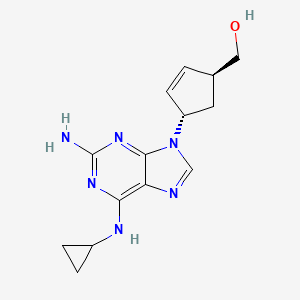
アバカビル
説明
アバカビルは、ヒト免疫不全ウイルス(HIV)および後天性免疫不全症候群(AIDS)の治療に主に用いられる、合成された環状核酸類似体逆転写酵素阻害剤です。この薬は、ジーゲンなどの商品名で販売されています。 アバカビルは、通常、他の抗レトロウイルス薬と組み合わせて使用され、単独での使用は推奨されません 。 アバカビルは、ウイルス複製に不可欠な逆転写酵素を標的とすることで、HIVの複製を阻害する能力で知られています .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: アバカビルの合成は、適切なジハロアミノピリミジン化合物から開始し、いくつかの段階を踏みます。主なステップは次のとおりです。
アミノアルコールとの反応: ジハロアミノピリミジンは、アミノアルコールと反応して中間体を形成します。
環化: この中間体は環化を受けて、重要な中間体を形成します。
シクロプロピルアミンの導入: 中間体中の塩素原子はシクロプロピルアミンで置換され、遊離塩基としてのアバカビルが生成されます.
工業的製造方法: アバカビルの工業的製造には、収率と純度を高く保つために、反応条件の最適化がしばしば必要です。これには、温度、pHの制御、および反応を促進するための特定の触媒の使用が含まれます。 このプロセスには、結晶化やクロマトグラフィーなどの精製ステップが含まれており、最終生成物を単離することができます .
反応の種類:
酸化: アバカビルは酸化分解を受け、電気化学的方法で研究することができます。
還元: アバカビルの特定の還元反応はあまり文書化されていませんが、特定の条件下で、アバカビルが還元を受ける可能性があります。
一般的な試薬と条件:
酸化: 過酸化水素、白金電極、ボロン・ドープ・ダイヤモンド電極。
置換: シクロプロピルアミン、さまざまな溶媒と触媒。
主な生成物:
4. 科学研究における用途
アバカビルは、特に化学、生物学、医学の分野で、科学研究において幅広い用途があります。
科学的研究の応用
Clinical Efficacy in HIV Treatment
Abacavir is FDA-approved for use in adults and children over three months old as part of combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). It is often administered alongside other agents such as lamivudine and dolutegravir.
Clinical Trials and Outcomes
- A pivotal study compared abacavir with zidovudine combined with lamivudine. At week 48, 70% of patients on abacavir achieved plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of ≤50 copies/mL, similar to the zidovudine group (69%) .
- The median increase in CD4+ cell counts was significantly higher in the abacavir group (209 cells/mm³) compared to the zidovudine group (155 cells/mm³), indicating a robust immunological response .
Pharmacokinetics
Abacavir exhibits a two-compartment pharmacokinetic model with high oral bioavailability. Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Clearance : Increased from a mean of 3.33 to 5.86 L/h/7 kg from day 1 to day 14 in severely malnourished children .
- Central Nervous System Penetration : Studies indicate that abacavir penetrates the central nervous system effectively, with a CSF/plasma concentration ratio of approximately 31% to 44% .
Safety Profile and Side Effects
While abacavir is generally well-tolerated, it has been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, particularly in individuals with the HLA-B*57:01 allele. This genetic predisposition can lead to severe allergic reactions upon exposure to the drug.
Cardiovascular Risks
Recent analyses have linked abacavir use to an increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). A meta-analysis indicated that current or past use of abacavir may elevate cardiovascular disease risk among HIV patients .
Off-Label Uses
Abacavir has been explored for various off-label applications, including:
- HIV Treatment in Special Populations : Research has demonstrated its efficacy in severely malnourished children, showing that WHO weight-band dosing recommendations are appropriate for this demographic .
- Potential Role in Cancer Therapy : Emerging studies are investigating the immunomodulatory effects of abacavir that may enhance responses to cancer therapies.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Several studies have documented the diverse applications and outcomes associated with abacavir:
作用機序
アバカビルは細胞内で活性代謝物であるカルボビル三リン酸に変換されます。この代謝物はデオキシグアノシン-5'-三リン酸(dGTP)の類似体であり、HIV逆転写酵素によってウイルスのDNAに組み込まれることを競合的に阻害します。 組み込まれると、鎖終結剤として作用し、ウイルスのDNAの伸長を阻止し、その結果、ウイルスの複製を阻害します .
類似化合物:
ラミブジン: アバカビルと組み合わせて使用される別のヌクレオシド逆転写酵素阻害剤。
ジドブジン: 作用機序が類似した、古いヌクレオシド逆転写酵素阻害剤。
テノホビル: 化学構造は異なるが、抗ウイルス活性は類似しているヌクレオチド逆転写酵素阻害剤。
比較:
ユニークさ: アバカビルは、環状核酸類似体としての構造がユニークです。それは、他のヌクレオシド類似体とは異なる、独特のシクロプロピルアミン基を持っています。
有効性: アバカビルは、高い生物学的利用能と迅速な吸収で知られており、併用療法で効果的です.
安全性プロファイル: アバカビルは、安全性のプロファイルが十分に文書化されていますが、過敏反応や潜在的な心血管リスクのリスクが関連付けられています.
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of abacavir involves several steps, starting from a suitable di-halo aminopyrimidine compound. The key steps include:
Reaction with Aminoalcohol: The di-halo aminopyrimidine is reacted with an aminoalcohol to form an intermediate compound.
Cyclization: This intermediate undergoes cyclization to form a key intermediate.
Introduction of Cyclopropylamine: The chlorine atom in the intermediate is displaced with cyclopropylamine to yield abacavir as a free base.
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of abacavir often involves optimizing the reaction conditions to ensure high yield and purity. This includes controlling the temperature, pH, and the use of specific catalysts to facilitate the reactions. The process may also involve purification steps such as crystallization and chromatography to isolate the final product .
Types of Reactions:
Oxidation: Abacavir undergoes oxidative degradation, which can be studied using electrochemical methods.
Reduction: While specific reduction reactions of abacavir are less documented, it is possible that under certain conditions, abacavir could undergo reduction.
Substitution: The synthesis of abacavir itself involves substitution reactions, particularly the displacement of chlorine with cyclopropylamine.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Hydrogen peroxide, platinum electrodes, boron-doped diamond electrodes.
Substitution: Cyclopropylamine, various solvents and catalysts.
Major Products:
類似化合物との比較
Lamivudine: Another nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in combination with abacavir.
Zidovudine: An older nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a similar mechanism of action.
Tenofovir: A nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a different chemical structure but similar antiviral activity.
Comparison:
Uniqueness: Abacavir is unique in its structure as a carbocyclic nucleoside analog. It has a distinct cyclopropylamine group that differentiates it from other nucleoside analogs.
Safety Profile: Abacavir has a well-documented safety profile, though it is associated with a risk of hypersensitivity reactions and potential cardiovascular risks.
生物活性
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) primarily used in the treatment of HIV infection. Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic efficacy, safety profile, and potential side effects, including hypersensitivity reactions. This article synthesizes findings from various studies and case reports to provide a comprehensive overview of abacavir's biological activity.
Abacavir is metabolized intracellularly to its active form, carbovir triphosphate (CBV-TP), which competes with natural deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA. This incorporation results in chain termination during reverse transcription, effectively inhibiting viral replication. Abacavir has demonstrated potency against HIV strains resistant to other NRTIs, making it a valuable option in antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of abacavir reveals significant insights into its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion:
- Absorption : Abacavir is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1.5 to 2 hours.
- Distribution : The drug penetrates the central nervous system (CNS) effectively, with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations significantly exceeding the inhibitory concentration for HIV .
- Metabolism : Abacavir is primarily metabolized by the liver through non-CYP450 pathways, reducing the risk of drug-drug interactions commonly associated with other antiretrovirals .
- Excretion : The drug is eliminated mainly via renal clearance, with minimal hepatic metabolism .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
Abacavir has been evaluated in numerous clinical trials demonstrating its efficacy as part of ART regimens:
- In a comparative study with zidovudine and lamivudine, abacavir showed non-inferior efficacy in maintaining viral suppression (70% vs. 69% at week 48) and a favorable CD4+ cell response (209 cells/mm³ vs. 155 cells/mm³) .
- A meta-analysis indicated that viral suppression rates ranged from 50% to 70% at six months and from 57% to 78% at twelve months in pediatric populations treated with abacavir .
Safety Profile and Hypersensitivity Reactions
While abacavir is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) in a subset of patients. The incidence of HSRs can be influenced by genetic factors such as HLA-B*5701 status:
- Case Study Example : A patient developed gastrointestinal symptoms and fever within days of initiating therapy with abacavir. Upon discontinuation, symptoms resolved rapidly, indicating a probable hypersensitivity reaction .
Table 1: Summary of Abacavir Hypersensitivity Reactions
| Study/Case | Population | Symptoms | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case #3 | Adult male | Vomiting, diarrhea, fever | Symptoms resolved post-discontinuation |
| Patel et al. (2020) | Pediatric patients | Variable symptoms | Incidence rate varied from 0% to 5.49% |
Research Findings on Oncogenic Activity
Recent studies have also explored the potential oncogenic effects of abacavir. Research indicates that abacavir can activate oncogenic transcription factors in gastric cancer cells, suggesting a complex role beyond its antiviral activity:
特性
IUPAC Name |
[4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)purin-9-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-yl]methanol | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H18N6O/c15-14-18-12(17-9-2-3-9)11-13(19-14)20(7-16-11)10-4-1-8(5-10)6-21/h1,4,7-10,21H,2-3,5-6H2,(H3,15,17,18,19) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCGSCOLBFJQGHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1NC2=C3C(=NC(=N2)N)N(C=N3)C4CC(C=C4)CO | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H18N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20861337 | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
286.33 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
136470-78-5, 914348-29-1 | |
| Record name | NSC742406 | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=742406 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















