MPI) in viral entry assays .
- Genotypic analysis : Env gp160 mutations (e.g., V3 loop changes like G316E/K), though no consistent pattern across subjects .
- Coreceptor switching : Longitudinal monitoring for X4/DM variants via enhanced tropism assays .
Q. How do researchers interpret conflicting data on this compound’s long-term safety, including malignancy risks?
In ACTG A5211, malignancies occurred in 6 this compound recipients vs. 2 placebo recipients, but causality was unclear due to small sample sizes and confounding factors (e.g., advanced HIV disease) . Mitigation strategies:
- Extended follow-up : Monitor malignancy rates in open-label extensions (median follow-up >40 weeks) .
- Comparative safety trials : Use matched cohorts in Phase III studies (e.g., VICTOR-E1) to assess risk-benefit ratios .
Q. Data Analysis & Contradictions
Q. How should researchers address contradictions in this compound’s dose-response relationships across trials?
Conflicting efficacy data (e.g., 15 mg underperforming vs. 10 mg in some studies) may stem from:
- OBR variability : Differential OBR potency across cohorts .
- Tropism assay sensitivity : Enhanced assays reclassify responders/non-responders .
- PK variability : Suboptimal trough levels in certain populations (e.g., CYP3A4 fast metabolizers) . Solutions include stratified analysis by OBR quality and PK-guided dosing.
Q. What statistical approaches are recommended for analyzing this compound’s efficacy in heterogeneous patient populations?
Use mixed-effects models to account for:
Properties
IUPAC Name |
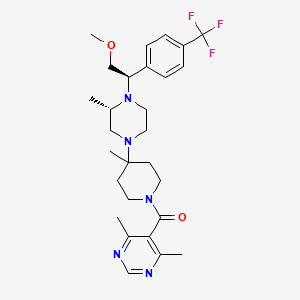
(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)-[4-[(3S)-4-[(1R)-2-methoxy-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethyl]-3-methylpiperazin-1-yl]-4-methylpiperidin-1-yl]methanone | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H38F3N5O2/c1-19-16-35(14-15-36(19)24(17-38-5)22-6-8-23(9-7-22)28(29,30)31)27(4)10-12-34(13-11-27)26(37)25-20(2)32-18-33-21(25)3/h6-9,18-19,24H,10-17H2,1-5H3/t19-,24-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CNPVJJQCETWNEU-CYFREDJKSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1CN(CCN1C(COC)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(F)(F)F)C3(CCN(CC3)C(=O)C4=C(N=CN=C4C)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C[C@H]1CN(CCN1[C@@H](COC)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(F)(F)F)C3(CCN(CC3)C(=O)C4=C(N=CN=C4C)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C28H38F3N5O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID40897719 | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40897719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
533.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Vicriviroc is a once daily oral inhibitor of CCR5. It noncompetitively binds to a hydrophobic pocket between transmembrance helices by the extracellular side of CCR5. This allosteric antagonism causes a conformational change in the protein preventing binding of gp120 to CCR5. This prevents the entry of HIV into the cell. | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06652 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
306296-47-9, 394730-30-4 | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=306296-47-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc [INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0306296479 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | SCH-D (Old RN) | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0394730304 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06652 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Vicriviroc | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40897719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | VICRIVIROC | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/TL515DW4QS | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















